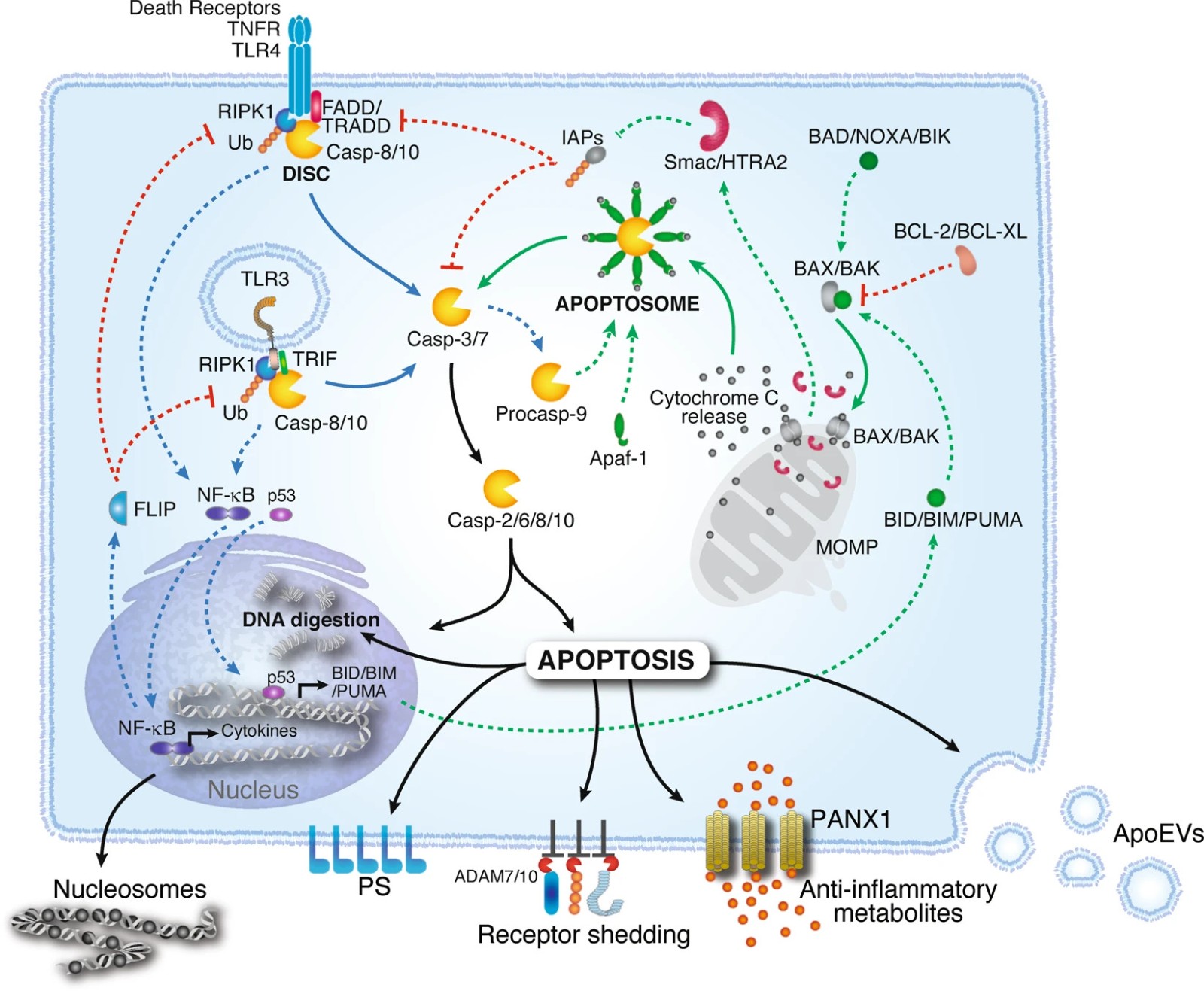
Apoptosis is a strictly regulated process that leads to orderly cell breakdown and clearance. Unlike necrotic cell death, apoptosis is well regulated and plays a critical role in development, immune function, and tissue homeostasis. Normal cells undergo apoptosis when subjected to various endogenous and exogenous stimuli to maintain a balance between cell survival and death.
Apoptotic cells exhibit unique characteristics such as DNA fragmentation, vacuolization of cell and plasma membrane, and formation of apoptotic bodies - cell fragments produced by apoptotic cell death. Specific cell surface markers, such as phosphatidylserine, distinguish apoptosis from other forms of cell death, such as necrosis. A key factor in cell apoptosis is that clearing cells does not cause tissue inflammation. Phagocytes and inflammatory cells can effectively eliminate apoptotic cells and apoptotic bodies without causing further damage to the tissue microenvironment.
| Target | Catalog# | Product Name | Reactivity | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Caspase 3 | AMRe85205 | Caspase 3 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody Antibody | Human | WB,IHC,ICC,IP |
| RIP (Phospho Ser166) | APRab20453 | RIP (Phospho Ser166) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Rat,Mouse | WB,IHC |
| Bax | AMRe21477 | Bax Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC,IF,IP,ELISA |
| Bad | AMRe21496 | Bad Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC,IF,IP,ELISA |
| MAPKAPK-2 (phospho Thr334) | APRab04972 | MAPKAPK-2 (phospho Thr334) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,ELISA |
Related Products
Super-sensitive ECL chemiluminescent reagent
References
- Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Elmore, S. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007. [PMID: 17562483]
- Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death. Bertheloot, D., et al. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021. [PMID: 33785842]
- Apoptosis. Fleisher TA. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997. [PMID: 9087147]
- Apoptosis: A Comprehensive Overview of Signaling Pathways, Morphological Changes, and Physiological Significance and Therapeutic Implications. Mustafa M, et al. Cells. 2024. [PMID: 39594587]

