What are Recombinant Antibodies?
Recombinant antibodies are generated through recombinant DNA and protein engineering technologies. The antibody coding genes are processed, modified, and reassembled according to different application requirements, then transfected into appropriate host cells for in vitro expression. By modifying or engineering the gene sequences, higher quality and sensitivity recombinant antibodies can be achieved, suitable for wide applications and enabling large-scale production.
Why Choose Recombinant Antibodies?
Inconsistent results from the same antibody in parallel experiments can often mislead scientists, and an unreliable antibody can cause significant losses. This is usually related to the antibody production process. Unlike conventional monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies, recombinant antibodies are derived from in vitro cell expression and undergo multiple rounds of rigorous screening and validation, providing solutions for researchers facing challenges in proteomics, human health, and drug discovery. Browse our comprehensive recombinant monoclonal antibody series covering protein targets from human, mouse, rat, monkey, chicken and more species. Each product undergoes rigorous quality control and application validation.
View All Recombinant Antibodies
Antibody Type Comparison Guide
Our Advantages
Experimental Data Validation
Our recombinant antibodies undergo rigorous validation across multiple experimental techniques to ensure reliable results in different application scenarios, the following examples demonstrate performance recombinant antibodies.
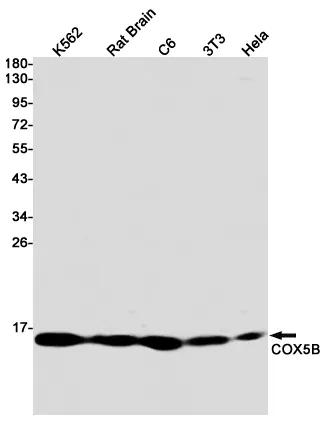
Specific target band recognition with low background
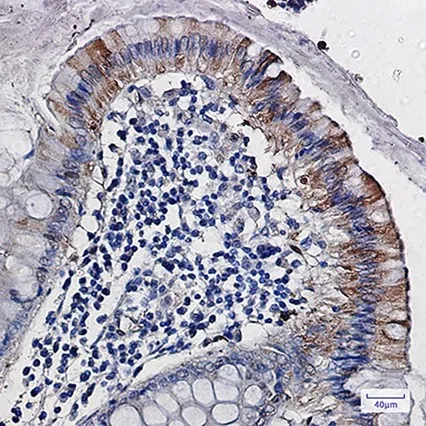
Clear tissue localization with uniform staining

Precise subcellular localization
