Endosomal Marker
Endosomes are formed by the invagination of the plasma membrane to form vesicles in an effort to recycle components of the cell (1). Endosomes can be coated in clathrin when vesicles form at clathrin-coated pits (2). Caveolins are 21-24 kDa integral proteins that interact with cholesterol and are the main structural components of the cholesterol/sphingolipid-enriched plasma membrane caveolae (3). Each stage of endosome maturation is marked by a unique set of proteins. EEA1 is an early endosome marker that is essential for membrane fusion and trafficking (4). Members of the ras superfamily of small Rab GTPases, specifically Rab5, Rab7, and Rab11 are markers of the early, late and recycling endosomes (5).
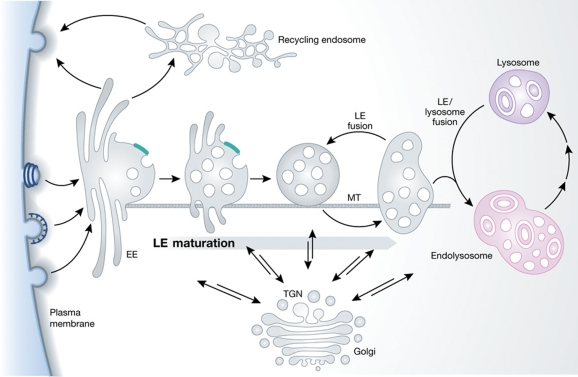
Endosomes formation mechanism
The primary endocytic vesicles deliver their contents and their membrane to EEs in the peripheral cytoplasm. After a period of about 8-15 min during which the EEs accumulate cargo and support recycling to the plasma membrane (directly or via recycling endosomes in the perinuclear region), conversion of the EEs to LE takes place. Thus, as the endosomes are moving towards the perinuclear space along microtubules (MT), the nascent LE are formed inheriting the vacuolar domains of the EE network. They carry a selected subset of endocytosed cargo from the EE, which they combine en route with newly synthesized lysosomal hydrolases and membrane components from the secretory pathway. They undergo homotypic fusion reactions, grow in size, and acquire more ILVs. Their role as feeder system is to deliver this mixture of endocytic and secretory components to lysosomes. To be able to do it, they continue to undergo a maturation process that prepares them for the encounter with lysosomes. The fusion of an endosome with a lysosome generates a transient hybrid organelle, the endolysosome, in which active degradation takes place. What follows is another maturation process; the endolysosome is converted to a classical dense lysosome, which constitutes a storage organelle for lysosomal hydrolases and membrane components.
Relevant Antibodies
| Catalog# | Product Name | Application | Reactivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMRe21284 | Caveolin-1 Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | WB,IHC,IF,IP,ELISA | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| AMRe21547 | Clathrin Heavy Chain Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | WB,IHC,IF,ELISA | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| AMRe21570 | EEA1 Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | WB,IHC,IF,IP,ELISA | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| AMRe21505 | Rab 5A Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | WB,IHC,IF,IP,ELISA | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| AMRe21482 | Rab7 Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | WB,IHC,IF,IP,ELISA | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| AMRe16767 | RAB11A (4O16) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | WB,IP | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| APS0635 | HRP-conjugated Polyclonal Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) Secondary Antibody | ELISA,WB,Dotblot | Mouse |
| AMRe80004 | GAPDH (12R9) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | WB,ELISA | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit,Dog,Monkey |
Related Products
Antibody Labeling Kit Western Blot Kits Super-sensitive ECL chemiluminescent reagent IHC Kit TSA mIHC Kits
References
- Huotari, J. and Helenius, A. (2011) EMBO J 30, 3481-500.
- Rodriguez-Boulan, E. et al. (2005) Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6, 233-47.
- Okamoto, T. et al. (1998) J Biol Chem 273, 5419-22.
- Christoforidis, S. et al. (1999) Nature 397, 621-5.
- Zerial, M. and McBride, H. (2001) Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2, 107-17.
 | Voisey Voisey is a technical support specialist at EnkiLife, proficient in immunology and cell biology. She is committed to providing customers with professional and efficient technical support. Additionally, she is involved in research on customers' fields of study and designs highly cost-effective solutions for them. |
