Transforming Growth Factor-β Superfamily
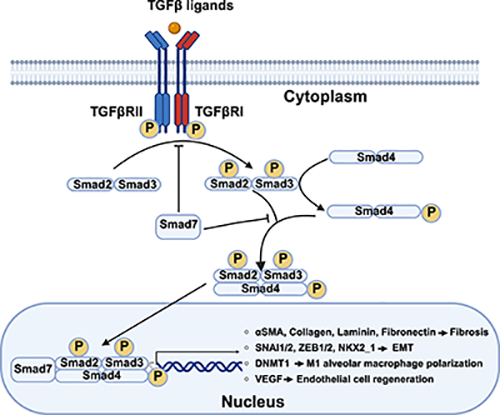
The transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) superfamily comprises over 30 members, including TGF-β, Activin, Inhibin, bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), and growth differentiation factors (GDFs). It can be roughly divided into two subfamilies: the TGF-β/Activin/Nodal subfamily and the BMP/GDF/MIS (Müllerian inhibiting substrate) subfamily. This superfamily plays crucial roles in regulating cell proliferation, lineage differentiation, migration, adhesion, and apoptosis, as well as embryonic development, extracellular matrix formation, and bone formation and remodeling. This cytokine was named "TGF-β" because it can induce phenotypic transformation of normal fibroblasts—specifically, in the presence of epidermal growth factor (EGF), it alters the growth characteristics of fibroblasts on the inner wall, enabling them to grow in agar and losing density-dependent inhibition during growth.
Dysregulation of TGF-β family signaling underlies a broad spectrum of disorders: excessive activity drives immune evasion, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and fibrosis in cancer and chronic organ injury, whereas insufficient signaling causes skeletal malformations, cardiovascular defects, and immune dysfunction. Consequently, TGF-β ligands, receptors, and Smads serve as valuable disease biomarkers.
Product List
| Target | Catalog# | Product Name | Reactivity | Predicted MW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TGFB3 | PHV1914 | Recombinant Human/Mouse/Rat TGFB3 | Human/Mouse/Rat | 12.7 KDa |
| TGF-beta 2 | PHV1624 | Recombinant Mouse/Rat TGF-beta 2 | Mouse/Rat | 12.7 KDa |
| TGF-beta 1 | PHV1622 | Recombinant Mouse/Rat TGF-beta 1 | Mouse/Rat | 12.8 KDa |
| TGFBR2 (C-Fc) | PHM1711 | Recombinant Mouse TGFBR2 (C-Fc) | Mouse | 42.3 KDa |
| TGFBR2 (C-6His) | PHM1710 | Recombinant Mouse TGFBR2 (C-6His) | Mouse | 16.2 KDa |
| Latent TGF Beta-1 (N-6His) | PHH1709 | Recombinant Human Latent TGF Beta-1 (N-6His) | Human | 29.3&12.8 KDa |
| TGFBR2 (C-Fc) | PHH1625 | Recombinant Human TGFBR2 (C-Fc) | Human | 42.6 KDa |
| TGF-beta 2 | PHH1623 | Recombinant Human TGF-beta 2 | Human | 12.7 KDa |
| TGF-beta 1 | PCH1621 | Recombinant Human TGF-beta 1 | Human | 12.8 KDa |
GDF-8 | Recombinant Human/Mouse/Rat GDF-8 | Human/Mouse/Rat | 13.1 kDa | |
GDF15 (N-8His-Flag) | Recombinant Mouse GDF15 (N-8His-Flag) | Mouse | 16.9 kDa | |
BMP-7 | Recombinant Human BMP-7 | Human | 15.5 kDa | |
| GDF-11 | Recombinant Human GDF-11 | Human | 12.5 kDa | |
| BMP-2 | Recombinant Human/Mouse/Rat BMP-2 | Human/Mouse/Rat | 13.3 kDa | |
| BMP-4 | Recombinant Human BMP-4 | Human | 13.3 kDa | |
| Persephin | PEH1312 | Recombinant Human Persephin | Human | 10.4 kDa |
| GDF-5 | PEH0722 | Recombinant Human GDF-5 | Human | 13.7 kDa |
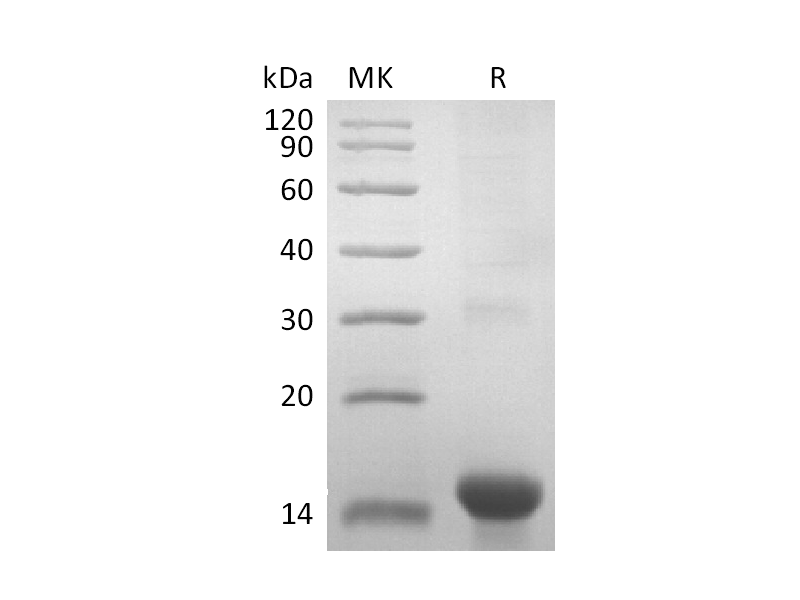
Validation Data
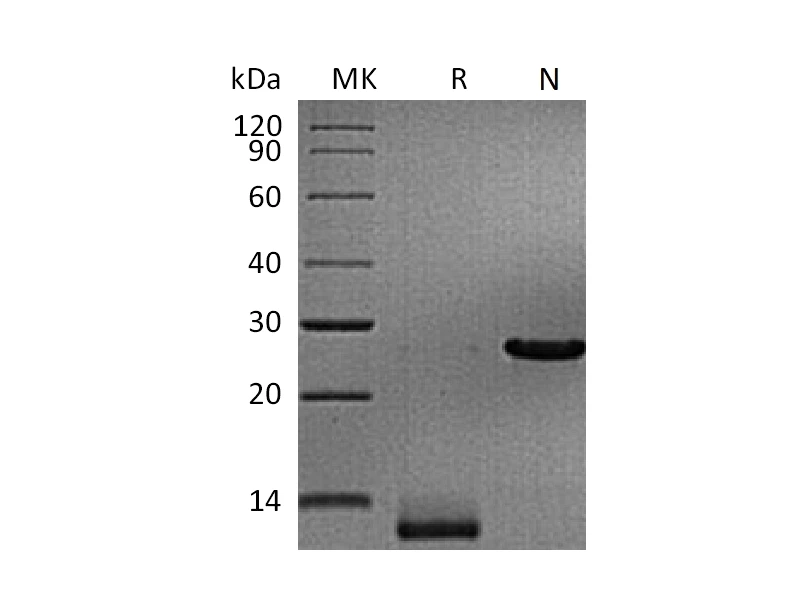
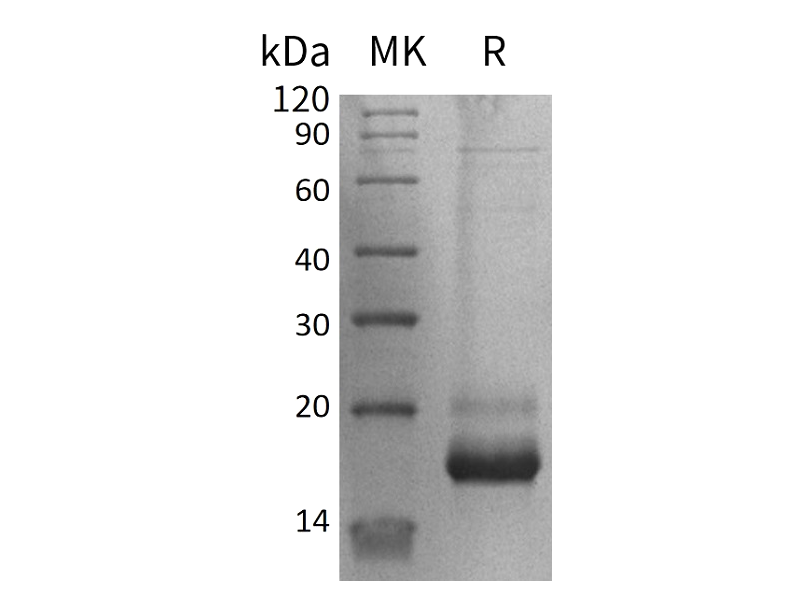
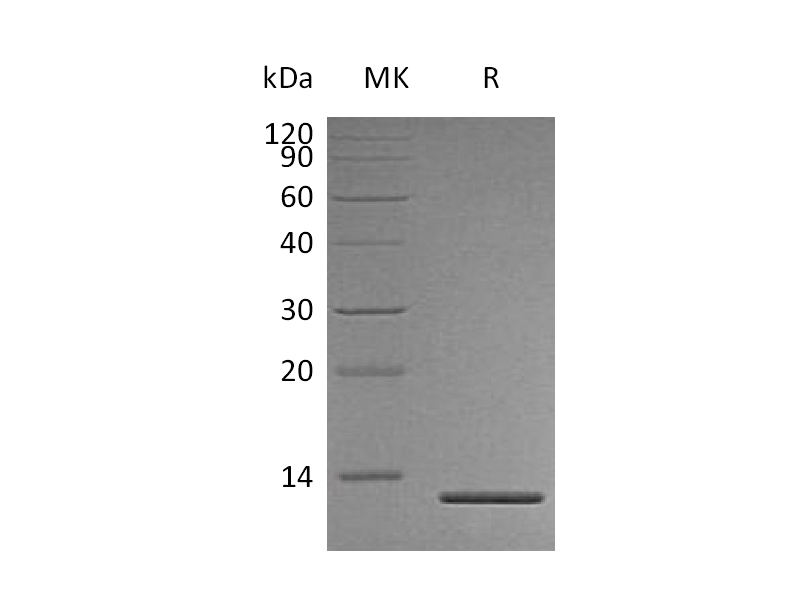
Recombinant Human Persephin (Catalog: PEH1312) Recombinant Mouse GDF15 (N-8His-Flag) (Catalog: PHM2405)
Related Products
Super-sensitive ECL chemiluminescent reagent
References
1. A stepwise mode of TGF β-SMAD signaling and DNA methylation regulates naïve-to-primed pluripotency and differentiation. Hao B, et al. Nat Commun. 2024. [PMID: 39578449]
2. Contextual determinants of TGF β action in development, immunity and cancer. David CJ, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018. [PMID: 29643418]
3. Transforming growth factor beta 1: three-dimensional structure in solution and comparison with the X-ray structure of transforming growth factor beta 2. Hinck AP, et al. Biochemistry. 1996. [PMID: 8679613]
4. TGF-beta signaling in tumor suppression and cancer progression. Derynck R, Nat Genet. 2001. [PMID:11586292]
5. Transforming growth factor Beta family: insight into the role of growth factors in regulation of fracture healing biology and potential clinical applications. Poniatowski ŁA, et al. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. [PMID:25709154]
6. Structural biology of the TGFβ family. Goebel EJ, et al. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2019. [PMID:31594405]
7. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Shi Y, et al. Cell. 2003. [PMID: 12809600]
8. Regulation of inflammatory lung injury and repair by transforming growth factors. Chakrabarti M, et al. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2025. [PMID: 40920668]