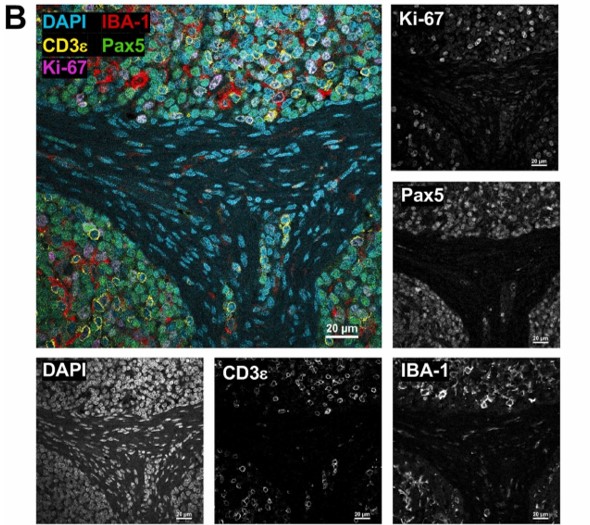
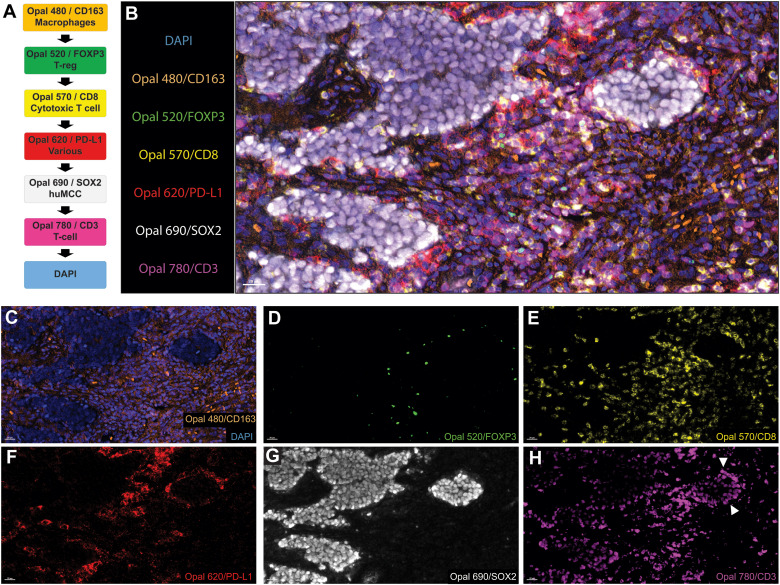
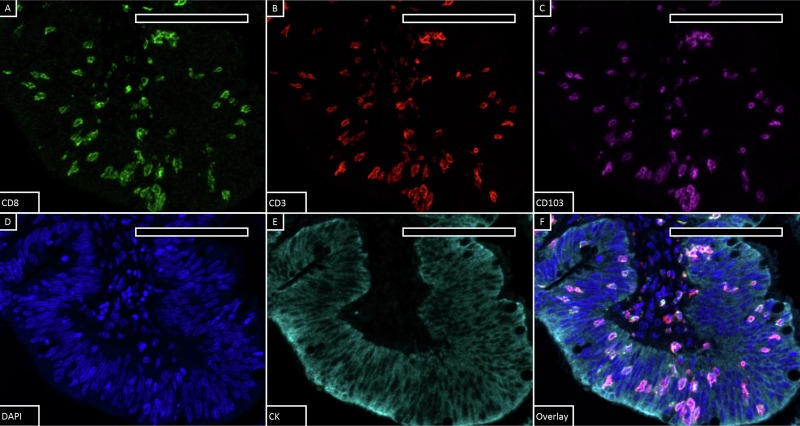
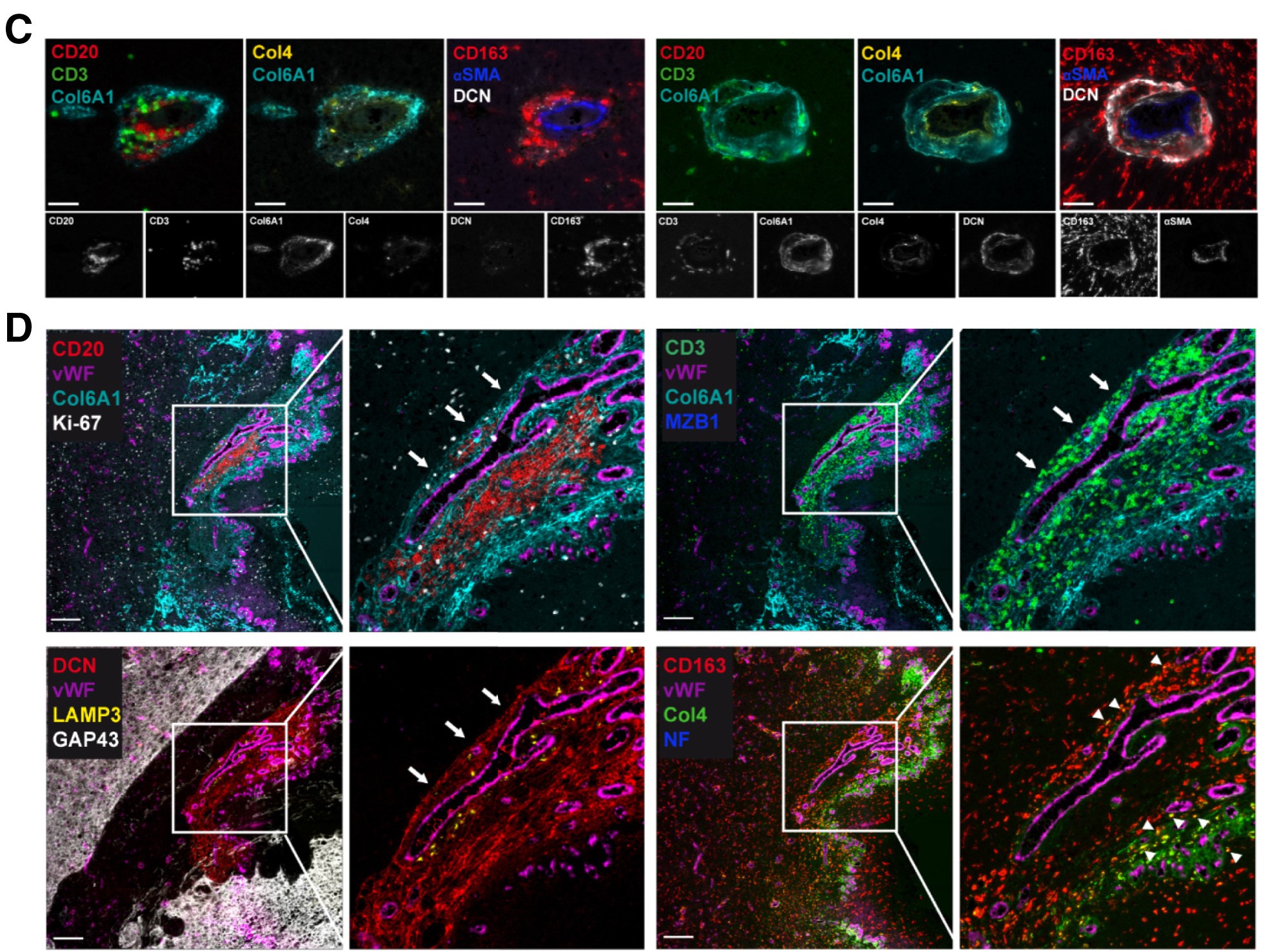
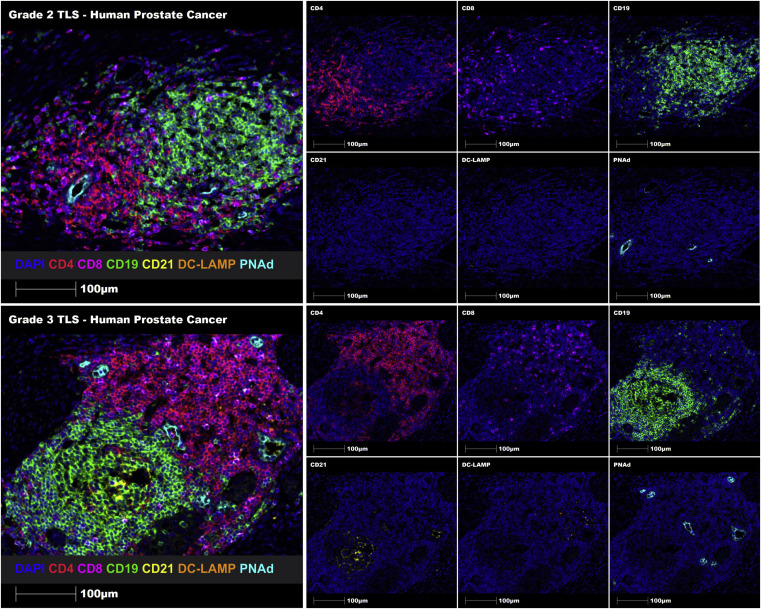
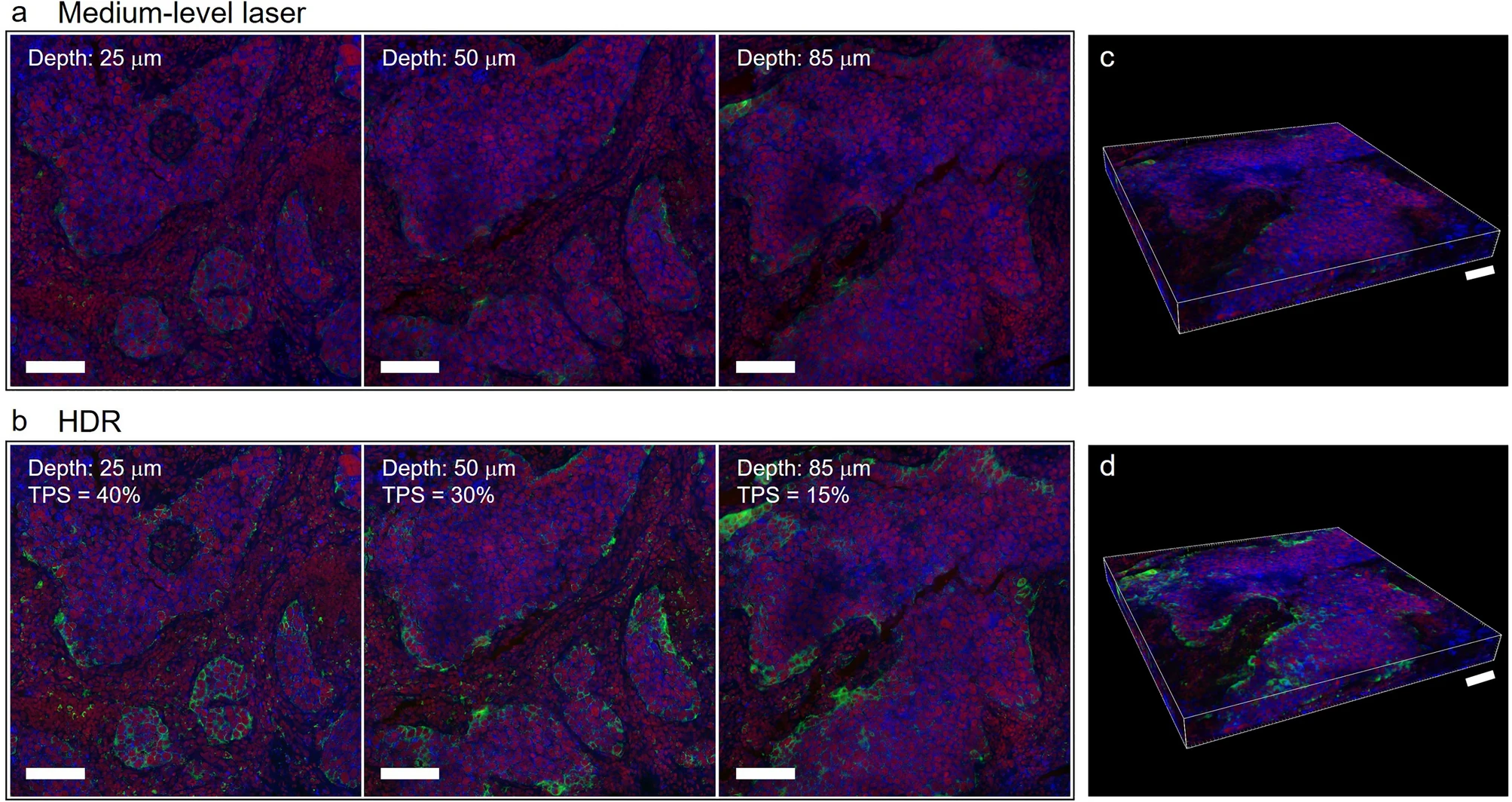
Literature Share: Multiplexed Fluorescent Staining of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Lesions Based on TSA
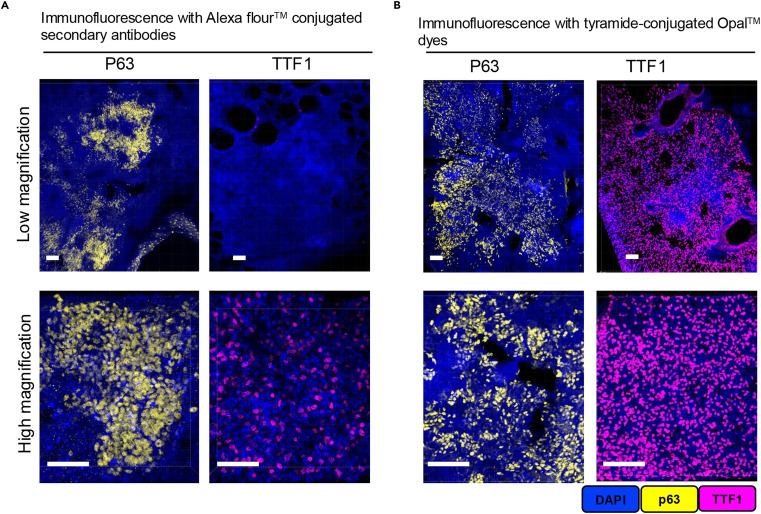
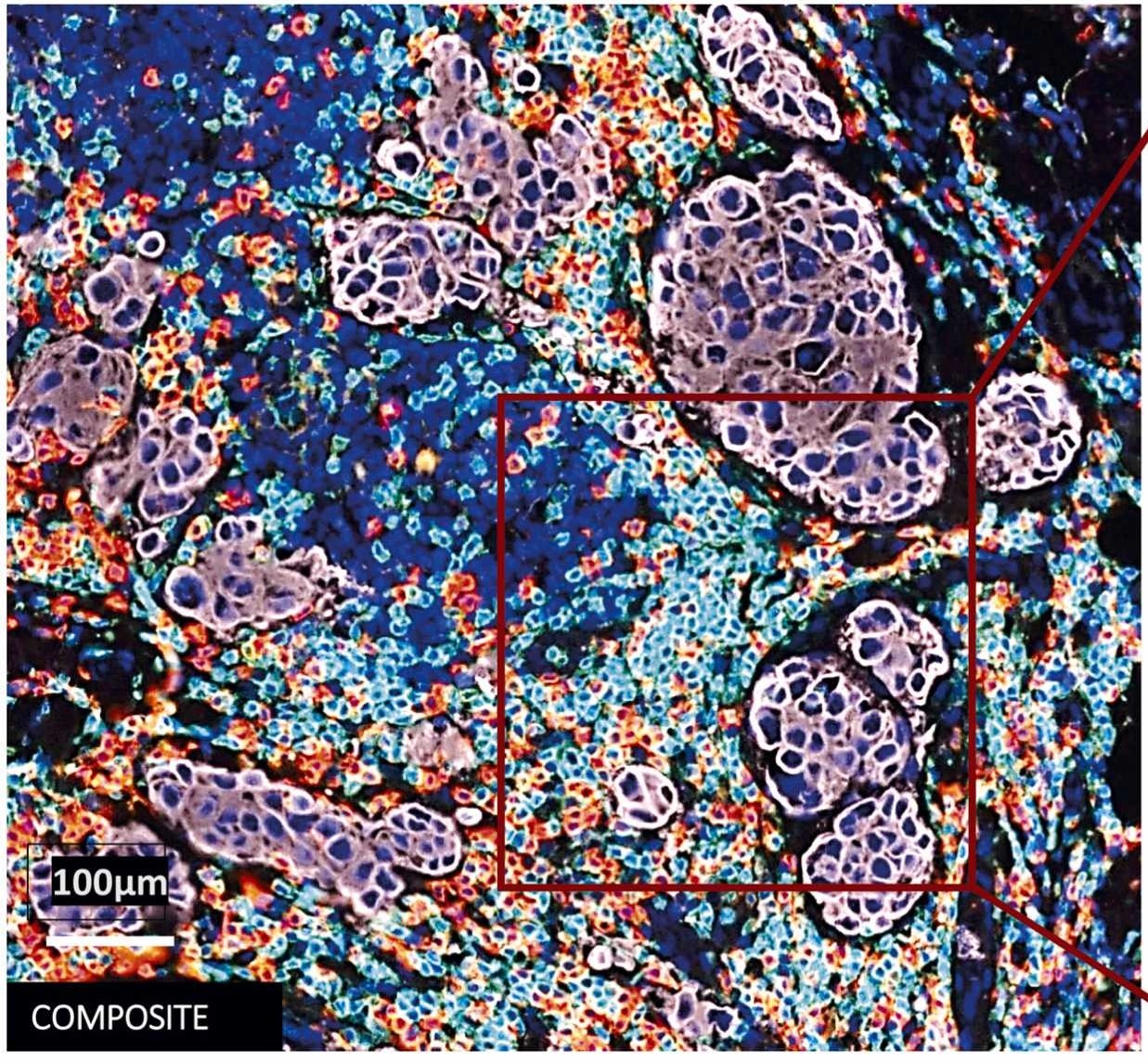
The core principle of TSA technology is that horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies, in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, catalyze the conversion of fluorescently labeled tyramides into active forms, which then covalently bind to tyrosine residues near target antigens, achieving cascade amplification of signals. The study selected Opal fluorescent dyes as labels, which, compared to traditional fluorescent secondary antibodies, significantly improve signal sensitivity and allow imaging at low laser power, reducing tissue photobleaching.