Size2:50μg price2:$465
Size3:500μg price3:$2325
| Name | Recombinant Mouse/Rat TGF-beta 2 |
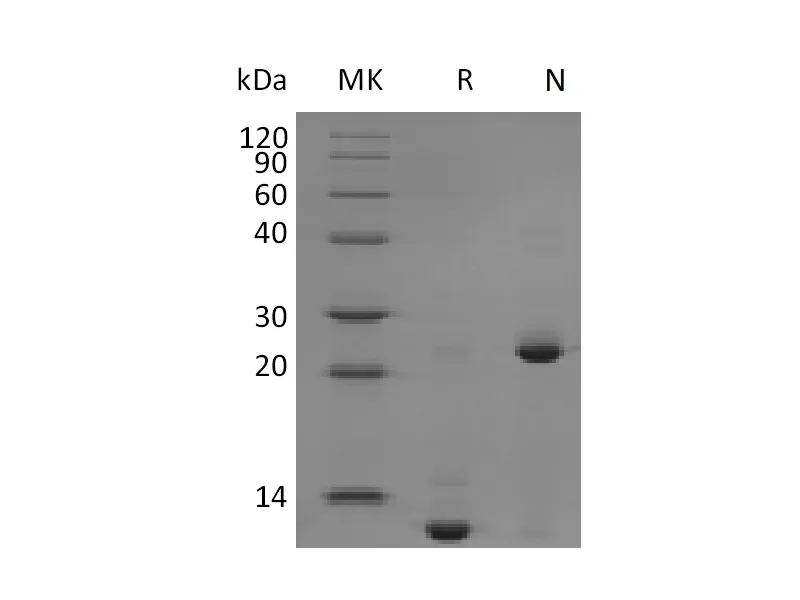
| Purity | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin level | <1 EU/µg as determined by LAL test. |
| Construction | Recombinant Mouse/Rat Transforming Growth Factor Beta 2 is produced by our Mammalian expression system and the target gene encoding Ala303-Ser414 is expressed. |
| Accession # | P27090 |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Species | Mouse/Rat |
| Predicted Molecular Mass | 12.7 KDa |
| Buffer | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 4mM HCl. |
| Form | Lyophilized |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature.Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature listed below. |
| Stability&Storage | Lyophilized protein should be stored at ≤ -20°C, stable for one year after receipt. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 2-8°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at ≤ -20°C for 3 months. |
| Reconstitution | Always centrifuge tubes before opening.Do not mix by vortex or pipetting.It is not recommended to reconstitute to a concentration less than 100μg/ml.Dissolve the lyophilized protein in 4mM HCl.Please aliquot the reconstituted solution to minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
Alternative Names
TGFB2; BSC-1 cell growth inhibitor; Cetermin; Glioblastoma-derived T-cell suppressor factor; G-TSF; MGC116892; Polyergin; TGF-beta2; TGF-beta-2; transforming growth factor beta-2
Background
Transforming growth factor beta 2 (TGF-β2) is a member of TGF-beta superfamily that shares a characteristic cysteine knot structure. Mice with TGF-β2 gene deletion show defects in development of cardiac, lung, craniofacial, limb, spinal column, eye, inner ear and urogenital systems. All TGF-β isoforms signal via the same heteromeric receptor complex, consisting of a ligand binding TGF-β receptor type II (TβR-II), and a TGF-β receptor type I (TβR-I). Signal transduction from the receptor to the nucleus is mediated via SMADs. TGF-β expression is found in cartilage, bone, teeth, muscle, heart, blood vessels, haematopoitic cells, lung, kidney, gut, liver, eye, ear, skin, and the nervous system.
Note
For Research Use Only , Not for Diagnostic Use.
