Size:50μL Price:$118
Size:100μL Price:$220
Size:200μL Price:$380
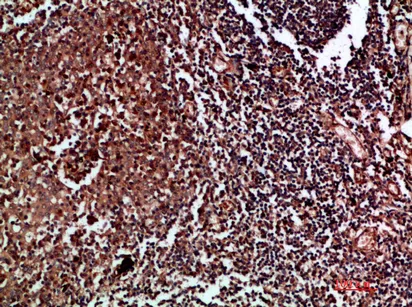
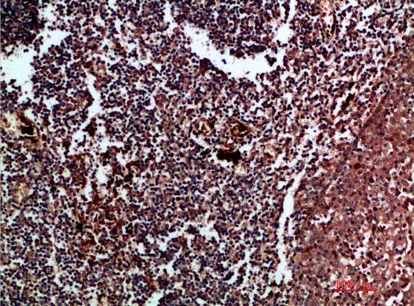
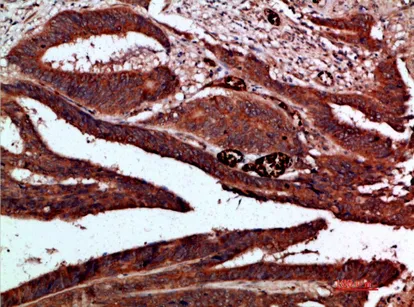
Application:WB,IHC,ICC/IF,ELISA
Reactivity:Human,Rat,Mouse
Conjugate:Unconjugated
Optional conjugates: Biotin, FITC (free of charge). See other 26 conjugates.
Gene Name:CDK6 CDKN6
Summary
| Production Name | Cdk6 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody |
| Description | Rabbit polyclonal Antibody |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Application | WB,IHC,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| Reactivity | Human,Rat,Mouse |
Performance
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Modification | Unmodified |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Form | Liquid |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Buffer | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% protective protein and 0.02% New type preservative N. |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
Immunogen
| Gene Name | CDK6 CDKN6 |
| Alternative Names | Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (EC 2.7.11.22;Cell division protein kinase 6;Serine/threonine-protein kinase PLSTIRE) |
| Gene ID | 1021 |
| SwissProt ID | Q00534 |
Application
| Dilution Ratio | WB 1:500-1:2000,IHC 1:50-1:200,ICC/IF 1:50-1:200,ELISA 1:10000-1:20000 |
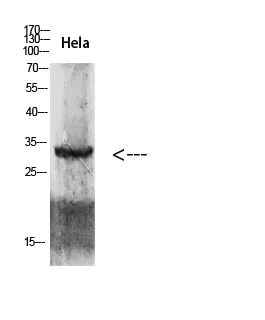
| Molecular Weight | 34kDa |
Background
cyclin dependent kinase 6(CDK6) Homo sapiens The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent protein kinase (CDK) family. CDK family members are highly similar to the gene products of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cdc28, and Schizosaccharomyces pombe cdc2, and are known to be important regulators of cell cycle progression. This kinase is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression and G1/S transition. The activity of this kinase first appears in mid-G1 phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits including D-type cyclins and members of INK4 family of CDK inhibitors. This kinase, as well as CDK4, has been shown to phosphorylate, and thus regulate the activity of, tumor suppressor protein Rb. Expression of this gene is up-regulated in some types of cancer. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefScatalytic activity:ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein.,function:Probably involved in the control of the cell cycle. Interacts with D-type G1 cyclins.,polymorphism:Genetic variations in CDK6 influences stature as a quantitative trait type 11 (STQTL11) [MIM:612223]. Adult height is an easily observable and highly heritable complex continuous trait. Because of this, it is a model trait for studying genetic influence on quantitative traits.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily.,similarity:Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. CMGC Ser/Thr protein kinase family. CDC2/CDKX subfamily.,similarity:Contains 1 protein kinase domain.,
Research Area
Cell_Cycle_G1S;Cell_Cycle_G2M_DNA;p53;Pathways in cancer;Pancreatic cancer;Glioma;Melanoma;Chronic myeloid leukemia;Small cell lung cancer;Non-small cell lung cancer;
