Size:100μL Price:$288
Size:200μL Price:$520
Application:WB
Reactivity:Mouse,Rat
Conjugate:Unconjugated
Optional conjugates: Biotin, FITC (free of charge). See other 26 conjugates.
Gene Name:Grin2A
Summary
| Production Name | NMDAR2A Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Description | Recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibody |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Application | WB |
| Reactivity | Mouse,Rat |
Performance
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Modification | Unmodified |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Form | Liquid |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Buffer | 50mM Tris-Glycine(pH 7.4), 0.15M NaCl, 40% Glycerol, 0.01% Sodium azide and 0.05% protective protein |
| Purification | Affinity Purification |
Immunogen
| Gene Name | Grin2A |
| Alternative Names | NR2A; GluN2A; NMDAR2A; GluRepsilon1 |
| Gene ID | 14811 |
| SwissProt ID | P35436 |
Application
| Dilution Ratio | WB 1:500-1:1000 |
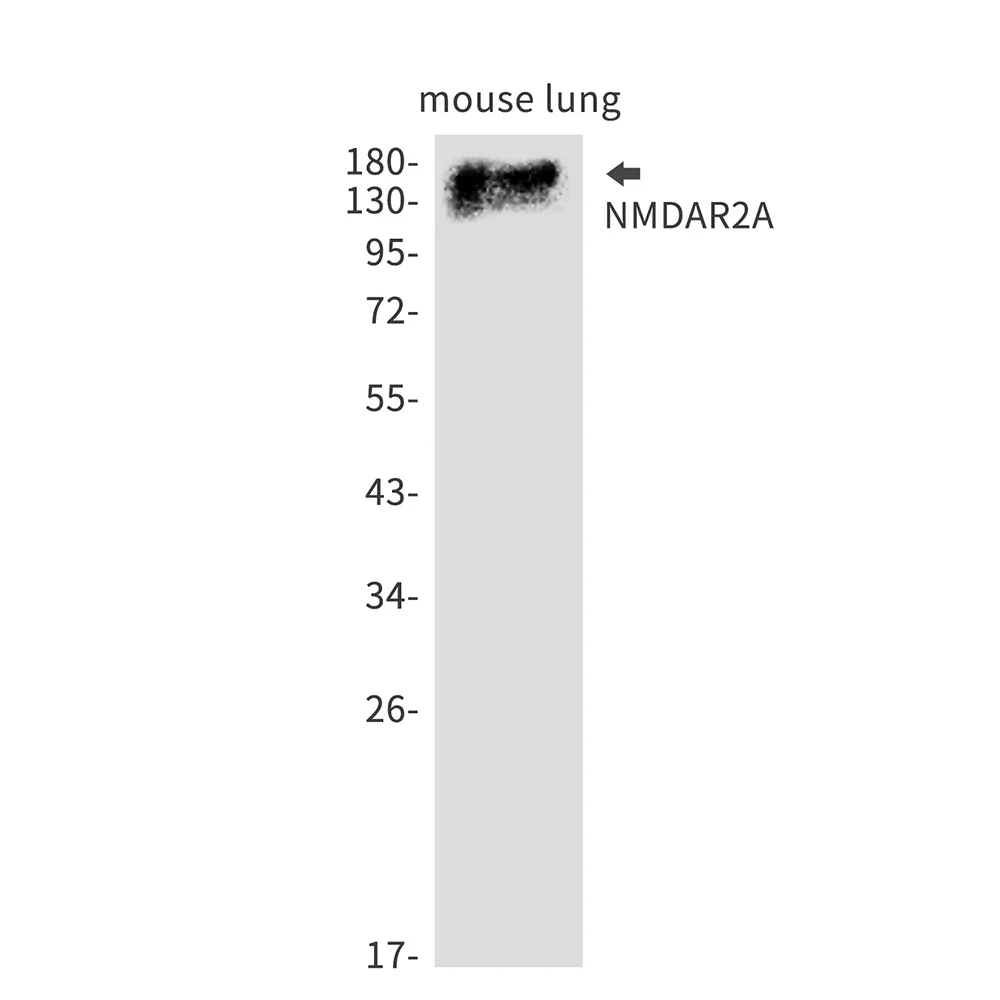
| Molecular Weight | Calculated MW: 165 kDa; Observed MW: 165 kDa |
Background
Component of NMDA receptor complexes that function as heterotetrameric, ligand-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Channel activation requires binding of the neurotransmitter glutamate to the epsilon subunit, glycine binding to the zeta subunit, plus membrane depolarization to eliminate channel inhibition by Mg2+. Sensitivity to glutamate and channel kinetics depend on the subunit composition; channels containing GRIN1 and GRIN2A have higher sensitivity to glutamate and faster kinetics than channels formed by GRIN1 and GRIN2B . Contributes to the slow phase of excitatory postsynaptic current, long-term synaptic potentiation, and learning.
Research Area
Neuroscience
