Size:50μL Price:$150
Size:100μL Price:$280
Size:200μL Price:$520
Application:WB,IHC,FC
Reactivity:Human
Conjugate:Unconjugated
Optional conjugates: Biotin, FITC (free of charge). See other 26 conjugates.
Gene Name:UBB
Summary
| Production Name | Ubiquitin Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody |
| Description | Rabbit polyclonal Antibody |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Application | WB,IHC,FC |
| Reactivity | Human |
Performance
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Modification | Unmodified |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Form | Liquid |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Buffer | 50mM Tris-Glycine(pH 7.4), 0.15M NaCl, 40% Glycerol, 0.01% Sodium azide and 0.05% protective protein |
| Purification | Affinity Purification |
Immunogen
| Gene Name | UBB |
| Alternative Names | FLJ25987; MGC8385; ubiquitin B; Ubiquitin; UBCEP1; UBCEP2; RPS27A |
| Gene ID | 7314 |
| SwissProt ID | P0CG47 |
Application
| Dilution Ratio | WB 1:500-1:1000,IHC 1:50-1:100,FC 1:50-1:100 |
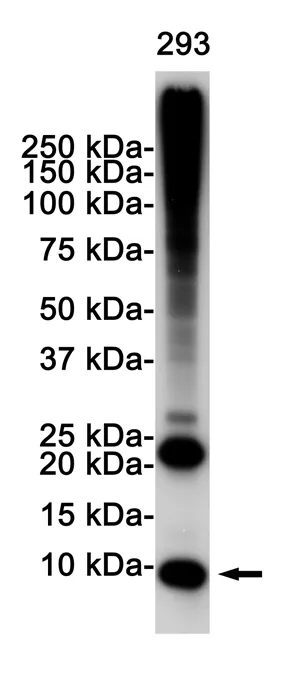
| Molecular Weight | Calculated MW: 26 kDa; Observed MW: 8 kDa |
Background
Plays an important role in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Ubiquitin can be covalently linked to many cellular proteins by the ubiquitination process, which targets proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome. Three components are involved in the target protein-ubiquitin conjugation process. Ubiquitin is first activated by forming a thiolester complex with the activation component E1; the activated ubiquitin is subsequently transferred to the ubiquitin-carrier protein E2, then from E2 to ubiquitin ligase E3 for final delivery to the epsilon-NH2 of the target protein lysine residue.
Research Area
Neuroscience
