Size:100μL Price:$230
Size:200μL Price:$380
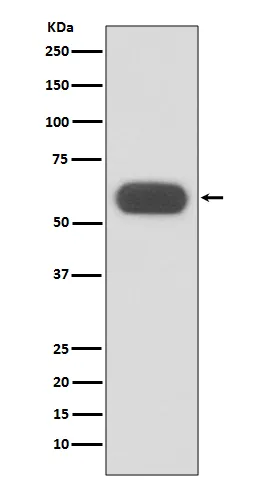
Application:WB,IHC
Reactivity:Human
Conjugate:Unconjugated
Optional conjugates: Biotin, FITC (free of charge). See other 26 conjugates.
Gene Name:GBA
Summary
| Production Name | GBA (1P9) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Description | Recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibody |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Application | WB,IHC |
| Reactivity | Human |
Performance
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Modification | Unmodified |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Form | Liquid |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Buffer | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% New type preservative N and 50% glycerol. Store at +4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle. |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
Immunogen
| Gene Name | GBA |
| Alternative Names | Alglucerase; betaGC; GBA1; GCase; GCB; GLUC; Glucosylceramidase; Imiglucerase; |
| Gene ID | 2629 |
| SwissProt ID | P04062 |
Application
| Dilution Ratio | WB 1:1000-1:5000,IHC 1:50-1:100 |
| Molecular Weight | 60kDa |
Background
Defects in GBA are the cause of Gaucher disease (GD) [MIM:230800]; also known as glucocerebrosidase deficiency. GD is the most prevalent lysosomal storage disease, characterized by accumulation of glucosylceramide in the reticulo-endothelial system. Glucosylceramidase that catalyzes, within the lysosomal compartment, the hydrolysis of glucosylceramide/GlcCer into free ceramide and glucose (PubMed:9201993, PubMed:24211208, PubMed:15916907). Thereby, plays a central role in the degradation of complex lipids and the turnover of cellular membranes (PubMed:27378698). Through the production of ceramides, participates in the PKC-activated salvage pathway of ceramide formation (PubMed:19279011). Also plays a role in cholesterol metabolism (PubMed:24211208, PubMed:26724485). May either catalyze the glucosylation of cholesterol, through a transglucosylation reaction that transfers glucose from glucosylceramide to cholesterol (PubMed:24211208, PubMed:26724485). The short chain saturated C8:0- GlcCer and the mono-unsaturated C18:0-GlcCer being the most effective glucose donors for that transglucosylation reaction (PubMed:24211208). Under specific conditions, may alternatively catalyze the reverse reaction, transferring glucose from cholesteryl-beta-D-glucoside to ceramide (PubMed:26724485). Finally, may also hydrolyze cholesteryl- beta-D-glucoside to produce D-glucose and cholesterol (PubMed:24211208, PubMed:26724485).
Research Area
