Size:100μL Price:$230
Size:200μL Price:$380
Application:WB,IHC,ICC/IF,IF-P
Reactivity:Human,Mouse,Rat
Conjugate:Unconjugated
Optional conjugates: Biotin, FITC (free of charge). See other 26 conjugates.
Gene Name:MAPT
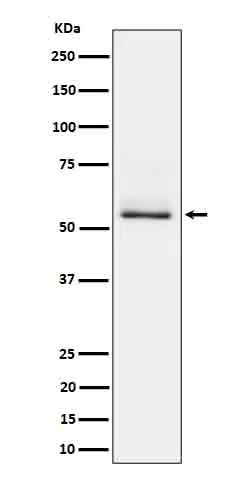
Summary
| Production Name | Phospho-Tau (S404) (13R18) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Description | Recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibody |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Application | WB,IHC,ICC/IF,IF-P |
| Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
Performance
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Modification | Phosphorylated |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Form | Liquid |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Buffer | Rabbit IgG in phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM NaCl, 0.02% New type preservative N and 50% glycerol. Store at +4°C short term. Store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze / thaw cycle. |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
Immunogen
| Gene Name | MAPT |
| Alternative Names | MAPT; Microtubule-associated protein tau; MTBT1; Neurofibrillary tangle protein; Paired helical filament-tau; PHF-tau |
| Gene ID | 4137 |
| SwissProt ID | P10636 |
Application
| Dilution Ratio | WB 1:500-1:2000,IHC 1:20-1:100,ICC/IF 1:20-1:50,IF-P 1:20-1:50 |
| Molecular Weight | 79kDa |
Background
Promotes microtubule assembly and stability, and might be involved in the establishment and maintenance of neuronal polarity. The C-terminus binds axonal microtubules while the N-terminus binds neural plasma membrane components, suggesting that tau functions as a linker protein between both. Promotes microtubule assembly and stability, and might be involved in the establishment and maintenance of neuronal polarity (PubMed:21985311). The C-terminus binds axonal microtubules while the N-terminus binds neural plasma membrane components, suggesting that tau functions as a linker protein between both (PubMed:21985311, PubMed:32961270). Axonal polarity is predetermined by TAU/MAPT localization (in the neuronal cell) in the domain of the cell body defined by the centrosome. The short isoforms allow plasticity of the cytoskeleton whereas the longer isoforms may preferentially play a role in its stabilization.
Research Area
MAPK_ERK_Growth;MAPK_G_Protein;Alzheimer's disease
