


Size:50μL Price:$118
Size:100μL Price:$220
Size:200μL Price:$380
Application:WB,IHC,ICC/IF,ELISA
Reactivity:Human,Mouse,Rat
Conjugate:Unconjugated
Optional conjugates: Biotin, FITC (free of charge). See other 26 conjugates.
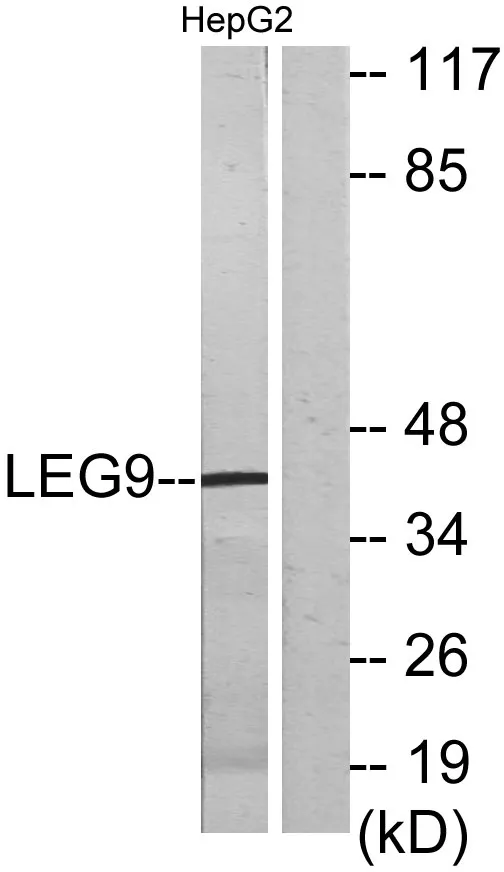
Gene Name:LGALS9
Summary
| Production Name | Galectin-9 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody |
| Description | Rabbit polyclonal Antibody |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Application | WB,IHC,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
Performance
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Modification | Unmodified |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Form | Liquid |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Buffer | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% protective protein and 0.02% New type preservative N. |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
Immunogen
| Gene Name | LGALS9 |
| Alternative Names | LGALS9; Galectin-9; Gal-9; Ecalectin; Tumor antigen HOM-HD-21 |
| Gene ID | 3965 |
| SwissProt ID | O00182 |
Application
| Dilution Ratio | WB 1:500-1:2000,IHC 1:100-1:300,ICC/IF 1:200-1:1000,ELISA 1:5000-1:20000 |
| Molecular Weight | 40kDa |
Background
The galectins are a family of beta-galactoside-binding proteins implicated in modulating cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions. The protein encoded by this gene is an S-type lectin. It is overexpressed in Hodgkin's disease tissue and might participate in the interaction between the H&RS cells with their surrounding cells and might thus play a role in the pathogenesis of this disease and/or its associated immunodeficiency. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],alternative products:Additional isoforms seem to exist,domain:Contains two homologous but distinct carbohydrate-binding domains.,function:Binds galactosides. Has high affinity for the Forssman pentasaccharide. May play a role in thymocyte-epithelial interactions relevant to the biology of the thymus. Inhibits cell proliferation. The isoform Short acts as an eosinophil chemoattractant. Is a ligand for HAVCR2/TIM3. Induces T-helper type 1 lymphocyte (Th1) death.,online information:Galectin-9,similarity:Contains 2 galectin domains.,subcellular location:May also be secreted by a non-classical secretory pathway.,subunit:Monomer.,tissue specificity:Peripheral blood leukocytes and lymphatic tissues. Overexpressed in Hodgkin's disease tissue.,
Research Area
