Size2:50μg price2:$186
Size3:500μg price3:$1250
| Name | Recombinant Human Beta-NGF |
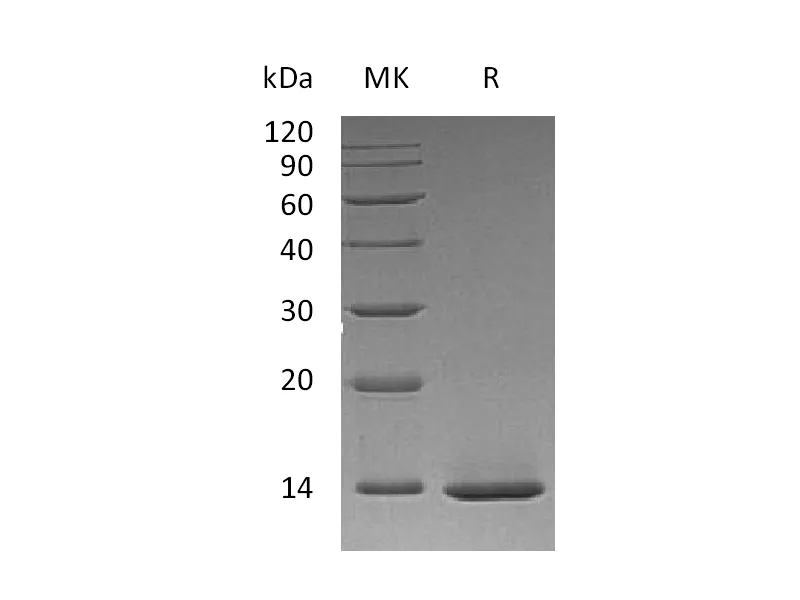
| Purity | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin level | <0.01 EU/µg as determined by LAL test. |
| Construction | Recombinant Human Beta-Nerve Growth Factor is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Ser122-Ala241 is expressed. |
| Accession # | P01138 |
| Host | E.coli |
| Species | Human |
| Predicted Molecular Mass | 13.4 KDa |
| Buffer | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. |
| Form | Lyophilized |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature.Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature listed below. |
| Stability&Storage | Lyophilized protein should be stored at ≤ -20°C, stable for one year after receipt. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 2-8°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at ≤ -20°C for 3 months. |
| Reconstitution | Always centrifuge tubes before opening.Do not mix by vortex or pipetting.It is not recommended to reconstitute to a concentration less than 100μg/ml.Dissolve the lyophilized protein in distilled water.Please aliquot the reconstituted solution to minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
Alternative Names
Beta-Nerve Growth Factor; Beta-NGF; NGF; NGFB;β-NGF
Background
Human β-Nerve Growth Factor (β-NGF) was initially isolated in the mouse submandibular gland. It is composed of three non-covalently linked subunits α, β, and γ; it exhibits all the biological activities ascribed to NGF. It is structurally related to BDNF, NT-3 and NT-4 and belongs to the cysteine-knot family of growth factors that assume stable dimeric structures. Β-NGF is a neurotrophic factor that signals through its receptor β-NGF, and plays a crucial role in the development and preservation of the sensory and sympathetic nervous systems. Β-NGF also acts as a growth and differentiation factor for B lymphocytes and enhances B-cell survival. These results suggest that β-NGF is a pleiotropic cytokine, which in addition to its neurotropic activities may have an important role in the regulation of the immune system. Human β-NGF shares 90% sequence similarity with mouse protein and shows cross-species reactivity.
Note
For Research Use Only , Not for Diagnostic Use.
