Size2:50μg price2:$465
Size3:500μg price3:$2325
| Name | Recombinant Mouse IL-12 |
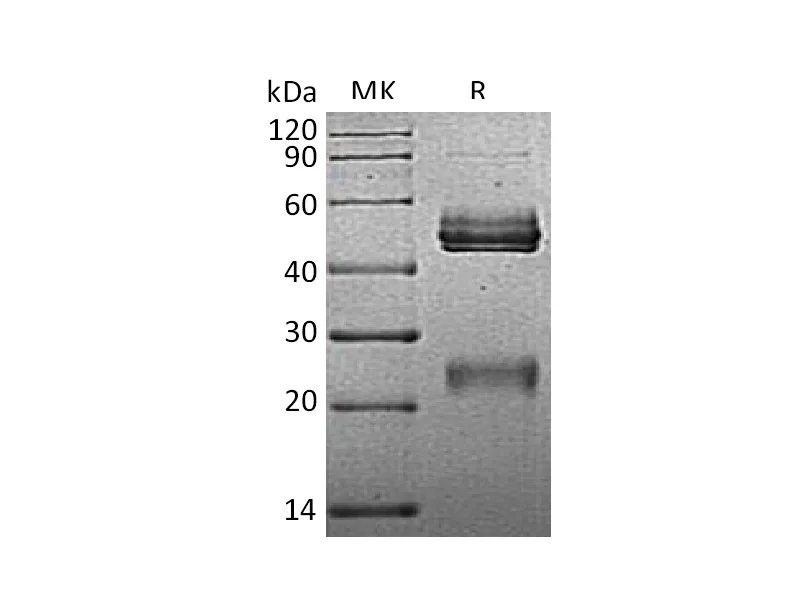
| Purity | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin level | <0.01 EU/µg as determined by LAL test. |
| Construction | Recombinant Mouse Interleukin-12 is produced by our Mammalian expression system and the target gene encoding Met23-Ser335&Arg23-Ala215 is expressed. |
| Accession # | P43432&P43431 |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Species | Mouse |
| Predicted Molecular Mass | 35.8&21.7 KDa |
| Buffer | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. |
| Form | Lyophilized |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature.Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature listed below. |
| Stability&Storage | Lyophilized protein should be stored at ≤ -20°C, stable for one year after receipt. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 2-8°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at ≤ -20°C for 3 months. |
| Reconstitution | Always centrifuge tubes before opening.Do not mix by vortex or pipetting.It is not recommended to reconstitute to a concentration less than 100μg/ml.Dissolve the lyophilized protein in distilled water.Please aliquot the reconstituted solution to minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
Alternative Names
IL-12; Interleukin 12; Interleukin-12 subunit alpha;IL-12A;Cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor 35 kDa subunit;CLMF p35;IL-12 subunit p35;Interleukin-12 subunit beta; IL-12B; Cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor 40 kDa subunit; CLMF p40; IL-12 subunit p40;
Background
Mouse IL-12 is a heterodimeric pleiotropic cytokine made up of a 40 kDa (p40) subunit and a 35 kDa (p35) subunit. Human and mouse IL‑12 share 70% and 60% amino acid sequence identity in their p40 and p35 subunits, respectively. While mouse IL‑12 is active on both human and mouse cells, human IL‑12 is not active on murine cells. It is involved in the differentiation of naive T cells into Th1 cells. It is known as a T cell-stimulating factor, which can stimulate the growth and function of T cells. It stimulates the production of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) from T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, and reduces IL-4 mediated suppression of IFN-γ. T cells that produce IL-12 have a coreceptor, CD30, which is associated with IL-12 activity. IL-12 plays an important role in the activities of natural killer cells and T lymphocytes.IL-12 mediates enhancement of the cytotoxic activity of NK cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes.
Note
For Research Use Only , Not for Diagnostic Use.
