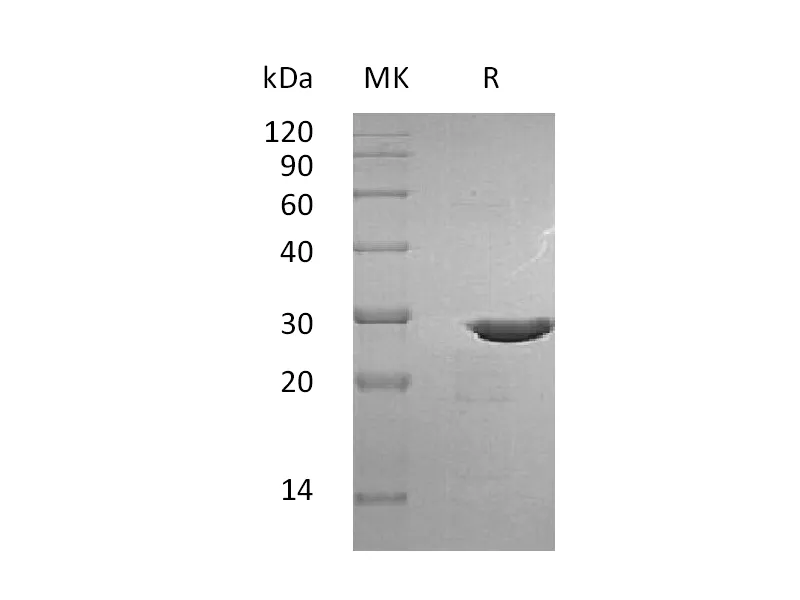
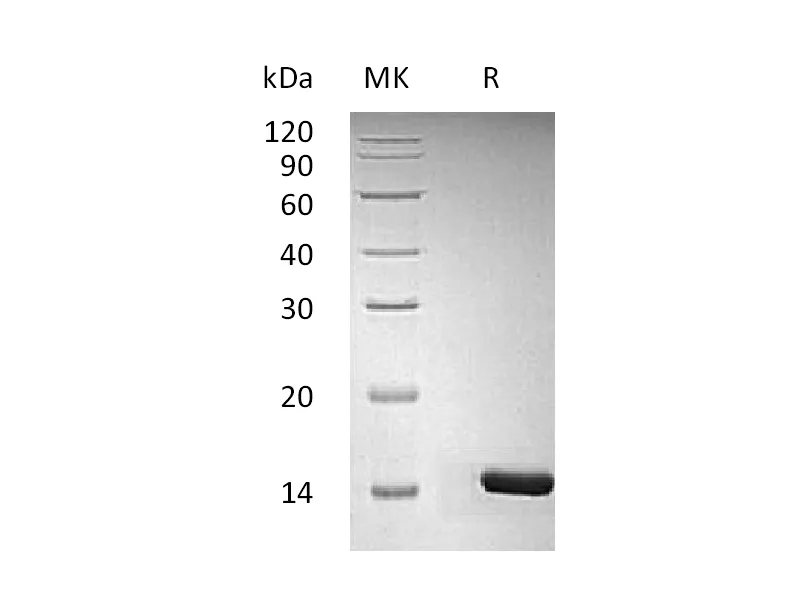
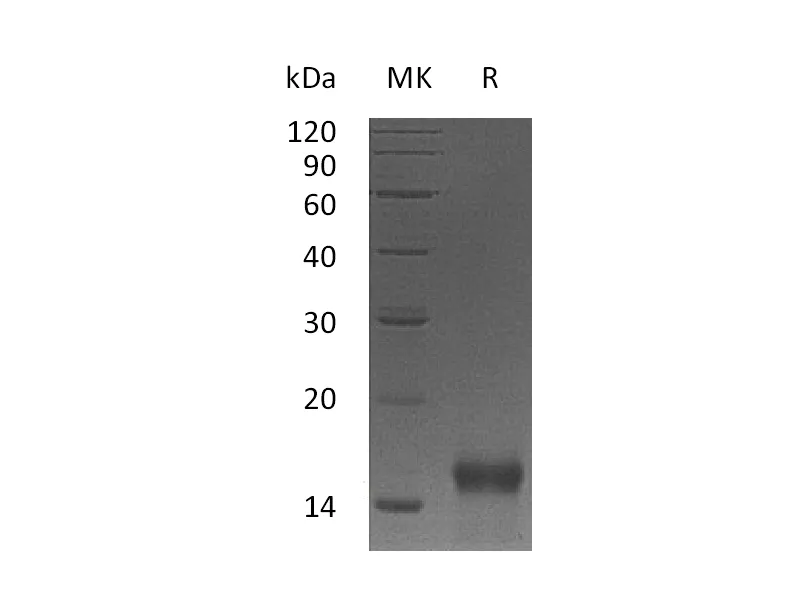
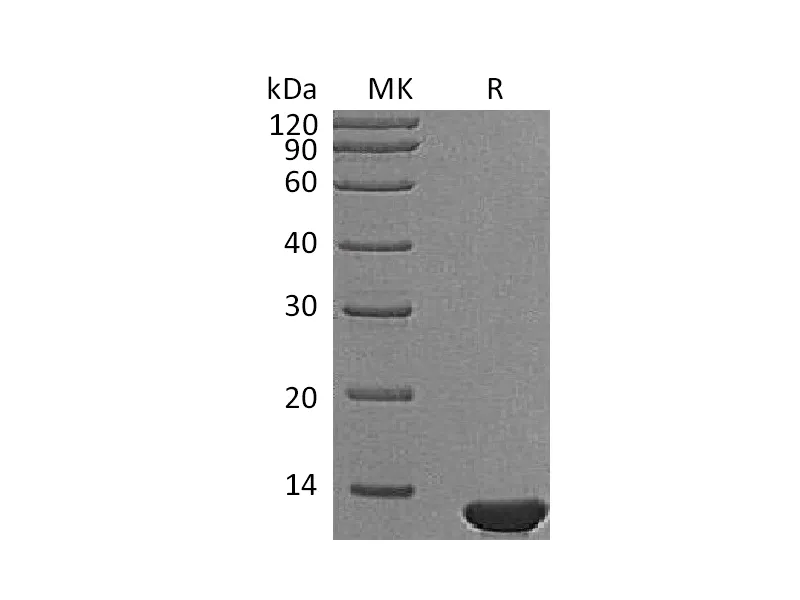
Alternative Names
Wnt Surrogate-Fc Fusion Protein; Wnt Surrogate
Background
Wnt-3a is one of 19 vertebrate members of the Wingless-type MMTV integration site (Wnt) family of highly conserved cysteine-rich secreted glycoproteins important for normal developmental processes. WNT signaling plays key roles in the control of development, homeostasis, and regeneration of many essential organs and tissues, including bone, liver, skin, stomach, intestine, lung, kidney, central nervous system, mammary gland, taste bud, ovary, cochlea, and vessels among many others. Modulation of WNT signaling pathways has potential for treatment of degenerative diseases and tissue injuries. And they signal through FZD1-10 and LRP5 or 6, two families of receptors. Endogenous WNTs bind to multiple FZDs and are heavily modified posttranslationally, making them difficult to manufacture consistently. WNT surrogate molecules phenocopied endogenous ligand activities in in vitro reporter assays and intestine organoid functional assays. WNT surrogate molecules can be selective for individual FZD or a subfamily of FZDs in combination with LRP5 or LRP6, depending on the binder specificities.
Note
For Research Use Only , Not for Diagnostic Use.