Size2:50μg price2:$465
Size3:500μg price3:$2325
| Name | Recombinant Rat IL-1a |
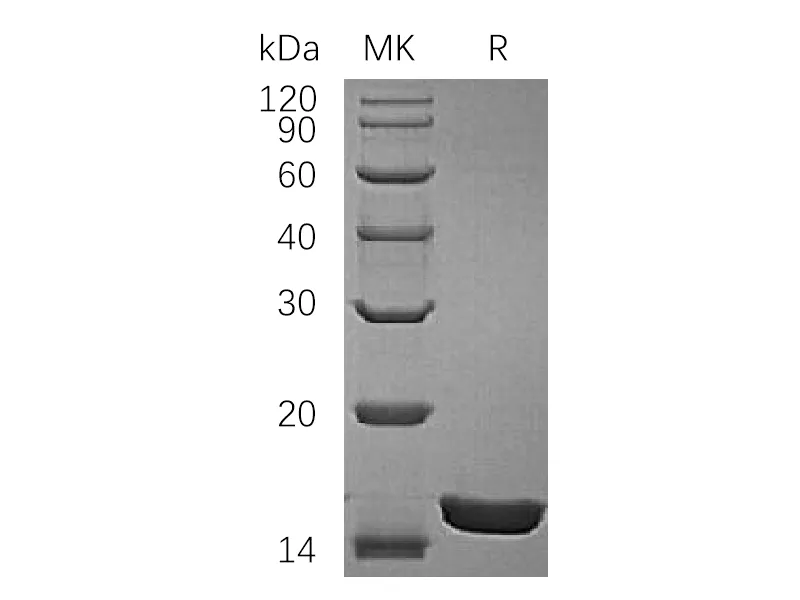
| Purity | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin level | <1 EU/µg as determined by LAL test. |
| Construction | Recombinant Rat Interleukin-1 Alpha is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Ser115-Ser270 is expressed. |
| Accession # | P16598 |
| Host | E.coli |
| Species | Rat |
| Predicted Molecular Mass | 17.9 KDa |
| Buffer | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 7.4. |
| Form | Lyophilized |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature.Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature listed below. |
| Stability&Storage | Lyophilized protein should be stored at ≤ -20°C, stable for one year after receipt. Reconstituted protein solution can be stored at 2-8°C for 2-7 days. Aliquots of reconstituted samples are stable at ≤ -20°C for 3 months. |
| Reconstitution | Always centrifuge tubes before opening.Do not mix by vortex or pipetting.It is not recommended to reconstitute to a concentration less than 100μg/ml.Dissolve the lyophilized protein in distilled water.Please aliquot the reconstituted solution to minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
Alternative Names
Interleukin-1 alpha; IL-1 alpha; Il1a
Background
Interleukin 1 (IL-1) is a name that designates two proteins, IL-1αand IL-1β, which are the products of distinct genes, but which show approximately 25% amino acid (aa) sequence identity and which recognize the same cell surface receptors. IL-1αand IL-1β are both synthesized as 31 kDa precursors that are subsequently cleaved into proteins with molecular weights of approximately 17,000 Da. Neither precursor contains a typical hydrophobic signal peptide sequence and most of the precursor form of IL-1α remains in the cytosol of cells, although there is evidence for a membranebound form of the precursor form of IL-1α. Although IL-1 production is generally considered to be a consequence of inflammation, evidence suggests that IL-1 is also temporally upregulated during bone formation and the menstrual cycle and can be induced in response to nervous system stimulation. In response to classic stimuli produced by inflammatory agents, infections or microbial endotoxins, a dramatic increase in the production of IL-1 by macrophages and various other cells is seen.
Note
For Research Use Only , Not for Diagnostic Use.
