Alternative Names
Diphtheria toxin receptor; DTR;HEGFL; heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor; DTS; DTSF; heparin-binding epidermal growth factor; proheparin-binding EGF-like growth factor; HB-EGF; pro HB-EGF
Background
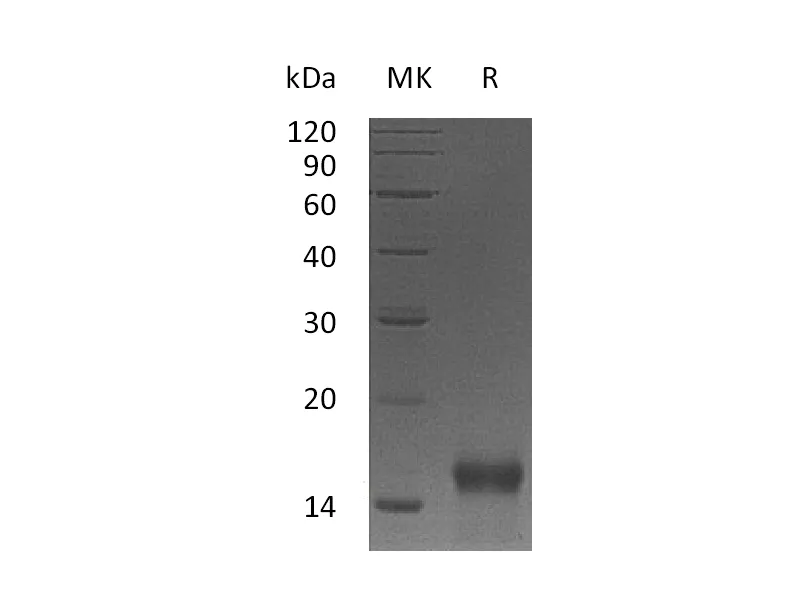
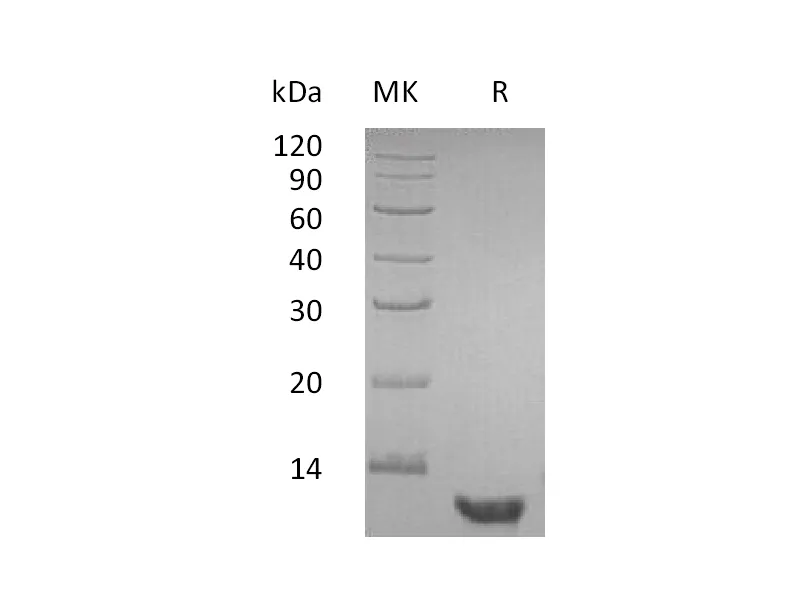
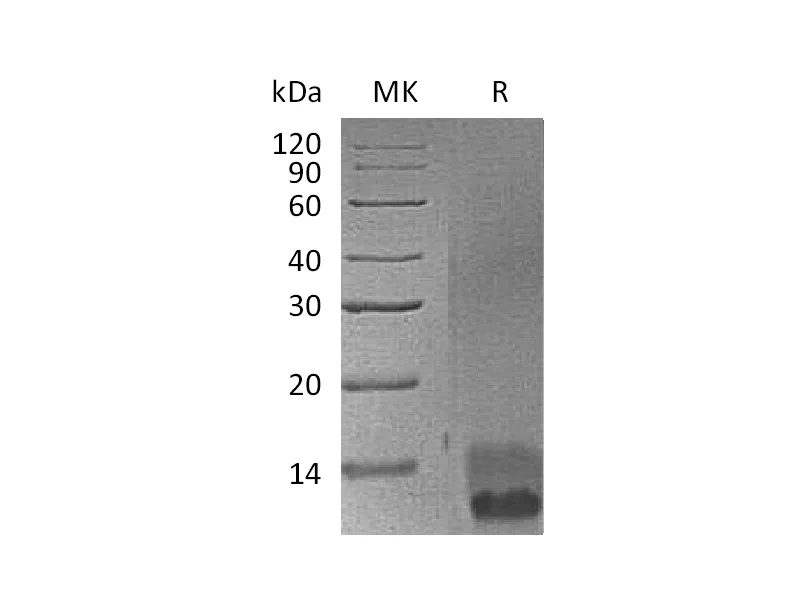
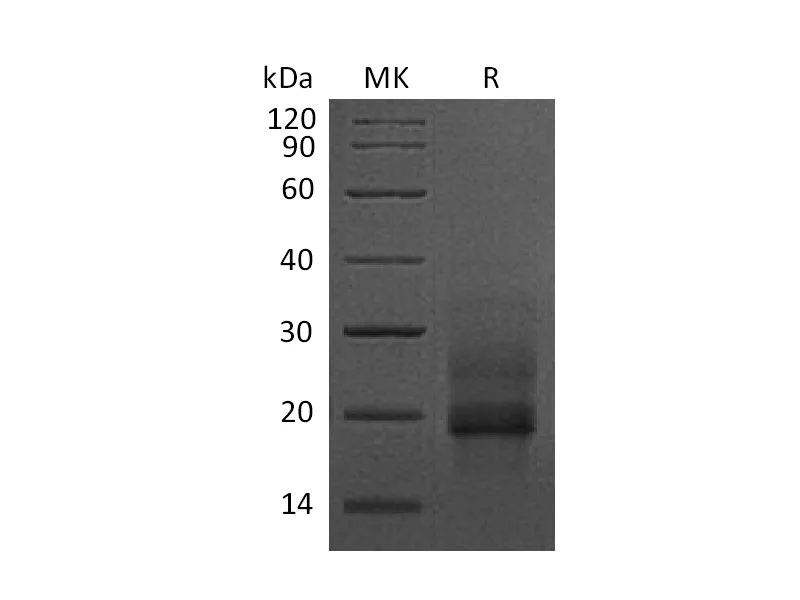
Heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor (HB-EGF) is a 12/xad16 kDa member of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family. It possesses an EGF/xadlike domain, and a heparin-binding motif. Mature HB/xadEGF is a soluble peptide that arises from proteolytic processing of the transmembrane form. Human HB/xadEGF shows 76% and 73% aa sequence identity with rat and mouse HB/xadEGF, respectively. It is required for normal cardiac valve formation and normal heart function, promotes smooth muscle cell proliferation. It may be involved in macrophage-mediated cellular proliferation; it is mitogenic for fibroblasts, but not endothelial cells. HB/xadEGF classified as a group 2 ErbB ligand based on its ability to activate both the EGF/ErbB1 and ErbB4 receptors. Activity associated with ErbB4 binding appears to be limited to non/xadmitogenic actions, while EGFR binding induces both mitogenic and non/xadmitogenic activity.
Note
For Research Use Only , Not for Diagnostic Use.