Human gastric cancer cells (undifferentiated) HGC-27
The human gastric cancer cell line HGC-27 is an undifferentiated human gastric cancer cell line commonly used for studying the biological characteristics and related mechanisms of gastric cancer.
Here are some key information about the HGC-27 cell line:
1. Cell source and characteristics: HGC-27 cells are derived from undifferentiated gastric cancer tissue, with epithelial morphology and adherent growth characteristics, and can secrete mucin. These cells exhibit strong tumorigenicity and have been used as research subjects for gastric cancer stem cells (CSCs) in some studies [9,13,14].
2. Cultivation conditions: HGC-27 cells are usually cultured in RPMI-1640 medium, supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% antibiotic antifungal agent (P/S), and incubated in a constant temperature incubator at 37℃ and 5% CO2. The passage ratio is generally 1:2 to 1:5, and the culture medium is changed every 2 to 3 days.
3. Freezing and Resuscitation: HGC-27 cells can be frozen using a freezing solution containing DMSO under liquid nitrogen vapor phase conditions. During resuscitation, the frozen solution needs to be melted in a 37 ℃ water bath and resuscitated according to the operating instructions.
4. Research application: HGC-27 cells are widely used to study the biological behaviors of gastric cancer, such as proliferation, migration, and invasion. For example, studies have shown that miRNA inhibitors can effectively inhibit the proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of HGC-27 cells [2]. In addition, HGC-27 cells have been used to study the effects of drugs on gastric cancer cells, such as piperine regulating the proliferation and invasion of HGC-27 cells by downregulating the expression of Wnt/β - catenin signaling molecules [10].
5. Safety and usage restrictions: The HGC-27 cell line is for scientific research purposes only and cannot be used for clinical treatment. During the production and cultivation process, it is necessary to strictly control the sterile conditions and decide whether to add antibiotics based on the actual situation.
6. Special characteristics: HGC-27 cells exhibit strong stem cell characteristics, capable of forming tumor spheroids and communicating with other cells through exosomes [9,13,14]. In addition, HGC-27 cells have shown high transplantation rates and low metastasis rates in certain experiments [11].
The HGC-27 cell line is an important tool for studying the biological characteristics of gastric cancer and its potential therapeutic targets. During use, strict aseptic procedures and freezing recovery steps must be followed to ensure the reliability and reproducibility of experimental results.
The specific application cases of HGC-27 cell line in gastric cancer research include the following aspects:
1. Research on migration and invasion ability:
The oHGC-27 cell line was used to evaluate the migration and invasion ability of gastric cancer cells. Through Transwell migration and invasion experiments, researchers were able to detect the migration and invasion ability of HGC-27 cells, and further analyze protein expression related to CD44 [19].
In another study, HGC-27 cells were used to evaluate the migration and invasion ability of cells under different conditions, including cells treated with 5-Aza-CdR and TSA [20].
2. Research on miRNA expression and function:
The oHGC-27 cell line was used to investigate the role of miRNA in gastric cancer. For example, studies have found that the expression levels of miR-433 and miR-127 are significantly reduced in HGC-27 cells, and these miRNAs can effectively inhibit the proliferation and cell cycle of tumor cells [20].
In another study, HGC-27 cells were used to evaluate the transfection efficiency of miRNA mimetics and negative control miRNAs, and mRNA expression was analyzed by RT-PCR [20].
3. Drug resistance research:
The oHGC-27 cell line was used to study drug resistance in gastric cancer cells. For example, studies have found that high expression of HCCR protein in HGC-27 cells is associated with 5-FU resistance, and HCCR expression is significantly upregulated in the resistant subtype HGC-27-R [21].
4. Metabolic research:
The oHGC-27 cell line was used to study the metabolic characteristics of gastric cancer cells. For example, by detecting glucose consumption and lactate production, measuring oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR), researchers can evaluate the metabolic status of HGC-27 cells [22].
5. Tumor suppression research:
The oHGC-27 cell line was used to evaluate the effects of different treatment strategies on tumor growth. For example, research has found that GQDs/ Cy5-miR@sEVs It can effectively inhibit the tumor growth of HGC-27 cells and achieve this effect by targeting the target gene CCND1 of miR-193a-3p [23].
6. Study on the inhibitory effect of drugs:
The oHGC-27 cell line was used to evaluate the inhibitory effect of curcumin analogue CH-5 on gastric cancer cells. Research has found that CH-5 can effectively inhibit the proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of HGC-27 cells, indicating that it may become a potential drug for treating gastric cancer [24].
How are the stem cell characteristics of HGC-27 cell line identified and validated?
The stem cell characteristics of HGC-27 cell line are mainly identified and validated through the following experimental methods:
1. Colony formation assay: During the logarithmic growth phase, HGC-27 cells are digested into a single-cell suspension and then added to 6-centimeter diameter culture dishes, each dish containing 1 × 10 ^ 3 cells. After 14 days of cultivation, collect the supernatant, wash and fix the colonies, and finally stain with Giemsa. Count the number of colonies using an optical microscope to calculate the colony formation efficiency. Colony formation is an important characteristic of stem cells, as stem cells have the ability to self renew and differentiate, and can form multicellular colonies [7].
2. Cell cycle analysis: Collect and wash logarithmic growth phase transfected HGC-27 cells using Cell Cycle and Apoptosis analysis kits, then add Proline iodide buffer in the dark and incubate at 37℃for 30 minutes before immediately performing flow cytometry analysis. By analyzing the distribution of cell cycle, the proliferation ability and stem cell characteristics of cells can be evaluated [7].
3. Fluorescein enzyme reporter gene experiment: According to the prediction of Targeted ScanHuman 7.0, SOX4 may be a potential target of miR-140. The wild-type and mutant 3'UTR fragments of SOX4 were synthesized using QuikChange Multi Site Directed Mutagenesis Kit, cloned into luciferase reporter gene vectors, and transfected together with miR-140 mimetics or controls. After 48 hours, the fluorescence intensity was detected by flow cytometry. This experiment can verify the expression of SOX4 in HGC-27 cells and its relationship with miR-140, indirectly reflecting stem cell characteristics [7].
4. Real time quantitative PCR (qPCR): Total RNA and miRNA are extracted using RNAiso or TRIzol reagents, and then reverse transcribed into complementary DNA (cDNAs). Use specific primers for qPCR, targeting miR-140 and other test genes, with U6 and GAPDH as internal reference genes. The experiment was repeated three times, and the data was analyzed using the 2 ^ - DCDt method. QPCR experiments can quantitatively analyze the expression levels of specific genes, thereby evaluating the expression of stem cell related genes [7].
5. Western blot experiment: Proteins were extracted after cell lysis, separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membrane, and subjected to immunoblotting analysis with specific antibodies. Western blot experiments can detect the expression levels of specific proteins, further verifying the expression of stem cell related proteins.
How do miRNA inhibitors specifically affect the proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of HGC-27 cells?
MiRNA inhibitors have a significant impact on the proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of HGC-27 cells. Specifically:
1. Proliferation:
The inhibition of omiR-191 and miR-425 significantly reduced the proliferation ability of HGC-27 cells. Through CCK-8 experiments, it was found that the proliferation of HGC-27 cells was significantly reduced after treatment with miR-191 and miR-425 inhibitors [2].
The inhibition of omiR-217 also significantly promoted the proliferation of HGC-27 cells [25].
2. Migration:
The inhibition of omiR-191 and miR-425 significantly reduced the migration ability of HGC-27 cells. In the experiment of artificial wound healing, inhibition of these two miRNAs significantly reduced cell migration [2].
The inhibition of omiR-217 also reduced the migration ability of HGC-27 cells [25].
3. Invasion:
The inhibition of omiR-191 and miR-425 significantly reduced the invasive ability of HGC-27 cells. Through Transwell invasion experiments, it was found that inhibiting these two miRNAs significantly reduced cell invasion [2].
The inhibition of omiR-217 also significantly reduced the invasive ability of HGC-27 cells [25].
MiRNA inhibitors affect the proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of HGC-27 cells through different mechanisms. The inhibition of miR-191 and miR-425 is mainly manifested by reducing cell proliferation and migration, while increasing the proportion of the S phase of the cell cycle [2]. The inhibition of miR-217 is manifested as promoting cell proliferation and reducing cell migration and invasion [25].
What is the specific mechanism by which piperine regulates HGC-27 cell proliferation and invasion through Wnt/β - catenin signaling molecules?
The specific mechanism by which piperine regulates the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cell line HGC-27 through Wnt/β - catenin signaling molecules is as follows:
1. Cell proliferation and vitality:
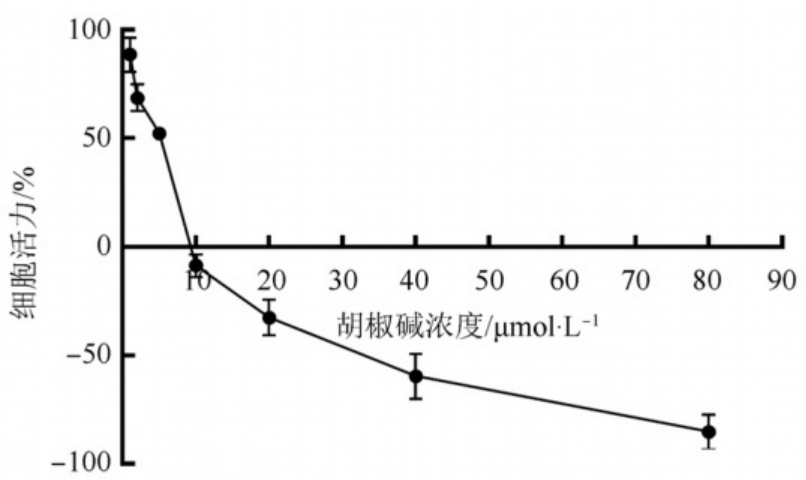
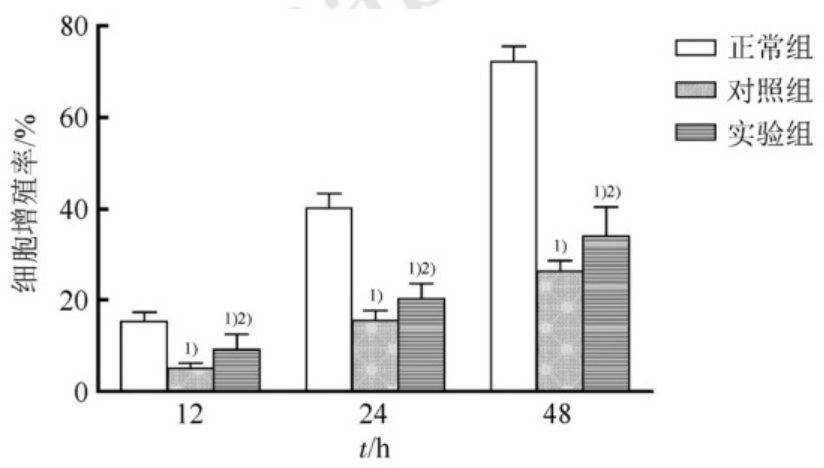
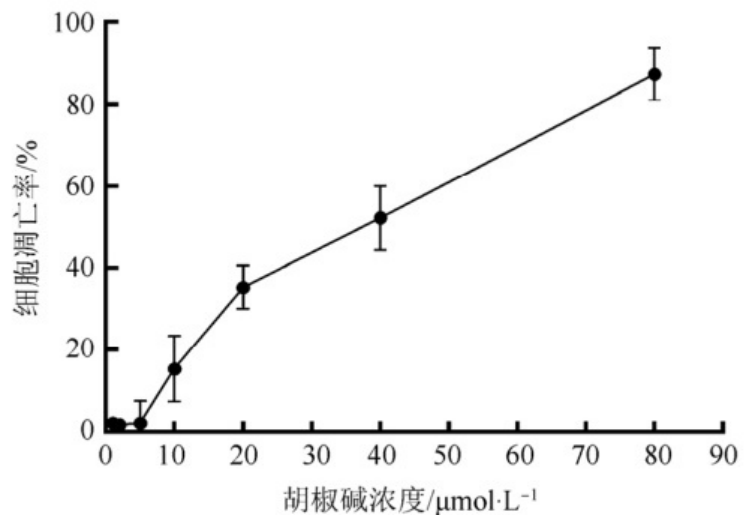
Low dose piperine (5 μmol·L^-1) has a significant effect on the proliferation and viability of HGC-27 cells. Research has shown that 5 μmol·L^-1 piperine can significantly reduce the proliferation rate and viability of HGC-27 cells after 12, 24, and 48 hours, but without significant cytotoxicity [10]. This indicates that piperine inhibits the proliferation of HGC-27 cells by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
2. Cell migration and invasion ability:
The scratch test and Transwell chamber test results showed that 5 μmol·L^-1 piperine can significantly reduce the migration and invasion ability of HGC-27 cells [10]. These results indicate that inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway can effectively reduce cell migration and invasion behavior.
3. Wnt/β - catenin signaling molecule expression:
Piperine significantly downregulated the expression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling molecules, including β-catenin, MMP2, MMP9, and N-cadherin [10]. The results of RT qPCR and Western blot both showed that the mRNA and protein levels of these key proteins were significantly lower in the experimental group than in the normal group and control group (Wnt/β-catenin inhibitor group), further confirming that piperine regulates cell behavior by downregulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling molecules [10].
Mechanism Summary:
In summary, low-dose piperine significantly inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of gastric cancer cell line HGC-27 by downregulating the expression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling molecules. This mechanism may be one of the important pathways for the anti-tumor effect of piperine [10].
Reference:
1. Correction to: DNA methylation downregulated mir-10b acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer. [PMID: 36136226]
2. Role of miR-191/425 Cluster in Tumorigenesis and Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer. [PMID: 24603541]
3. Ginsenoside Rh4 Suppresses Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via SIX1-Dependent TGF-β/Smad2/3 Signaling Pathway. [PMID: 35458126]
4. Garcinol acts as an antineoplastic agent in human gastric cancer by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.[PMID: 32565991]
5. Inhibition of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway by Dextran Sulfate suppresses angiogenesis of Gastric Cancer. [PMID: 33442403]
6. Identification of aberrantly expressed glycans in gastric cancer by integrated lectin microarray and mass spectrometric analyses.[ PMID: 27895315]
7. MicroRNA-140 Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Gastric Cancer Cell Line HGC-27 by Suppressing SOX4. [ PMID: 27353653]
8. Effect of TBL-12 on Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Apoptosis of Gastric Cancer Cell HGC-27. Kai Zhou et al.
9. LncRNA H19-rich extracellular vesicles derived from gastric cancer stem cells facilitate tumorigenicity and metastasis via mediating intratumor communication network. [ PMID: 37005676]
10. Study on the mechanism of antitumor effect of capsaicin based on Wnt/β-catenin signal. Guo Li et al..[2018-12-31]
11. High Engraftment and Metastatic Rates in Orthotopic Xenograft Models of Gastric Cancer via Direct Implantation of Tumor Cell Suspensions. [PMID: 38398149]
12. Bone marrow-derived stromal cells are associated with gastric cancer progression.Br J Cancer 2015 Jul 28;113(3):443-52. [PMID: 26125445]
13. Methylated lncRNAs suppress apoptosis of gastric cancer stem cells via the lncRNA-miRNA/protein axis. [PMID: 38600465]
14. hnRNPA2B1 regulates the alternative splicing of BIRC5 to promote gastric cancer progression. [PMID: 34044823]
15. Targeting cadherin-17 inactivates Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling and inhibits cell proliferation in gastric cancer. [PMID: 24465527]
16. Synthesis and cytotoxic activity of C-vinyl rhamnose glycoside derivatives. Ji Yu et al..
17. Serum tRF-27-FDXXE6XRK45 as a Promising Biomarker for the Clinical Diagnosis in Gastric Cancer. [PMID: 37575270]
18. Inhibitory effect of Ganoderma lucidum immunomodulatory protein on different gastric cancer cells in vitro. Xu Yan et al.[2016-05-24]
19. Exosomal CD44 Transmits Lymph Node Metastatic Capacity Between Gastric Cancer Cells via YAP-CPT1A-Mediated FAO Reprogramming. [PMID: 35359362]
20. The Tumor Suppressor Roles of miR-433 and miR-127 in Gastric Cancer.[ PMID: 23880861]
21. Targeting HCCR expression resensitizes gastric cancer cells to chemotherapy via down-regulating the activation of STAT3. [PMID: 27052330]
22.HBXIP Regulates Gastric Cancer Glucose Metabolism and Malignancy Through PI3K/AKT and p53 Signaling. [PMID: 32368094]
23. Visualization of microRNA therapy in cancers delivered by small extracellular vesicles. [PMID: 38031152]
24. Chalcones Repressed the AURKA and MDR Proteins Involved in Metastasis and Multiple Drug Resistance in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. [PMID: 30104527]
25. Retraction: The MicroRNA-217 Functions as a Potential Tumor Suppressor in Gastric Cancer by Targeting GPC5. [PMID: 36989230]
26. MicroRNA-27a promotes proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting MAP2K4 in human osteosarcoma cells. [PMID: 24556602]
27. MicroRNA-27a Induces Mesangial Cell Injury by Targeting of PPARγ, and its In Vivo Knockdown Prevents Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy. [PMID: 27184517]
28. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001306 Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Regulate FBXW7 Expression by Sponging miR-527 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. [PMID: 34659544]
29.CRISPR-based dissection of microRNA-23a ~ 27a ~ 24-2 cluster functionality in hepatocellular carcinoma. [PMID: 39112518]
30. miR-217 suppresses proliferation, migration, and invasion promoting apoptosis via targeting MTDH in hepatocellular carcinoma. [PMID: 28184926]
