Transferrin
Transferrin (TRF) is an important glycoprotein in human plasma, mainly synthesized in the liver. It is composed of 679 amino acid residues, with glycose accounting for about 6%. It has two highly homologous domains, the N - terminal and C - terminal. Each domain has a Fe³⁺ binding site and can reversibly bind two Fe³⁺. Transferrin can be divided into common transferrin, iron - saturated transferrin, etc. according to the iron - containing number, and can be divided into common - type transferrin and iso - type transferrin according to the configuration. Its main function is to act as a carrier for iron transport, transporting iron ions from absorption and storage sites to red blood cells and other iron - requiring cells, participating in the regulation of iron metabolism and balance, and also playing a role in respiration, cell proliferation, immune system regulation, and antibacterial and bactericidal aspects.
Product List
| Target | Catalog# | Product Name | Reactivity | Predicted MW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Transferrin(HOLO) | GMP Recombinant Human Transferrin | Human | 75.2 kDa | |
Transferrin(APO) | GMP Recombinant Human Transferrin(APO) | Human | 75.2 kDa | |
Transferrin | GMP Recombinant Bovine Transferrin | Bovine | 75.8 kDa | |
Transferrin | PCM90059 | GMP Recombinant Mouse Transferrin | Mouse | 74.5 kDa |
Validation Data
GMP Recombinant Human Transferrin (HOLO) (Catalog: PCH90044)
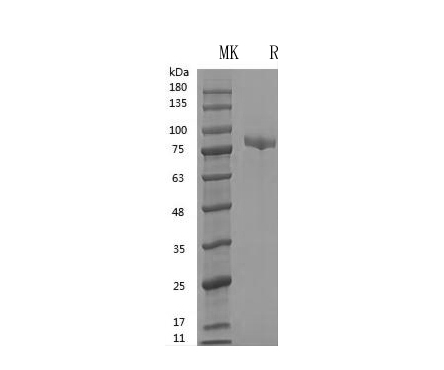
Transferrin (HOLO) SDS-PAGE image
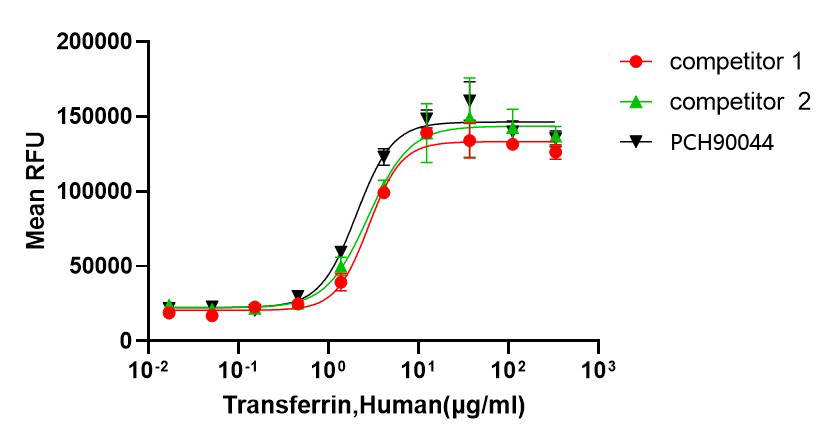 Bioactivity image: The ED50 for this effect is 0.5-2 μg/mL.
Bioactivity image: The ED50 for this effect is 0.5-2 μg/mL.GMP Recombinant Human Transferrin(APO) (Catalog: PCH90046)
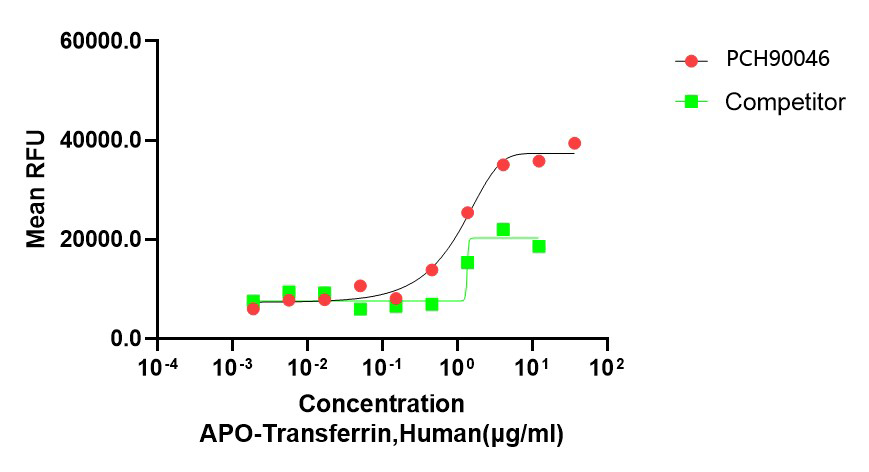 Bioactivity image: The ED50 for this effect is ≤5 μg/mL.
Bioactivity image: The ED50 for this effect is ≤5 μg/mL.References
1. Lobe specificity of iron binding to transferrin modulates murine erythropoiesis and iron homeostasis. Parrow NL, et al. Blood. 2019. [PMID: 31434707]
