Basic information of human esophageal cancer cell TE-1
Source and History
TE-1 human esophageal cancer cell line is an epithelial like cell line derived from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, with the characteristic of adherent growth and a doubling time of about 60-80 hours. It is widely used in research on esophageal cancer. This cell line was isolated from the digestive tract tissue of a 58 year old Japanese male patient with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by Japanese scientists Nishihara et al. in 1976.
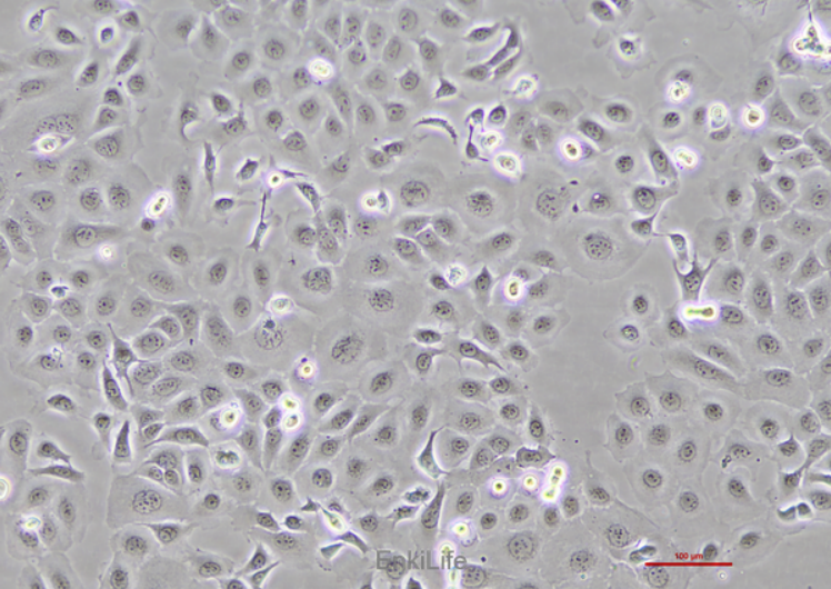
Cell characteristics
1. Morphology and growth characteristics: TE-1 cells have an epithelial like morphology and adhere to the wall, making them unable to be transplanted into nude mice.
2. Biological characteristics: This cell line exhibits highly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma features, but its biological characteristics and gene expression patterns limit its tumorigenicity in nude mice.
3. Genetic testing: Through STR identification, it has been confirmed that the TE-1 cell line is free of mycoplasma contamination, and the test results show that its genotype is consistent with the original tissue.
Cultivation conditions
1. Culture medium: RPMI-1640 medium is recommended, containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin streptomycin (P/S).
2. Environmental conditions: The incubator needs to maintain an environment of 95% air and 5% carbon dioxide at a temperature of 37 ℃.
3. Passage method: The recommended passage ratio is 1:2 to 1:4, with a passage interval of 2-3 weeks.
Freezing and transportation
1. Freezing conditions: Use serum-free freezing solution (such as DMSO) for freezing, the freezing solution needs to be prepared and used immediately, and stored in liquid nitrogen.
Transportation method: Dry ice transportation or recovery shipping can be used, and care should be taken to avoid thawing of cells during transportation.
application area
TE-1 cells are widely used in the study of esophageal cancer, including:
Drug screening: used to evaluate the efficacy of anti-tumor drugs.
Drug sensitivity and therapeutic targets
1. β- catenin significantly inhibits the survival of TE-1 cells by downregulating HSP70 expression [3].
2. Curcumin inhibits the proliferation of TE-1 cells by regulating the miR-590-3p and JNK3/caspase-3 signaling pathways [9].
3. Pyrotinib combined with X-ray irradiation can significantly inhibit the proliferation and migration of TE-1 cells [8].
Drug resistance and radiosensitivity
TE-1 cells treated with radiation exhibit stronger invasiveness and drug resistance, but reduced sensitivity to cisplatin [7].
Chemotherapy resistance
1. Overexpression of miR-7 can increase EGFR nuclear translocation, leading to resistance of esophageal cancer cells to cisplatin [20].
2. Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) induced by streptomycin (TM) can promote autophagy and apoptosis in TE-1 cells, providing a possible mechanism for chemotherapy resistance [17].
Molecular mechanism research:
Genes and Molecular Mechanisms
TCEAL7 gene: Overexpression of TCEAL7 gene can inhibit the invasion and migration ability of TE-1 cells [1].
SATB1 gene: Knocking down the SATB1 gene can significantly inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis of TE-1 cells, indicating that SATB1 plays an important role in esophageal cancer [5].
CHST15 gene: Knockdown of CHST15 can inhibit the proliferation and growth of TE-1 cells, and induce apoptosis [4].
Overexpression of miR-21 can reduce the sensitivity of TE-1 cells to cisplatin, while inhibition of miR-21 enhances its sensitivity [6].
MiR-27a: miR-27a inhibits the proliferation and invasion of TE-1 cells by targeting KRAS [10].
Gene expression analysis:
Gene regulation and therapeutic targets:
Overexpression of CBP (Cyclic AMP Response Element Binding Protein) can significantly inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and migration ability of TE-1 cells, indicating its potential as a therapeutic target [12].
Knockdown of SATB1 gene can significantly inhibit the proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis of TE-1 cells [14].
6. N-acetyltransferase (NAA10) inhibits the proliferation of TE-1 cells by blocking the G1 phase and inducing apoptosis [23].
Clinical significance and research value
TE-1 cells are widely used to study the biological characteristics of esophageal cancer, such as proliferation, migration, invasion, and drug sensitivity. For example, the functions of genes such as CHST15 and SATB1 were studied using RNA interference technology, revealing their potential therapeutic targets in esophageal cancer [4,5]
According to the search results, TE-1 cells have been used in multiple studies to investigate the proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis, and molecular mechanisms related to the tumor microenvironment in esophageal cancer.
1. Proliferation and apoptosis:
The proliferation ability of TE-1 cells can be inhibited in various ways. For example, β - Elemene significantly inhibits the proliferation of TE-1 cells by downregulating the Heat Shock Protein 70/Mothers against Decapentaplegic 2 (HSP70/MAD2) pathway. In addition, vitamin E succinate (VES) can significantly inhibit the proliferation of TE-1 cells and induce apoptosis at high doses [18].
The β - cyclodextrin inclusion complex of HeCheTeng alcohol significantly inhibits the proliferation of TE-1 cells by blocking the cell cycle and promoting apoptosis [16].
2. Migration and invasion:
TE-1 cells have strong invasion and migration abilities. Research has shown that the invasion ability of TE-1 cells can be evaluated through Transwell experiments, and treatment with β - catenin can significantly inhibit their migration and invasion ability [3]. In addition, p75NTR positive cells exhibit stronger proliferation ability and tumorigenicity in TE-1, exhibiting characteristics of tumor stem cells [2].
The migration and invasion ability of TE-1 cells can be regulated through various molecular mechanisms. For example, overexpression of miR-148a can significantly inhibit the migration and invasion ability of TE-1 cells, and downregulate the expression of c-Myc and matrix metalloproteinase MMP-9 [22].
Tipoprotein (Tip) inhibits ABCE1 acetylation through the Wnt signaling pathway, significantly suppressing the migration and invasion ability of TE-1 cells [15].
3. Tumor microenvironment and molecular markers:
OSNORA42 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of esophageal cancer cells by interacting with DHX9 [13].
OcircPDE3B adsorbs miR-4776-5p through sponge, upregulates LAMA1 expression, and promotes the progression of esophageal cancer [11].
Therefore, the TE-1 cell line has important application value in the study of esophageal cancer, and its biological characteristics such as proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis can be regulated through various molecular mechanisms. These studies provide potential targets and strategies for the treatment of esophageal cancer.
Other research progress:
OEGCG nanoparticles have a significant inhibitory effect on the proliferation of TE-1 cells and significantly increase their micronucleus rate, apoptosis rate, and necrosis rate [21].
Flavonoids such as puerarin can affect water transport in esophageal cancer cells by upregulating AQP1 mRNA expression [19].
TE-1 cells are an important model of esophageal cancer, and their research not only helps to understand the pathogenesis of esophageal cancer, but also provides important basis for developing new treatment strategies.
References
1. Deng Qianxi et al.TCEAL7 gene overexpression inhibits the invasion and metastasis of human esophageal carcinoma cell line TE-1 in vitro. 21st National Conference on Gastrointestinal Diseases, Chinese Medical Association.[2021-12-16]
2. Li Xiaolei et al. Effects of SATB1 gene silencing on the invasion and migration ability of cancer stem-like cells in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma TE-1.[2018-01-01]
3. Beta-Elemene Suppresses Metastasis of Human Esophageal Cancer Cell by Downregulating Heat Shock Protein 70/Mothers against Decapentaplegic Homolog 2Pathway. W. C. Gao et al.
4. CHST15 promotes the proliferation of TE 1 cells via multiple pathways in esophageal cancer. [PMID: 31746400]
5. Effect of SATB1 silencing on the proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of TE-1 esophageal cancer cells. [PMID: 28521398]
6. Li Chenhui et al. The influence of miRNAs on the occurrence and development of esophageal cancer and the intervention effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Zhongnan Pharmaceutical .22, No.2 (Total No.217). Zhongnan Pharmaceutical.
7. mRNA and methylation profiling of radioresistant esophageal cancer cells: the involvement of Sall2 in acquired aggressive phenotypes. Judong Luo et al.[ PMID: 28367244]
8. Radiosensitization of HER2-positive esophageal cancer cells by pyrotinib. [PMID: 32022229]
9. Qin Wenbing et al. The effect of curcumin on the sensitivity of 5-FU chemotherapy in esophageal carcinoma cells. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine. Vol. 45, No.3, March 2023.
10. microRNA-27a functions as a tumor suppressor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting KRAS. [PMID: 24154848]
11. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000277 sequesters miR-4766-5p to upregulate LAMA1 and promote esophageal carcinoma progression. [PMID: 34226522]
12. Overexpression of Csk-binding protein decreases growth,invasion, and migration of esophageal carcinoma cells by controlling Src activation. [PMID: 25684946]
13. SNORA42 Promote Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Development Through Interacting With Dhx9. et al. [PMID: 34182081]
14. Effect of SATB1 silencing on the proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of TE-1 esophageal cancer cells. [ PMID: 28521398]
15. Tip60-siRNA Regulates ABCE1 Acetylation and Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Esophageal Cancer via the Wnt Pathway.” Journal of Biosciences and Medicines(2022).
