GH Family
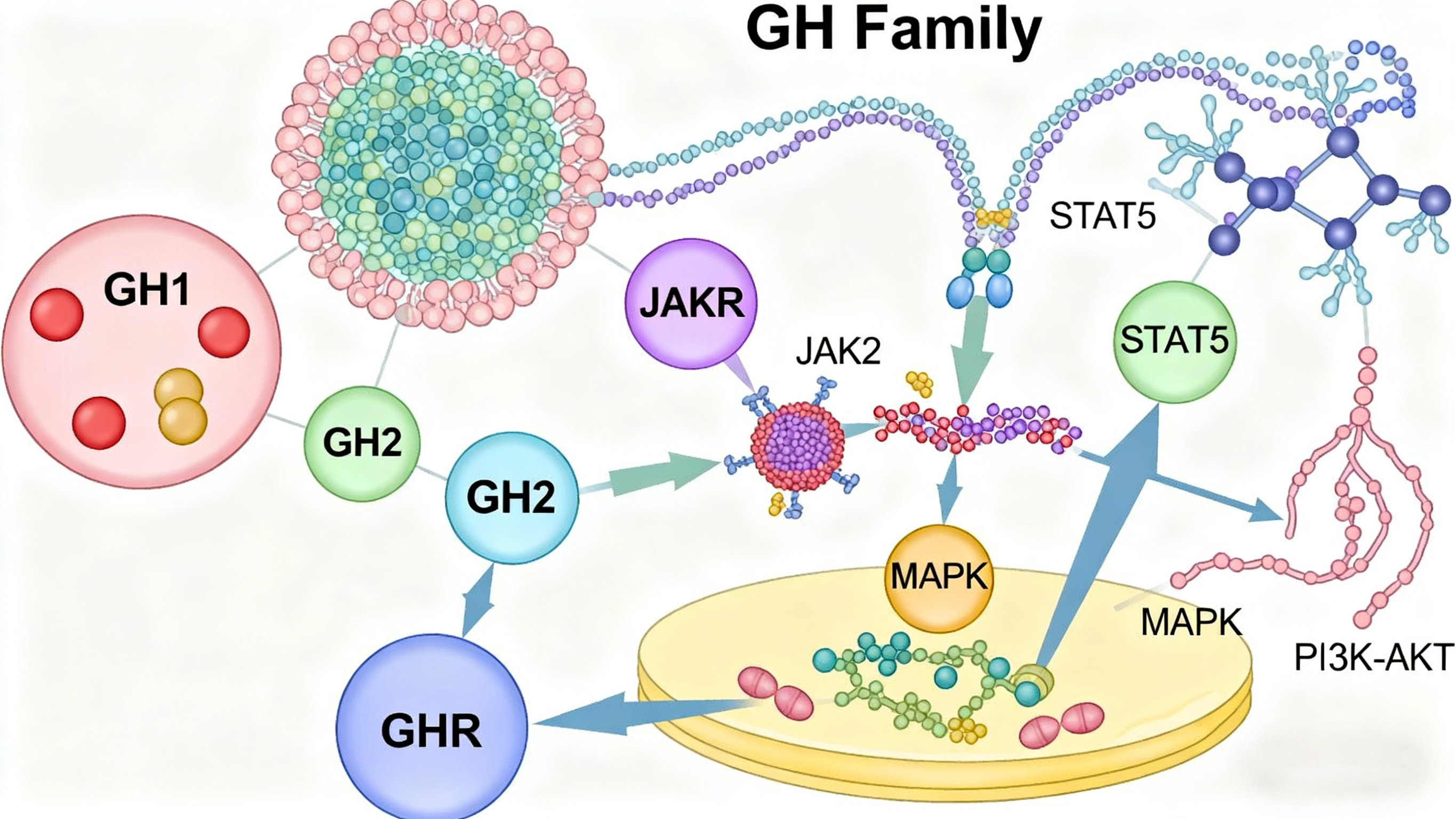
The growth hormone (GH) family comprises pituitary GH, placental lactogens (PLs), and prolactin (PRL)—evolutionarily related hormones that signal through single-pass, class-I cytokine receptors coupled to JAK2-STAT, MAPK, and PI3K cascades. Among them, GH is primarily synthesized and secreted by somatotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland, promoting the growth and differentiation of tissues such as bone and muscle while regulating carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism. PRL is mainly secreted by lactotrophs in the pituitary gland; its core function is to promote mammary gland development and lactation, and it also participates in the regulation of reproductive function and immune cell activity. PL is secreted by placental trophoblast cells, regulating maternal metabolism to meet fetal nutritional needs and promoting mammary gland development in preparation for lactation.
The functional realization of the Growth Hormone Family depends on binding to specific receptors on the surface of target cells. Abnormalities in their signaling pathways or imbalances in hormone levels are closely associated with various diseases. For instance, insufficient GH secretion in childhood can lead to pituitary dwarfism, while excessive secretion may cause gigantism. Excessive GH secretion in adulthood can result in acromegaly, accompanied by skeletal deformation and metabolic disorders. Abnormally elevated PRL levels (hyperprolactinemia) may cause amenorrhea and galactorrhea in women, and sexual dysfunction in men. Additionally, members of this family have important clinical applications: recombinant human GH is widely used to treat childhood growth hormone deficiency, Turner syndrome, and other diseases, while PRL-related agents play a role in assisted reproductive technology and breast disease research. In recent years, studies have also revealed the potential roles of GH family members in aging regulation and tumor development (e.g., breast cancer, prostate cancer), providing new directions for mechanistic research and therapeutic target development for related diseases.
Product List
| Target | Catalog# | Product Name | Reactivity | Predicted MW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GH | GMP Recombinant Human GH | Human | 22 kDa | |
Prolactin | GMP Recombinant Human Prolactin | Human | 21.8 kDa |
Validation Data
GMP Recombinant Human GH (Catalog: PCH90054)
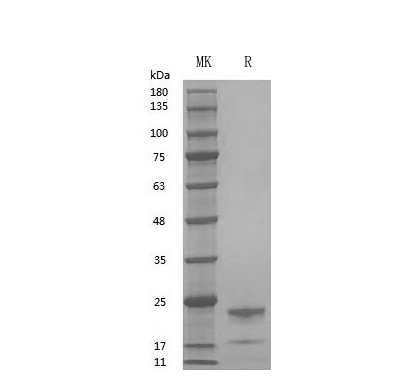
GH SDS-PAGE image
References
1. Guidelines for Growth Hormone and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Treatment in Children and Adolescents: Growth Hormone Deficiency, Idiopathic Short Stature, and Primary Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I Deficiency. Grimberg A, et al. Horm Res Paediatr. 2016. [PMID: 27884013]
2. Prolactin: structure, function, and regulation of secretion. Freeman ME, et al. Physiol Rev. 2000. [PMID: 11015620]
3. Growth Hormone, Hypothalamic Inflammation, and Aging. Velloso LA, et al. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2024. [PMID: 39639711]
4. Berryman DE, Puri V, Lee KY, Jorgensen JOL. The effects of growth hormone on adipose tissue: old observations, new mechanisms. Kopchick JJ, et al. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020. [PMID: 31780780]
