VEGF Family
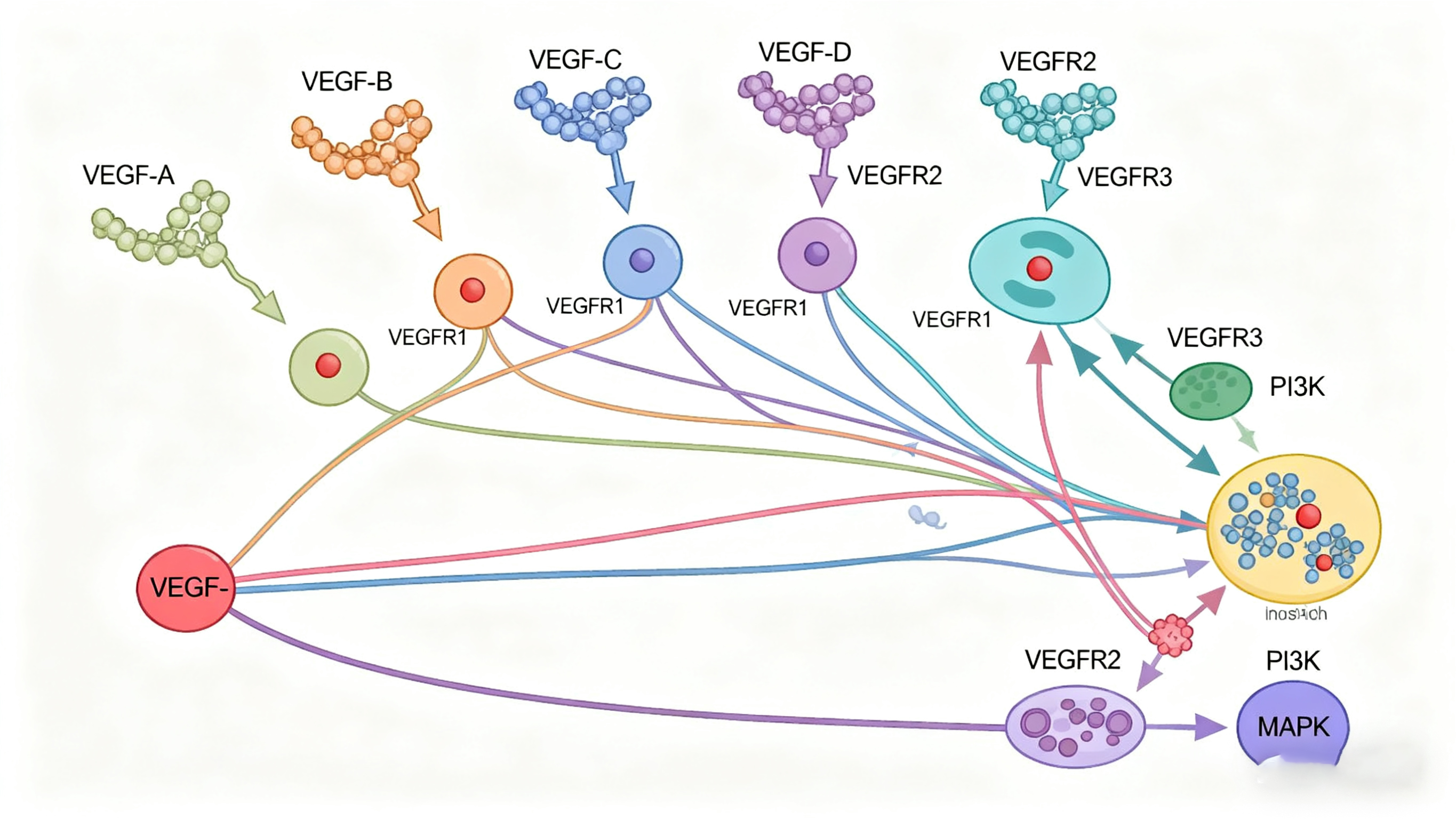
The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family comprises five secreted homodimeric glycoproteins—VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, VEGF-D and placental growth factor (PlGF)—that selectively bind to VEGFR-1, -2, -3 and the co-receptors neuropilin-1/2, thereby orchestrating angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and vascular permeability. VEGF-A is the principal driver of endothelial proliferation, migration and tube formation under hypoxia, growth-factor or oncogenic stimulation. VEGF-B acts predominantly in tumors that do not undergo active neovascularization; VEGF-C and -D preferentially activate VEGFR-3 to promote lymphatic endothelial survival and expansion; VEGF-E is a potent angiogenic factor; and PlGF cooperates with VEGF-A to enhance pathological vessel permeability and inflammatory cell recruitment. Collectively, VEGF signaling is essential for embryonic vasculogenesis, post-natal tissue repair and tumor microenvironment construction, and constitutes the primary target of anti-angiogenic therapies.
Product List
| Target | Catalog# | Product Name | Reactivity | Predicted MW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
VEGF165 | PCH90047 | GMP Recombinant Human VEGF165 | Human | 19.1 kDa |
VEGF165(His Tag) | PCH90061 | GMP Recombinant Human VEGF165(His Tag) | Human | 20 kDa |
Validation Data
GMP Recombinant Human VEGF165 (Catalog: PCH90047)
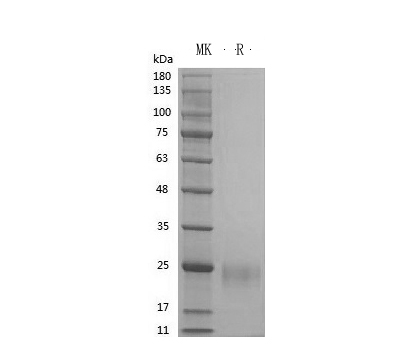
VEGF165 SDS-PAGE image
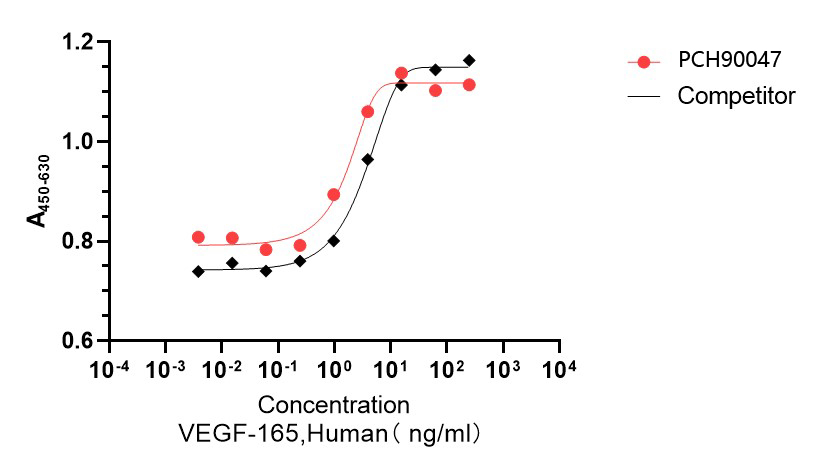
Bioactivity image: The ED50 for this effect is 0.2-5 ng/mL
GMP Recombinant Human VEGF165 (His Tag) (Catalog: PCH90061)
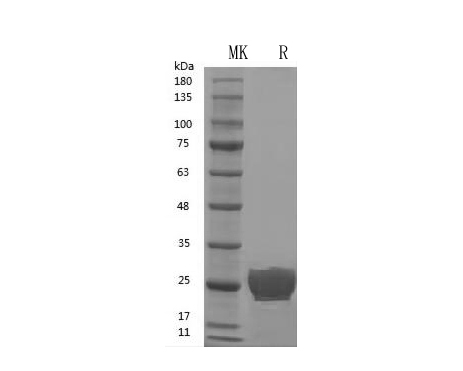
VEGF165(His Tag) SDS-PAGE image
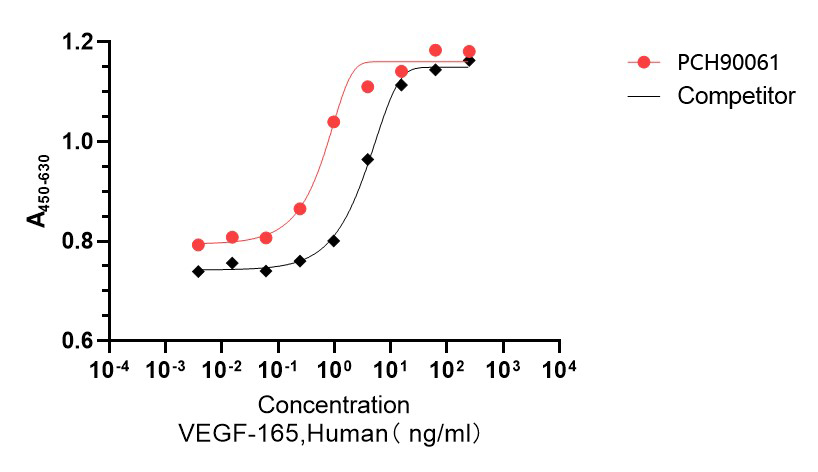
Bioactivity image: The ED50 for this effect is 0.2-10 ng/mL
References
1. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family: angiogenic factors in health and disease. Ferrara N, et al. Trends Cell Biol. 2003. [PMID: 15693956]
2. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Ferrara N, et al. Nat Med. 2003. [PMID: 12778165]
3. VEGF receptor signalling—in control of vascular function. Olsson A-K, et al. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006. [PMID: 16633338]
