IFN Family
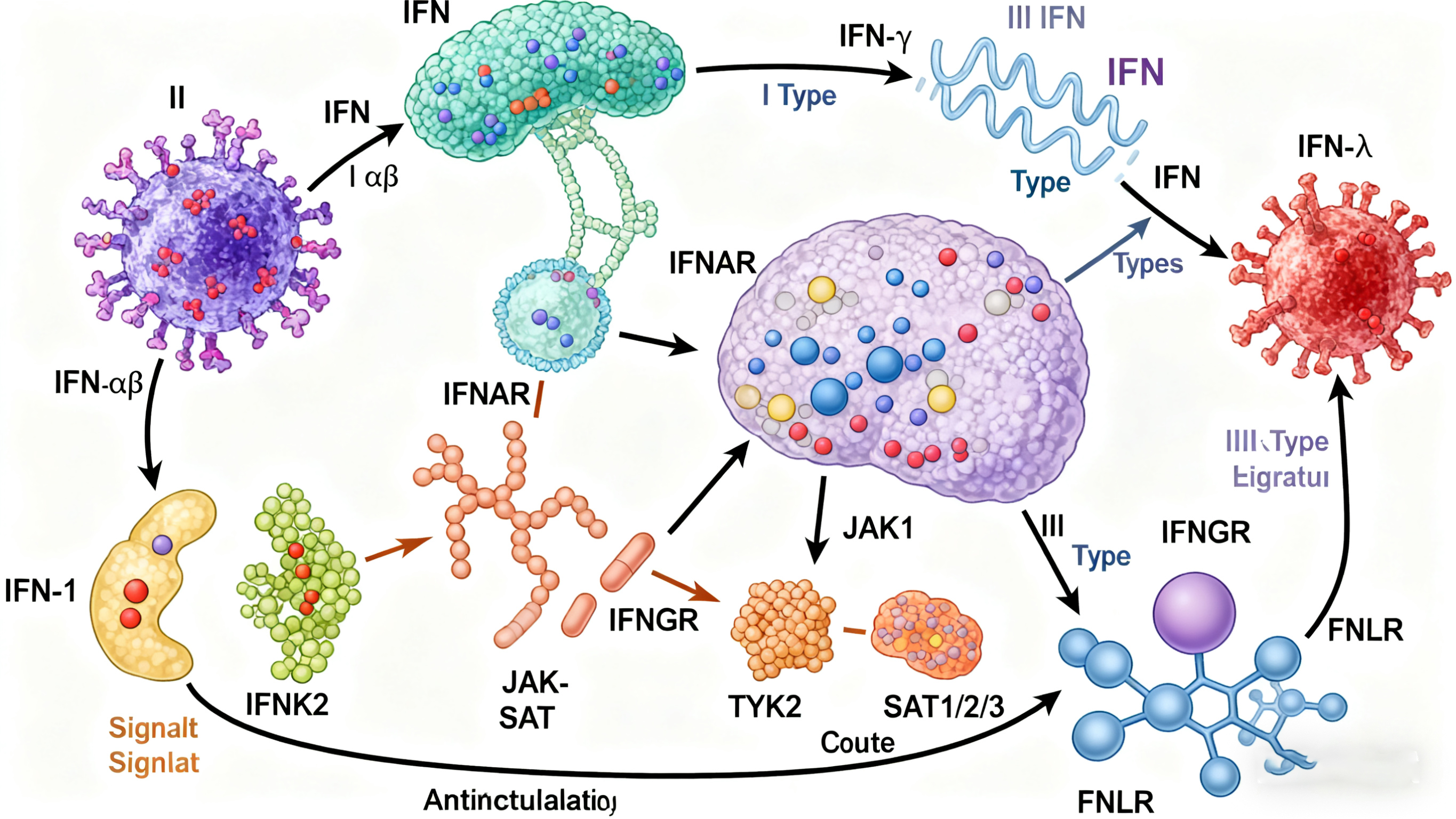
The interferon (IFN) family comprises three classes: type I (IFN-α/β/κ/ε/ω), type II (IFN-γ) and type III (IFN-λ1/2/3). Type I IFNs are rapidly produced upon viral or nucleic-acid sensing and signal through IFNAR1/2 to activate JAK-STAT1/2, inducing hundreds of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs) that establish an antiviral state. Type II IFN, secreted by NK and Th1 cells, engages IFNGR1/2 to enhance macrophage activation and antigen presentation. Type III IFNs act locally at mucosal surfaces via IFNLR1/IL-10R2, also using STAT1/2. Beyond antiviral defense, IFNs modulate cell proliferation, apoptosis and tumor immune surveillance; dysregulation underlies chronic infection, autoimmunity and cancer immune evasion, making them central targets for IFN-based therapies and immune checkpoint strategies.
Product List
| Target | Catalog# | Product Name | Reactivity | Predicted MW |
|---|---|---|---|---|
IFNγ | PCH90019 | GMP Recombinant Human IFNγ | Human | 16.8 kDa |
IFNα2b | PCH90018 | GMP Recombinant Human IFNα2b | Human | 19.2 kDa |
Validation Data
GMP Recombinant Human IFNγ (Catalog: PCH90019)
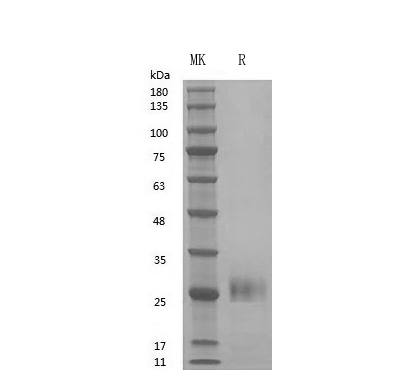
IFNγ SDS-PAGE image
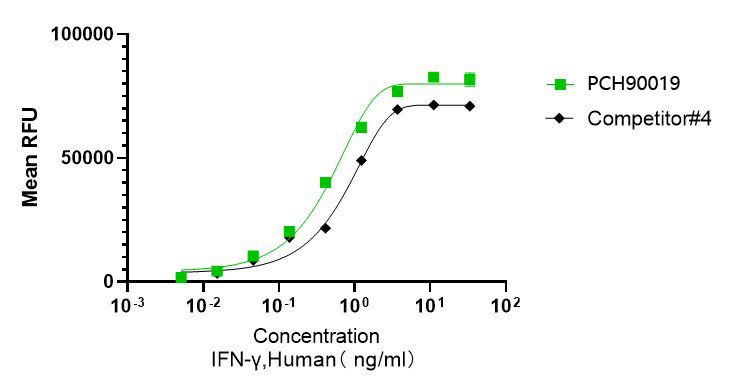
Bioactivity image: The ED50 for this effect is ≤ 2 ng/mL
GMP Recombinant Human IFNα2b (Catalog: PCH90018)
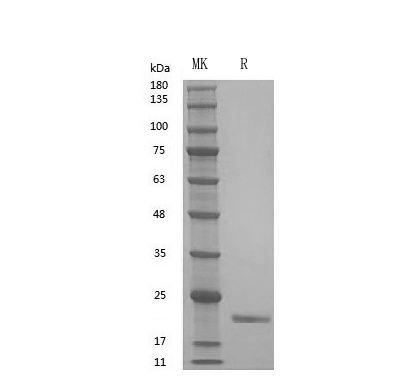
IFNα2b SDS-PAGE image
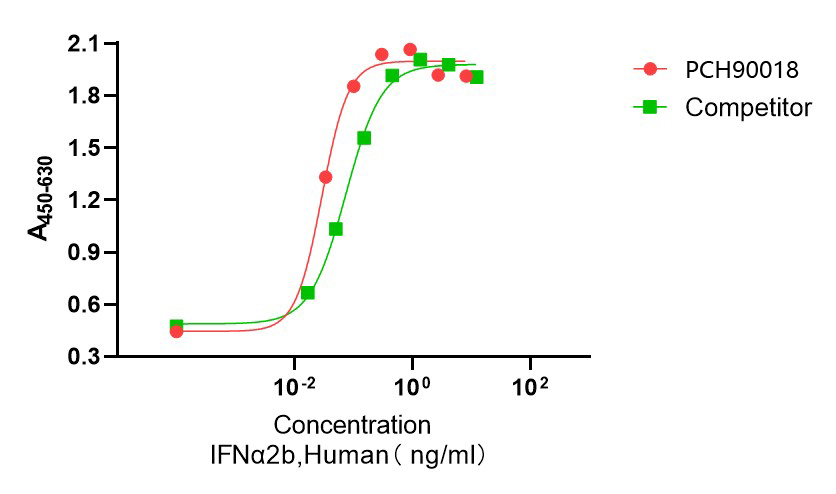
Bioactivity image: The ED50 for this effect is ≤100 pg/mL, corresponding to a specific activity is ≥1×107 units/mg
References
1. Type I IFN family members: similarity, differences and interaction. Capobianchi MR, et al. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015. [PMID: 25466633]
2. Type III interferons: Balancing tissue tolerance and resistance to pathogen invasion. Broggi A, et al. J Exp Med. 2020. [PMID: 31821443]
3. The Role of Structure in the Biology of Interferon Signaling. Walter MR. Front Immunol. 2020. [PMID: 33281831]
