Size:50μL Price:$118
Size:100μL Price:$220
Size:200μL Price:$380
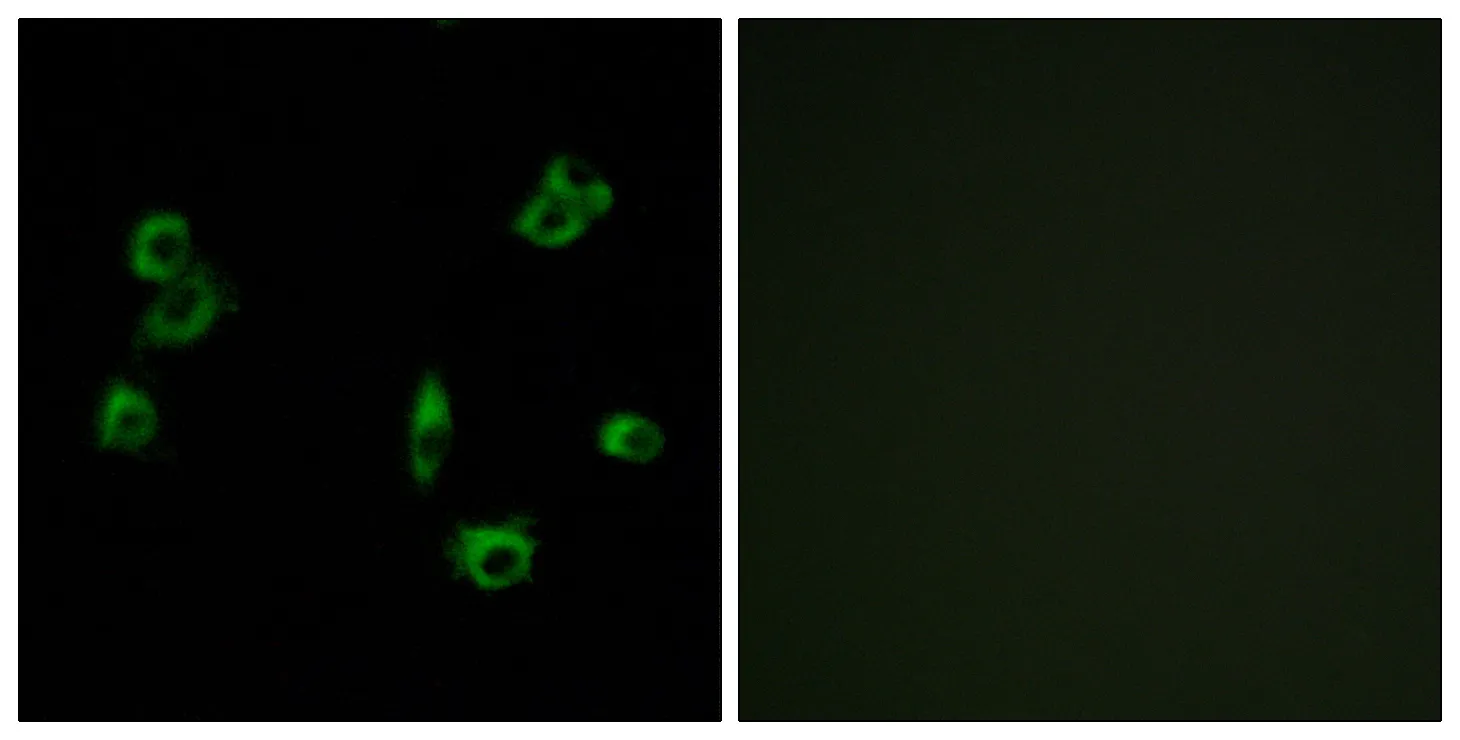
Application:WB,ICC/IF,ELISA
Reactivity:Human,Rat,Mouse
Conjugate:Unconjugated
Optional conjugates: Biotin, FITC (free of charge). See other 26 conjugates.
Gene Name:SLC52A2
Summary
| Production Name | GPR172A Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody |
| Description | Rabbit polyclonal Antibody |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Application | WB,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| Reactivity | Human,Rat,Mouse |
Performance
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Modification | Unmodified |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Form | Liquid |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Buffer | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% protective protein and 0.02% New type preservative N. |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
Immunogen
| Gene Name | SLC52A2 |
| Alternative Names | SLC52A2; GPR172A; PAR1; RFT3; Solute carrier family 52; riboflavin transporter, member 2; Porcine endogenous retrovirus A receptor 1; PERV-A receptor 1; Protein GPR172A; Riboflavin transporter 3; hRFT3 |
| Gene ID | 79581 |
| SwissProt ID | Q9HAB3 |
Application
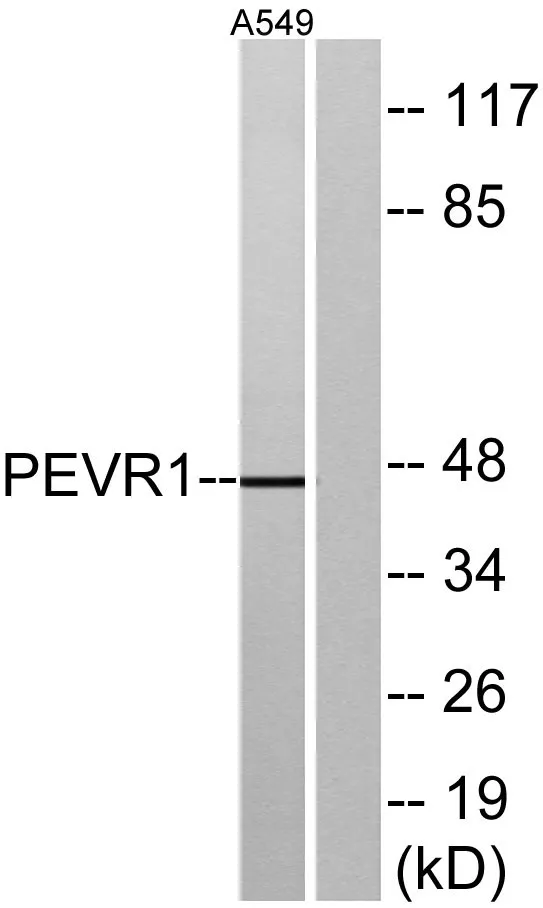
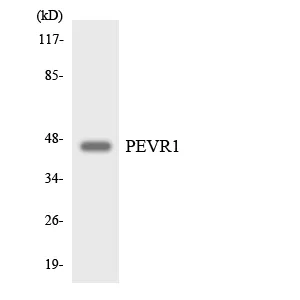
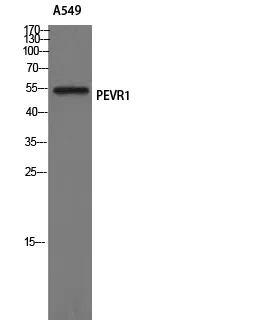
| Dilution Ratio | WB 1:500-1:2000,ICC/IF 1:200-1:1000,ELISA 1:5000-1:20000 |
| Molecular Weight | 46kDa |
Background
This gene encodes a membrane protein which belongs to the riboflavin transporter family. In humans, riboflavin must be obtained by intestinal absorption because it cannot be synthesized by the body. The water-soluble vitamin riboflavin is processed to the coenzymes flavin mononucleotide (FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) which then act as intermediaries in many cellular metabolic reactions. Paralogous members of the riboflavin transporter gene family are located on chromosomes 17 and 20. Unlike other members of this family, this gene has higher expression in brain tissue than small intestine. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere syndrome 2 - an autosomal recessive progressive neurologic disorder characterized by deafness, bulbar dysfunctiofunction:Acts as cell surface receptor for porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV-A).,similarity:Belongs to the PERVR family.,tissue specificity:Detected in a wide variety of tissues. High expression in testis.,
Research Area
