Size2:50μg price2:$378
Size3:500μg price3:$1890
| Name | Recombinant Human Ezrin |
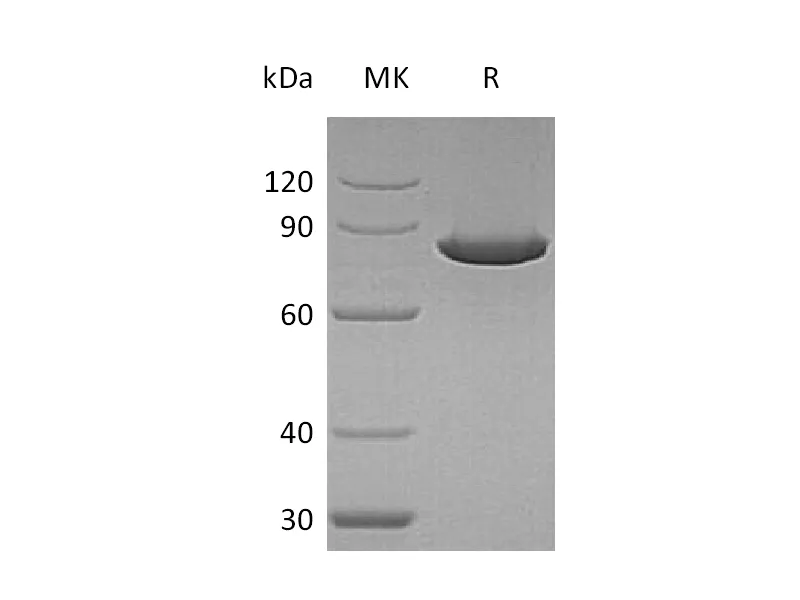
| Purity | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin level | <1 EU/µg as determined by LAL test. |
| Construction | Recombinant Human Ezrin is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-Leu586 is expressed. |
| Accession # | P15311 |
| Host | E.coli |
| Species | Human |
| Predicted Molecular Mass | 69.4 KDa |
| Buffer | Supplied as a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 10mM HEPES, pH 7.4. |
| Form | Liquid |
| Shipping | The product is shipped on dry ice/polar packs.Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature listed below. |
| Stability&Storage | Store at ≤-70°C, stable for 6 months after receipt.Store at ≤-70°C, stable for 3 months under sterile conditions after opening. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
Alternative Names
Ezrin; Cytovillin; Villin-2; p81; EZR; VIL2
Background
Ezrin is expressed in cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, hippocampus, hypophysis, and optic nerve. The N-terminus of ezrin contains a FERM domain which is further subdivided into three subdomains. The C-terminus contain a ERM domain. As a member of the ERM protein family, Ezrin serves as an intermediate between the plasma membrane and the actin cytoskeleton. It plays a key role in cell surface structure adhesion, migration, and organization. Ezrin probably involved in connections of major cytoskeletal structures to the plasma membrane. The N-terminal FERM domain strongly binds sodium-hydrogen exchanger regulatory factor (NHERF) proteins (involving long-range allostery). The C-terminal binds to actin, phosphatidylinositol bis-phosphate (PIP2) and membrane proteins like CD44 and ICAM-2. In epithelial cells, Ezrin is required for the formation of microvilli and membrane ruffles on the apical pole. Along with PLEKHG6, Ezrin is required for normal macropinocytosis.
Note
For Research Use Only , Not for Diagnostic Use.
