Size:100μL Price:300 $180
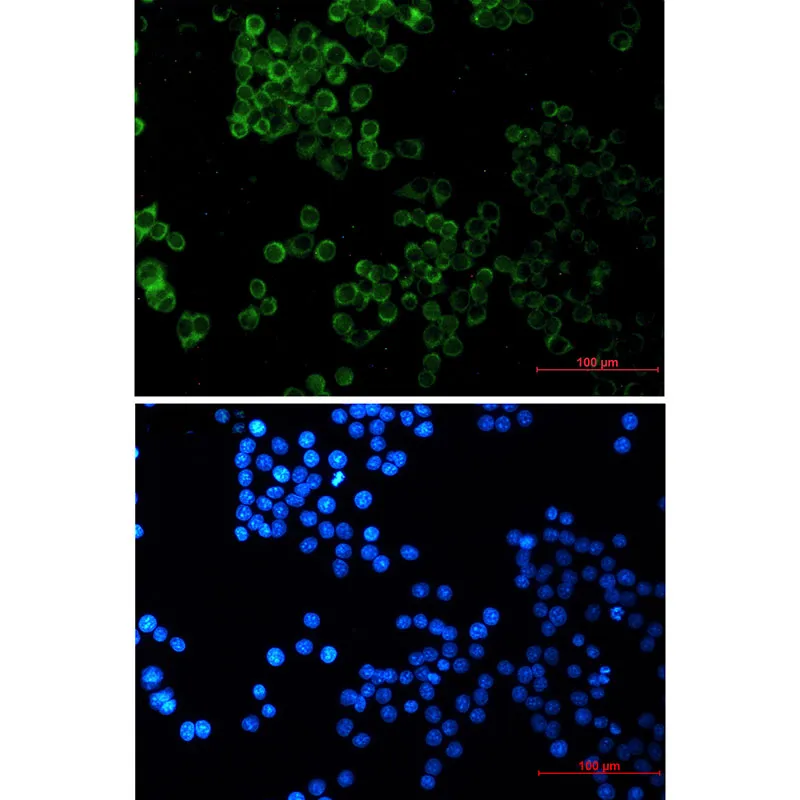
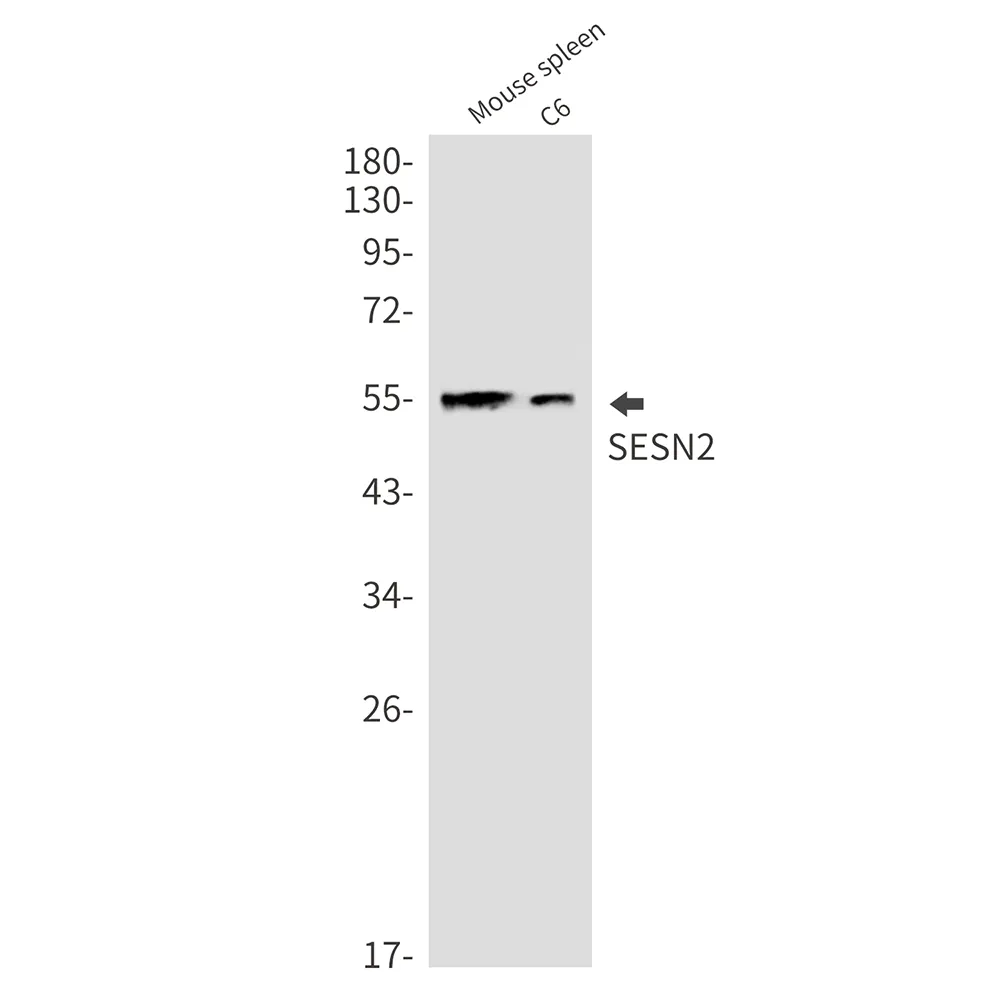
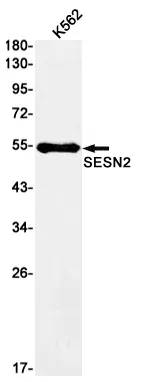
Application:WB,ICC/IF,IP
Reactivity:Human,Mouse,Rat
Conjugate:Unconjugated
Optional conjugates: Biotin, FITC (free of charge). See other 26 conjugates.
Gene Name:SESN2
Summary
| Production Name | SESN2 Rabbit Monoclonal antibody |
| Description | Recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibody |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Application | WB,ICC/IF,IP |
| Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat |
Performance
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Modification | Unmodified |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Form | Liquid |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Buffer | 50mM Tris-Glycine(pH 7.4), 0.15M NaCl, 40% Glycerol, 0.01% Sodium azide and 0.05% protective protein |
| Purification | Affinity Purified |
Immunogen
| Gene Name | SESN2 |
| Alternative Names | HI95; SES2; SEST2 |
| Gene ID | 83667 |
| SwissProt ID | P58004 |
Application
| Dilution Ratio | WB 1:500-1:1000,ICC/IF 1:50-1:200,IP 1:20-1:50 |
| Molecular Weight | Calculated MW: 54 kDa; Observed MW: 54 kDa |
Background
Functions as an intracellular leucine sensor that negatively regulates the TORC1 signaling pathway through the GATOR complex. In absence of leucine, binds the GATOR subcomplex GATOR2 and prevents TORC1 signaling (PubMed:18692468, PubMed:25263562, PubMed:25457612, PubMed:26449471, PubMed:26612684, PubMed:26586190). Binding of leucine to SESN2 disrupts its interaction with GATOR2 thereby activating the TORC1 signaling pathway (PubMed:26449471, PubMed:26586190). This stress-inducible metabolic regulator also plays a role in protection against oxidative and genotoxic stresses. May negatively regulate protein translation in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress, via TORC1 (PubMed:24947615). May positively regulate the transcription by NFE2L2 of genes involved in the response to oxidative stress by facilitating the SQSTM1-mediated autophagic degradation of KEAP1 (PubMed:23274085). May also mediate TP53 inhibition of TORC1 signaling upon genotoxic stress (PubMed:18692468). Has an alkylhydroperoxide reductase activity born by the N-terminal domain of the protein (PubMed:26612684). Was originally reported to contribute to oxidative stress resistance by reducing PRDX1 (PubMed:15105503). However, this could not be confirmed (PubMed:19113821).
Research Area
Cardiovascular
