Size2:50μg price2:$465
Size3:500μg price3:$2350
| Name | Recombinant Mouse VEGF 164 |
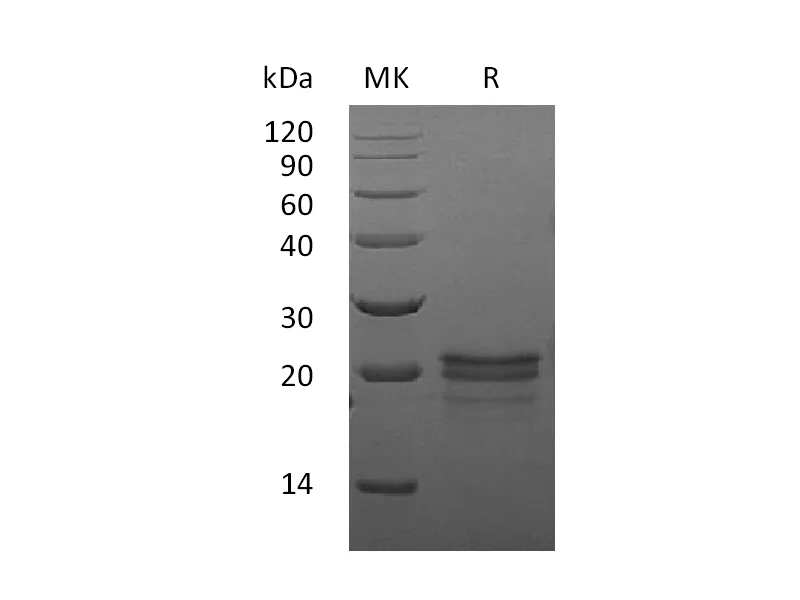
| Purity | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin level | <1 EU/µg as determined by LAL test. |
| Construction | Recombinant Mouse Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A is produced by our Yeast expression system and the target gene encoding Ala27-Arg190 is expressed. |
| Accession # | Q00731-2 |
| Host | P. pastoris |
| Species | Mouse |
| Predicted Molecular Mass | 19.27 KDa |
| Buffer | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM PB, 250mM NaCl, pH7.0. |
| Form | Lyophilized |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature.Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature listed below. |
| Stability&Storage | Store at ≤-70°C, stable for 6 months after receipt.Store at ≤-70°C, stable for 3 months under sterile conditions after opening. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution | Always centrifuge tubes before opening.Do not mix by vortex or pipetting.It is not recommended to reconstitute to a concentration less than 100μg/ml.Dissolve the lyophilized protein in distilled water.Please aliquot the reconstituted solution to minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
Alternative Names
Vascular endothelial growth factor A; VEGF-A; Vascular permeability factor; VPF; VEGFA; VEGFA164; VEGF164
Background
Mouse Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF or VEGF/xadA), is a potent mediator of both angiogenesis and vasculogenesis in the fetus and adult. It is a member of the PDGF/VEGF growth factor family that is characterized by a cystine knot structure formed by eight conserved cysteine residues. Alternately spliced isoforms of 120, 164 and 188 aa found in mouse. VEGF binds the type I transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases VEGF R1 (also called Flt/xad1) and VEGF R2 (Flk/xad/KDR) on endothelial cells.Although affinity is highest for binding to VEGF R1, VEGF R2 appears to be the primary mediator of VEGF angiogenic activity. VEGF is required during embryogenesis to regulate the proliferation, migration, and survival of endothelial cells.It may play a role in increasing vascular permeability during lactation, when increased transport of molecules from the blood is required for efficient milk protein synthesis.
Note
For Research Use Only , Not for Diagnostic Use.
