Size2:50μg price2:$378
Size3:500μg price3:$1890
| Name | Recombinant Human Tau-F |
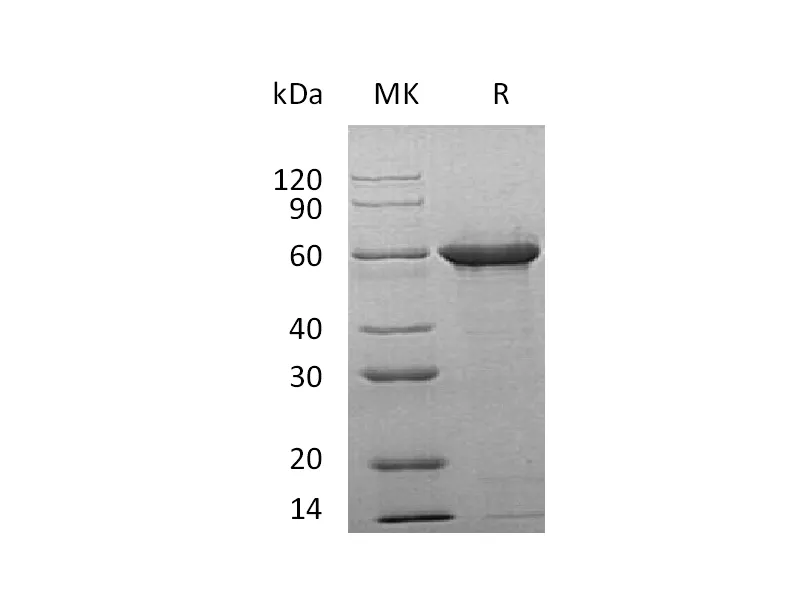
| Purity | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin level | <1 EU/µg as determined by LAL test. |
| Construction | Recombinant Human Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau-F is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Met1-Leu441 is expressed. |
| Accession # | P10636-8 |
| Host | E.coli |
| Species | Human |
| Predicted Molecular Mass | 45.85 KDa |
| Buffer | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of 20mM PB, 150mM NaCl, 1mM EDTA, pH 7.4. |
| Form | Lyophilized |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature.Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature listed below. |
| Stability&Storage | Store at ≤-70°C, stable for 6 months after receipt.Store at ≤-70°C, stable for 3 months under sterile conditions after opening. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution | Always centrifuge tubes before opening.Do not mix by vortex or pipetting.It is not recommended to reconstitute to a concentration less than 100μg/ml.Dissolve the lyophilized protein in distilled water.Please aliquot the reconstituted solution to minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
Alternative Names
Microtubule-associated protein tau; MAPTL; Neurofibrillary tangle protein; MTBT1; Paired helical filament-tau; TAU and MAPT
Background
Tau proteins are proteins which contain four Tau/MAP repeats. They promote microtubule assembly and stability, and might be involved in the establishment and maintenance of neuronal polarity. They are abundant in neurons of the central nervous system and are less common elsewhere, but are also expressed at very low levels in CNS astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. The tau proteins are the product of alternative splicing from a single gene that in humans is designated MAPT. When tau proteins are defective, and no longer stabilize microtubules properly, they can result in several neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimers disease, Picks disease, frontotemporal dementia, cortico-basal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy.
Note
For Research Use Only , Not for Diagnostic Use.
