Size2:50μg price2:$378
Size3:500μg price3:$1890
| Name | Recombinant Human FABP3 (N-6His) |
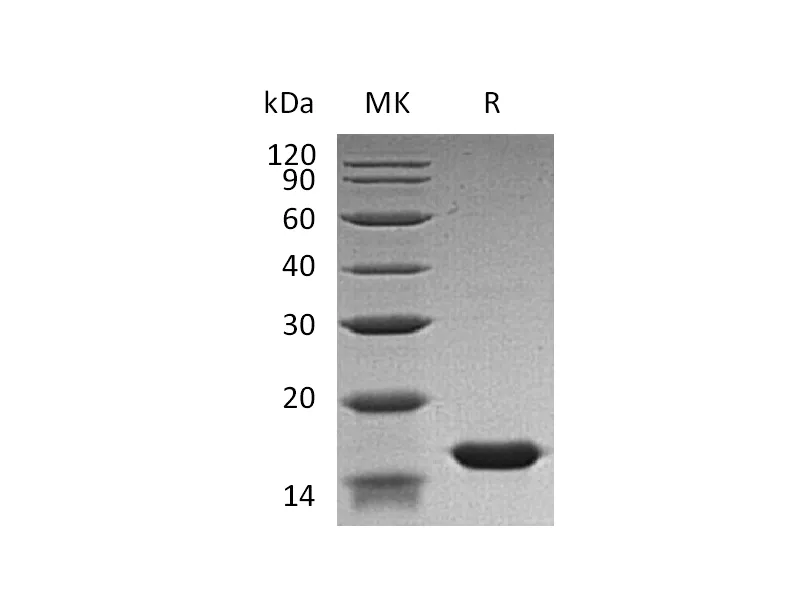
| Purity | Greater than 95% as determined by reducing SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin level | <1 EU/µg as determined by LAL test. |
| Construction | Recombinant Human Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 3 is produced by our E.coli expression system and the target gene encoding Val2-Ala133 is expressed with a 6His tag at the N-terminus. |
| Accession # | P05413 |
| Host | E.coli |
| Species | Human |
| Predicted Molecular Mass | 17.02 KDa |
| Buffer | Lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution of PBS, pH 6.5. |
| Form | Lyophilized |
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature.Upon receipt, store it immediately at the temperature listed below. |
| Stability&Storage | Store at ≤-70°C, stable for 6 months after receipt.Store at ≤-70°C, stable for 3 months under sterile conditions after opening. Please minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution | Always centrifuge tubes before opening.Do not mix by vortex or pipetting.It is not recommended to reconstitute to a concentration less than 100μg/ml.Dissolve the lyophilized protein in distilled water.Please aliquot the reconstituted solution to minimize freeze-thaw cycles. |
Alternative Names
Fatty Acid-Binding Protein Heart; Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 3; Heart-Type Fatty Acid-Binding Protein; H-FABP; Mammary-Derived Growth Inhibitor; MDGIMuscle Fatty Acid-Binding Protein; M-FABP; FABP3; FABP11; MDGI
Background
Fatty Acid Binding Protein 3 (FABP3) is a small cytoplasmic protein (15 kDa) that is released from cardiac myocytes following an ischemic episode. Like the nine other distinct FABPs that have been identified, FABP3 is involved in active fatty acid metabolism where it transports fatty acids from the cell membrane to mitochondria for oxidation. FABPs are divided into at least three distinct types, namely the hepatic-, intestinal- and cardiac-types. They form 14-15 kDa proteins and are thought to participate in the uptake, intracellular metabolism and/or transport of long-chain fatty acids. They may also be responsible in the modulation of cell growth and proliferation. The FABP3 gene contains four exons and its function is to arrest growth of mammary epithelial cells. This gene is also a candidate tumor suppressor gene for human breast cancer. FABP3 is a sensitive biomarker for myocardial infarction and can be detected in the blood within one to three hours of onset of pain.
Note
For Research Use Only , Not for Diagnostic Use.
