Product Introduction
Hemoglobin (HB or HGB) is an iron-containing metalloprotein responsible for carrying oxygen in higher organisms. Hemoglobin is mainly found in red blood cells, accounting for 97% of the dry weight of red blood cells. In addition, hemoglobin also exists in other tissues as an antioxidant. It is precisely because of the presence of iron-containing hemoglobin that human blood is red. Hemoglobin in the human body is composed of four subunits, two α subunits and two β subunits, and each subunit is composed of a peptide chain and a heme molecule. Under physiological conditions, the peptide chain will coil and fold into a sphere, wrapping the heme molecule inside. The spherical structure formed by this peptide chain is also called globin. Heme molecule is a small molecule with a porphyrin structure. In the center of the porphyrin molecule, the nitrogen atoms on the four pyrrole rings in the porphyrin are coordinated with a ferrous ion. When hemoglobin is not bound to an oxygen molecule, a water molecule is coordinated with the ferrous ion from the bottom of the porphyrin ring; and when hemoglobin carries oxygen, the oxygen molecule replaces the water molecule. This characteristic of hemoglobin enables red blood cells to transport oxygen. In lung tissue, hemoglobin can fully bind to oxygen and transport oxygen to peripheral tissues through red blood cells to maintain cell vitality. In addition to the function of transporting oxygen molecules, hemoglobin also plays an important role in maintaining the normal morphology of red blood cells.
Hemoglobin is one of the most commonly used indicators for anemia screening and clinical diagnosis. A decrease in hemoglobin concentration is common in various types of anemia caused by bleeding, lack of iron, vitamin B12 or folic acid; while an increase in hemoglobin concentration is more common in polycythemia vera, cyanotic congenital heart disease, and diseases caused by various clinical causes such as heat stroke and dehydration. Therefore, hemoglobin content is an important clinical indicator for the diagnosis of various diseases such as anemia, polycythemia and dehydration.
Product Features
This kit has the advantages of convenient operation, high sensitivity, low cost, wide linear range, and suitable for high-throughput detection. The lower limit of detection can reach below 0.1 mg/dl, and the upper limit of detection can reach 80 mg/dl.
Principle
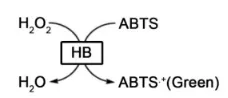
Hemoglobin (HB) catalyzes hydrogen peroxide to produce oxygen and oxidizes the colorimetric reagent to produce a green product with a maximum absorption wavelength at 410 nm. Refer to the figure below :
Components
Serial number | Components | Size(100T) | Storage |
Reagent 1 | Chromogen | 22ml | Store at -20℃, away from light. |
Reagent 2 | Hydrogen Peroxide Solution (30 × ) | 12ml | Store at -20℃, away from light. |
Reagent 3 | Hemoglobin (100 mg/dl) | 0.4ml | -20℃ |
Consumable 1 | Microplate(96 wells) | 1 plate | RT |
Consumable 2 | Plate Sealer | 2 pieces | RT |
Storage
The unopened kit can be stored at -20℃ for 12 months.
Notes
This product is intended for scientific research use only by professionals and must not be used for clinical diagnosis or treatment, in food or drugs, or stored in ordinary residences.



