NCI-H1299 is a cell line derived from human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), specifically from the site of lymph node metastasis in a 43-year-old white male patient who had received radiation therapy prior to sample collection.
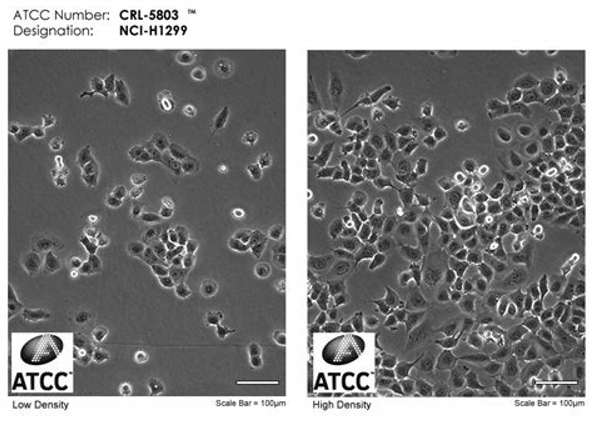
NCI-H1299 cells have the following major characteristics:
1. Genetic characteristics: These cells exhibit partial loss of p53 protein and do not express p53 protein. In addition, they carry KRAS mutations, which affect their growth, proliferation, migration, and invasion characteristics.
2. Morphology and growth characteristics: NCI-H1299 cells exhibit epithelial like growth and adhere to the wall, with a doubling time of approximately 22-30 hours. These cells are suitable for in vitro culture and are ideal transfection hosts.
3. Protein synthesis ability: These cells are capable of synthesizing neuropeptide B (NMB) at a concentration of 0.1 pmol/mg protein, but do not synthesize gastric juice releasing peptide (GRP).
4. Application: NCI-H1299 cells are widely used in basic cell biology and biomedical research such as lung cancer proliferation, inhibitor development, tumor formation and metastasis. They are used in drug screening to test the effectiveness and reliability of new drugs, accelerating drug development and providing patients with more treatment options.
5. Cultivation conditions: RPMI-1640 medium is recommended, containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% antibiotics/antifungal agents (P/S), and cultured at 37 ℃and 5% CO2.
NCI-H1299 cells, due to their unique genetic background and biological characteristics, have become an important tool for studying non-small cell lung cancer, helping to understand the molecular mechanisms of lung cancer, develop new treatment strategies, and conduct preclinical drug testing.
What are the specific types and locations of KRAS mutations in the NCI-H1299 cell line?
The specific type and location of KRAS mutation in NCI-H1299 cell line is wild-type (WT), and no KRAS gene mutation has occurred.
What are the application cases of NCI-H1299 cells in lung cancer drug screening?
The application cases of NCI-H1299 cells in lung cancer drug screening include the following aspects:
Using phage display technology, a peptide ZT-1 specifically targeting NCI-H1299 cells was screened from the phage displayed 12 peptide library. This peptide can specifically bind to NCI-H1299 cells and also bind to the surface of tumor cells in biopsy specimens, but cannot bind to normal lung tissue samples, other cancer cells, or non tumor adjacent lung tissue. This suggests that ZT-1 may be a potential candidate biomarker ligand for targeted drug delivery in lung cancer treatment [3].
Research has found that Evodiamine (EVO) has significant anti-tumor activity against NCI-H1299 cells. Through CCK-8 assay, it was found that EVO can significantly inhibit the proliferation activity of NCI-H1299 cells, and the cell proliferation activity shows a decreasing trend with increasing concentration and time. In addition, EVO can induce NCI-H1299 cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase and induce programmed necrosis by activating RIP1, RIP3, and MLKL [4].
Research has shown that platinum based drugs such as cisplatin (CDDP) can induce upregulation of PD-L1 expression in NCI-H1299 cells, which can be detected by 68Ga-NOTA-Nb109. However, NCI-H1299 has low sensitivity to platinum based drugs, with an IC50 value of 26.70±3.22 μM, indicating that chemotherapy may be difficult to achieve effective control of this type of lung cancer [5].
The study reported that hederagenin enhances cisplatin and paclitaxel mediated cytotoxicity by inhibiting autophagy. The experiment included transfection, lysosome labeling, transmission electron microscopy observation, and reactive oxygen species detection, further validating the effectiveness of hederagenin in a human lung cancer xenograft model. These studies suggest that hederagenin may be an effective lung cancer treatment drug [6].
What are the research progress of NCI-H1299 cell line in simulating lung cancer metastasis?
The research progress of NCI-H1299 cell line in simulating lung cancer metastasis mainly focuses on the following aspects:
The NCI-H1299 cell line is widely used to study the metastatic ability of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Research has shown that NCI-H1299 cells have high metastatic potential, which can be validated through various experimental methods. For example, through Transwell migration experiments and wound healing experiments, the migration and invasion ability of NCI-H1299 cells can be quantitatively analyzed. [11]
Multiple studies have explored the molecular mechanisms that affect the metastasis of NCI-H1299 cells. For example, high expression of KHSRP (RNA binding protein) in NCI-H1299 cells is associated with higher metastatic potential [12]. In addition, miR-924 inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of NCI-H1299 cells by suppressing RHBDD1 [16]. These studies reveal the role of different molecular pathways in lung cancer metastasis.
The study also explored the effects of different drugs on the metastasis of NCI-H1299 cells. For example, pristimerin has been found to induce apoptosis in NCI-H1299 cells and significantly inhibit their migration and invasion abilities [12]. In addition, 19-HB treatment also showed inhibitory effects on NCI-H1299 cell migration and invasion [11].
The study also focused on the impact of gene expression regulation on lung cancer metastasis. For example, miR-144-3p inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of NCI-H1299 cells by targeting HGF (hepatocyte growth factor) [15]. This gene expression regulation mechanism provides a new target for lung cancer treatment.
The NCI-H1299 cell line was also used to construct a nude mouse model for studying lung metastasis of lung cancer. For example, ANKRD49 protein promotes lung metastasis of NCI-H1299 cells in a nude mouse model, further validating the application value of this cell line in simulating lung cancer metastasis [14].
The research progress of NCI-H1299 cell line in simulating lung cancer metastasis includes evaluation of metastasis ability, study of molecular mechanisms, effectiveness of drug intervention, gene expression regulation, and application of experimental models.
What are the latest research findings and future research directions of NCI-H1299 cell line?
The NCI-H1299 cell line is a widely used in vitro model for studying non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In recent years, many important discoveries have been made in the study of NCI-H1299 cells, and future research directions have been pointed out.
Latest research findings
1. The effect of hirsuteine (HTE) on NCI-H1299 cells:
Research has shown that HTE is a natural compound isolated from black medicine, which has significant anti proliferative and apoptosis inducing effects. HTE inhibited the proliferation of NCI-H1299 cells and induced G0/G1 phase arrest by regulating the Bax/Bcl-2 signaling pathway and the mechanism mediated by cyclin E-CDK2 [17].
OHTE also increases the activity of Bax, caspase-3, and caspase-9 by activating mitochondrial mediated signaling pathways, leading to mitochondrial dysfunction, release of apoptotic factors, and activation of caspase-9, thereby triggering cell apoptosis [17].
In addition, HTE transfers ubiquitin induced apoptosis factor (AIF) from mitochondria to the cytoplasm through a mitochondrial mediated pathway, further promoting cell apoptosis [17].
2. Combination therapy strategy:
Research has found that the combination of TCS (tumor necrosis factor related cytotoxic ligand) and TRAIL (tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis inducing ligand) can effectively inhibit the invasion of NCI-H1299 cells and induce cell cycle redistribution. Combination therapy significantly reduced levels of invasion related proteins and altered cell cycle distribution, thereby enhancing anti-tumor efficacy [19].
3. Gene expression and metabolic analysis:
We used siRNA mediated knockdown and fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) techniques to investigate the effects of SLC7A5 or RXRA gene knockdown on NCI-H1299 cells. In addition, comprehensive studies were conducted on cellular metabolic changes and gene regulation mechanisms through amino acid analysis, metabolomics LC-MS analysis, and gene expression analysis. [18]
4. Phage display technology:
Use phage display technology to screen peptides that can specifically bind to NCI-H1299 cells. Research has found that ZT-1 peptide has high specificity and can specifically bind to NCI-H1299 cells, exhibiting good tissue distribution characteristics in animal models. This indicates that ZT-1 peptide may have potential application value in the diagnosis of lung cancer or as a delivery tool for anti-tumor therapeutic agents [3].
future research directions
1. In depth mechanism research:
Although previous studies have revealed the mechanisms of action of HTE and other compounds on NCI-H1299 cells, these mechanisms still require further validation and in-depth research. For example, more in vivo experiments are needed to evaluate the stability and efficacy of these compounds [17].
2. Optimization of combination therapy strategy:
The combination therapy strategy has shown good anti-tumor effects, and future research should further optimize these strategies to improve treatment efficacy and reduce side effects [19].
3. Exploration of metabolic and gene regulatory mechanisms:
Continue to explore the metabolic changes and gene regulatory mechanisms of NCI-H1299 cells, especially through metabolomics and gene expression analysis, to reveal more potential therapeutic targets [18].
4. Development of new drugs and treatment methods:
The new peptides and other molecules screened using phage display technology can serve as novel drug delivery tools or therapeutic targets, and future research should focus on developing new drugs and therapeutic methods based on these molecules [3].

References
1. Small cell and non small cell lung cancer form metastasis on cellular 4D lung model. Dhruva K Mishra et al. [PMID: 29669530]
2. Capturing the Metabolomic Diversity of KRAS Mutants in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Laura Brunelli et al. [PMID: 24952473]
3. Screening and identification of a peptide specifically targeted to NCI-H1299 cells from a phage display peptide library. Xianggan Tu et al. [PMID: 21475935]
4. wujiuzhi alkaloid on human lung cancer NCI-H1299 cells. Qingdao University Medical Center of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, etc. [2024-01-31]
5. Immuno PET Imaging of 68Ga Labeled Nanobody Nb109 for Dynamic Monitoring the PD L1 Expression in Cancers. Qingzhu Liu et al. [PMID: 33386467]
6. Hederagenin potentiated cisplatin- and paclitaxel-mediated cytotoxicity by impairing autophagy in lung cancer cells. Kun Wang et al. [PMID: 32792495]
7. MiR-223-3p promotes the expression of LncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 by targeting TGFBR3 to inhibit the proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells. Chen Ping et al. [2023-12-31]
8. Biomimetic nanoparticles for targeted delivery of HDACIs and their preparation methods and applications. China National Intellectual Prop [2021-08-05]
9. Comprehensive analysis and validation reveal DEPDC1 as a potential diagnostic biomarker associated with tumor immunity in non-small-cell lung cancer.[PMID: 38564630]
10. Pristimerin induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, migration in H1299 Lung Cancer Cells. Jiaju Li et al. [PMID: 33033518]
11. 19-Hydroxybufalin inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and promotes cell apoptosis via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Wei Yu et al. [PMID: 34696818]
12. RNA-binding protein KHSRP promotes tumor growth and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. Mingxia Yan et al. [PMID: 31775888]
13. Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Modulate the Development of Human CD1c+ Conventional Dendritic Cell Subsets Mediated by CD103 and CD205. [PMID: 31921114]
14. ANKRD49 promotes the metastasis of NSCLC via activating JNK-ATF2/c-Jun-MMP-2/9 axis. Jia Sun et al. [PMID: 37964204]
15. MiR-144-3p inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of lung cancer A549 cells via targeting HGF. Guiju Fang et al. [PMID: 35568918]
16. MiR-924 as a tumor suppressor inhibits non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting RHBDD1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Huaishi Wang et al. [PMID: 33041671]
17. PDFInhibitory effect and mechanism of hirsuteine on NCI H1299 lung cancer cell lines. XUELIN YUN et al. [PMID: 37113396]
18. Reciprocal regulation of amino acid import and epigenetic state through Lat1 and EZH2. Stephen. Stephen G Dann et al. [PMID: 25979827]
19. Trichosanthin enhances sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) TRAIL-resistance cells. Chengcheng You et al.[PMID: 29483839]
20. RNAi Targeting-STIL Suppresses Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis of Lung Cancer NCI-H1299 Cells via Inactivation of Akt/SAPK/TAK1 Pathways.
21. The Role of CENPO Expression in the Progression of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Yanlong Yang.
