Human colon cancer cell line HT-29 is a cancer cell line derived from a 44 year old white female colon cancer patient, first described by Fogh et al. in 1975. Its cell line has important biological and genetic research value.
1.Source and Basic Information
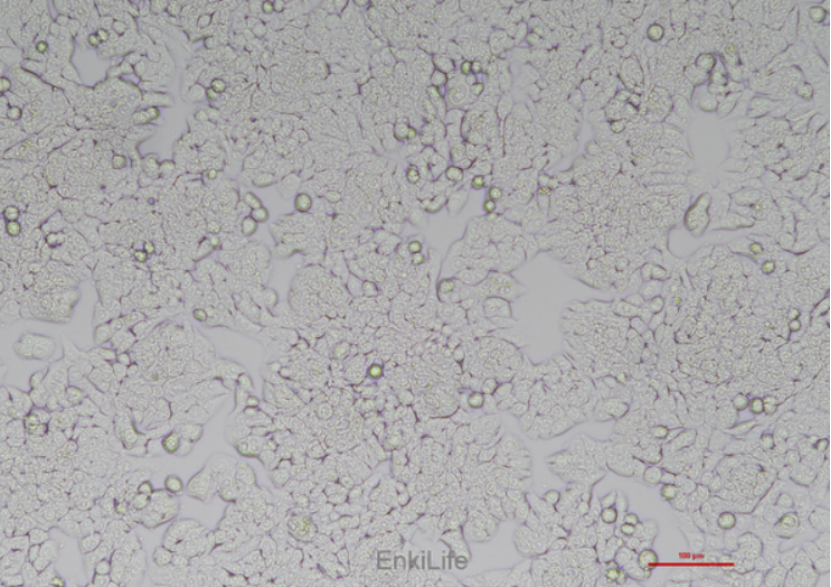
The oHT-29 cell line is derived from a female colon cancer patient and obtained through anatomical methods. The cells have the characteristic of adherent growth and are in the form of epithelial like cells, usually arranged in a single or multiple layers.
The cell line carries multiple oncogenic gene mutations, such as myc, K-ras, H-ras, N-ras, myc, sis, fos, and p53 gene mutations, and there is a G>A mutation at position 273 of the p53 gene.
The cells express urokinase receptor but do not express plasminogen activator activity, CD4 negative, and surface express galactose ceramide.
2. Biological functions
OHT-29 cells can secrete mucins, express AM-3 epitopes, etc., have tumorigenicity, and can be infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), leading to persistent infection.
Cells are sensitive to various chemotherapy drugs, such as 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin, which can be used to study the chemotherapy mechanism of colon cancer.
In vitro culture, HT-29 cells exhibit good differentiation ability and can form highly differentiated adenocarcinoma (grade I) tissue.
3. Cultivation and preservation
The culture conditions for oHT-29 cells are usually McCoy's 5A medium, supplemented with fetal bovine serum, penicillin, and streptomycin, and cultured in an environment of 37℃and 5% CO2.
The recommended passaging ratio is 1:3, passaging once every 3-4 days, with a liquid change cycle of twice a week, and a cryoprotectant formula of complete medium 95%+DMSO 5%.
Cells are sensitive to digestion and need to avoid excessive digestion to prevent cell death or floating.
Human colon cancer cell HT-29 is a widely used cell model for studying the biological characteristics of colon cancer and the anti-tumor effects of drugs. According to the search results, HT-29 cells have shown sensitivity to different compounds and drugs in various experiments, revealing their important value in anti-tumor drug screening and mechanism research.
1. Basic characteristics of HT-29 cells
HT-29 cells are derived from human colon adenocarcinoma and have high proliferation ability and invasiveness. Research has shown that HT-29 cells exhibit significant sensitivity to a variety of compounds, including monomeric compounds of Strychnos alkaloids, polysaccharides from Astragalus membranaceus, and ginsenoside Rh2. These compounds exert their effects through mechanisms such as inhibiting cell proliferation, inducing apoptosis, or blocking the cell cycle [1,2,3].
2. Research on inducing apoptosis
Multiple studies have shown that HT-29 cells can be induced to apoptosis through various pathways. For example:The combined effect of oxalic acid and TRAIL significantly promotes apoptosis in HT-29 cells, while upregulating the expression of Caspase family proteins [4].
Golden Lotus Flower Total Flavonoids: Inducing apoptosis in HT-29 cells through the mitochondrial pathway and downregulating anti apoptotic genes Bcl-2 and Bcl xL [5].
Extract of Hedyotis diffusa: induces apoptosis in HT-29 cells by upregulating Bax expression and downregulating Bcl-2 expression [9,15].
Half branch lotus extract: induces apoptosis through mitochondrial membrane potential loss and Caspase family protein activation [10,17].
3. Inhibit proliferation and invasion ability
The proliferation and invasion ability of HT-29 cells are important indicators for studying anti-tumor drugs. For example:
Ke Liu Wan: significantly inhibits the proliferation and invasion ability of HT-29 cells [11].
Lactic acid bacteria fermented barley extract (LFBE): inhibits HT-29 cell proliferation by inducing changes in cell morphology and apoptosis [6].
Low molecular weight polysaccharides from Agaricus bisporus: reduce the adhesion ability between HT-29 cells and endothelial cells, and decrease tumor cell migration [12].
4. Cycle arrest and gene regulation
Research on HT-29 cell cycle regulation has shown that certain compounds can inhibit its proliferation by blocking the cell cycle progression. For example:
ONGX6 gene: By downregulating the expression of cyclinE and cyclinD1, the proportion of HT-29 cells in the G0/G1 phase is increased [16].
Extract of Hedyotis diffusa: Inhibits HT-29 cell proliferation by blocking the G1/S phase of the cell cycle [8].
5. Autophagy related research
Autophagy is an emerging field in the anti-tumor research of HT-29 cells. For example:
Sodium valproate: induces autophagic cell death in HT-29 cells by blocking the mTOR Akt signaling pathway [13].
6. Research on other mechanisms
Regulation of Ca²+: Berberine inhibits HT-29 cell proliferation by suppressing Ca²+ release.
ORNA interference technique: By targeting the FucT VII gene, the adhesion ability between HT-29 cells and endothelial cells is reduced [14].
HT-29 cells, as a research model for colon cancer, have been widely used in screening anti-tumor drugs and studying their mechanisms. It exhibits sensitivity to various compounds and can exert anti-tumor effects through various mechanisms such as apoptosis, cycle arrest, and autophagy. These studies not only provide theoretical basis for the treatment of colon cancer, but also lay the foundation for further development of new anti-tumor drugs.
References
