🧠 Glioma
Gliomas are tumors that originate from glial cells in the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord), accounting for approximately 40%-50% of all primary brain tumors. They are also one of the most common and malignant types of tumors in adults' central nervous system. Based on the originating cell type, they can be classified into astrocytomas, ependymomas, or oligodendrogliomas. Due to their infiltrative growth characteristics, they are difficult to treat, have a high recurrence rate, and significantly impact the neurological function and survival period of patients[1,2].
At the molecular level, the occurrence of gliomas is closely related to various genetic mutations and abnormalities in signaling pathways. For example, IDH mutations, inactivation of TP53 and RB1 genes, mutations in genes such as EGFR and PDGFRA, and abnormal activation of RAS/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways all contribute to the development and progression of gliomas. Additionally, epigenetic modifications, such as abnormal DNA methylation and histone modifications, also regulate gene expression and influence tumor progression[3].
The pathogenesis of gliomas also involves the tumor microenvironment and immune escape. Glioma cells achieve immune escape by inhibiting T cell function, promoting the activation and differentiation of immunosuppressive cells (such as macrophages and dendritic cells), and upregulating the expression of immune checkpoint molecules. Furthermore, abnormal metabolic pathways in gliomas, such as fatty acid metabolism and purine metabolism, may also become new targets for treatment[4].
The pathogenesis of gliomas is complex, involving various molecular, genetic, and environmental factors. In-depth research into the molecular mechanisms of these signaling pathways will help develop more effective diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
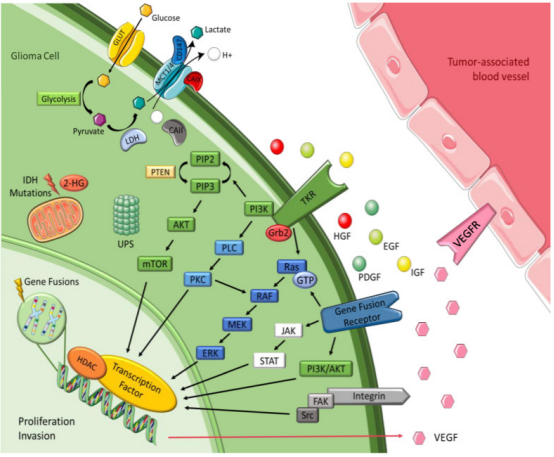
The molecular mechanisms of metabolism, signal transduction, and interaction with tumor-associated blood vessels in glioma cells[5].
Target Proteins Associated with Glioma
| Target | Catalog# | Product Name | Reactivity | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer Stemness: | ||||
| CD44 | AMRe08400 | CD44 (19J7) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,IP,IF-P |
| CD70 | APRab08443 | CD70 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse | IHC-P,IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| c-Myc | AMRe05879 | Phospho-c-Myc (S62) (9Z2) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,ICC/IF,FC,IP,IF-P |
| c-Myc | AMRe05880 | Phospho-c-Myc (S62) (9Z2) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,ICC/IF,FC |
| Oct-4 | AMRe06329 | 45569(2Y12) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse | WB,IHC-P,ICC/IF,FC,IP,IF-P |
| Olig2 | AMRe02564 | Olig2 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB, IHC-P, ICC/IF |
| Sox2 | AMRe18134 | SOX2 (6X19) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB,IHC-P,IP,IF-P |
| S100A4 | AMRe02564 | S100A4 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF,IP |
| ALDH1A1 | AMRe01481 | ALDH1A1 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse | WB,IHC-P,IP |
| STAT3 | AMRe06021 | Phospho-STAT3 (Y705) (13H8) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,ICC/IF,FC,IP,IF-P |
| STAT3 | AMRe03947 | STAT3 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF,FC |
| CD133 | AMRe08203 | CD133 (5M9) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB,IHC-P,IF-P |
| CD90 | AMRe08485 | CD90 / Thy1 (2D12) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB,IHC-P,ICC/IF,IF-P |
| CD24 | APRab08302 | CD24 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | IHC-P,IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| ABCG2 | APRab06426 | ABCG2 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,WB,IHC-P,ELISA |
| L1CAM | APRab14438 | NCAM-L1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| Cancer Type Differentiation: | ||||
| GFAP | AMRe02031 | GFAP Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | Human,Rat | WB,IHC-P,IP |
| GFAP | AMRe01503 | GFAP Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | Human,Rat | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF |
| Synaptophysin | AMRe02655 | Synaptophysin Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | Human,Rat | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF |
| ATRX | APRab07357 | ATRX Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse | IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| Notch1 | APRab00818 | Cleaved-Notch1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| Shh | AMRe02627 | Sonic Hedgehog Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF |
| SALL4 | AMRe02570 | Sall4 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB,IHC-P |
| Cell Cycle, Growth, and Proliferation: | ||||
| CXCR4 | AMRe09561 | CXCR4 (8E12) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,ICC/IF,IF-P |
| EGFR | AMRe04076 | EGFR Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB,IHC-P,IP |
| EGFR | AMRe10340 | EGFR (ErbB 1) (9C2) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,ICC/IF,FC,IP,IF-P |
| Histone H3 | AMRe03910 | MonoMethyl-Histone H3 (Lys9) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF |
| Histone H3 | AMRe02834 | TriMethyl-Histone H3 (Lys27) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF,IP,ChIP |
| Ki-67 | AMRe13001 | Ki67 (19I8) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,ICC/IF,FC,IF-P |
| P53 | AMRe03901 | Phospho-p53 (Ser392) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,IP |
| P53 | AMRe02388 | p53 Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | Mouse | WB,ICC/IF,IP |
| PTEN | AMRe16636 | PTEN (16Q18) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,FC,IP,IF-P |
| Cell Survival and Drug Resistance: | ||||
| DAXX | AMRe02966 | Daxx Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB,ICC/IF |
| GLI1 | APRab11462 | GLI-1 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse | WB,ELISA |
| IDH1 | AMRe12352 | IDH1 (2P17) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,FC,IP,IF-P |
| Invasion and Metastasis: | ||||
| Cathepsin D | APRab08016 | Cathepsin D Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| IL-13RA2 | APRab12500 | IL-13Rα2 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| L1CAM | AMRe02198 | L1CAM Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human | WB,IHC-P |
| LDHA | AMRe03782 | Lactate Dehydrogenase A Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF,IP |
| LDHA | AMRe13262 | LDHA (4H19) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,ICC/IF,FC,IF-P |
| S100A9 | APRab06076 | S100A9 (Phospho-Thr113) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB |
| TNC | AMRe18788 | Tenascin C (7E16) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,IF-P |
| VEGFA | AMRe02757 | VEGFA Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB |
| VEGFR1 | AMRe19767 | VEGF Receptor 1 (16I17) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,IP,IF-P |
| VEGFR2 | APRab04679 | Flk-1 (phospho Tyr1214) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| VEGFR2 | APRab04678 | Flk-1 (phospho Tyr1175) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| VEGFR3 | APRab11039 | Flt-4 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,ELISA |
ELISA Kits
| Target | Catalog# | Product Name | Reactivity | Detection Range | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEGFA | EM10657 | Mouse VEGF-A (Vascular Endothelial Cell Growth Factor A) ELISA Kit | Mouse | 31.25–2000 pg/mL | 18.75 pg/mL |
| EGFR | EH10387 | Human EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) ELISA Kit | Human | 0.31–20 ng/mL | 0.19 ng/mL |
Related Products
References
- Yei J, Lee NK, Ryu S, Ryu SE, Lee J, Park T, Jeong Y, Kang R, Kwon HK, Kim SG, Park JC, Park CG, Suh M. Glioma-Associated Microglia Potentiate Neuronal Hyper-Excitability in the Glioma Environment. Neuro Oncol. 2025 Jul 30:noaf181. Epub ahead of print. [PMID: 40741716].
- Poorva P, Mast J, Cao B, Shah MV, Pollok KE, Shen J. Killing the killers: Natural killer cell therapy targeting glioma stem cells in high-grade glioma. Mol Ther. 2025 Jun 4;33(6):2462-2478. Epub 2025 Mar 3. [PMID: 40040281].
- He Y, Li W, Zhang X, Cui Z. Oncolytic Virus Targeted Therapy for Glioma via Intravenous Delivery. Adv Healthc Mater. 2025 Mar;14(7):e2404965. Epub 2025 Jan 13. [PMID: 39801205].
- Luo K, Zhuang K, Wu H, Chen Y, Liu Y, Yang F, Wang Z. PLIN1 suppresses glioma progression through regulating lipid metabolism. Cell Death Dis. 2025 Jan 27;16(1):48. [PMID: 39870645].

