Acetyl-Histone H3/H4
In eukaryotic nuclei, ~150 bp of DNA is wrapped around the histone octamer, which consists of two copies of four core histones (i.e., H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) to form a nucleosome, the fundamental unit of chromatin. Post-translational modifications on these histones play a critical role in genome function, including the regulation of transcription and the maintenance of genome integrity [1]. Since H3 and H4 are more stably integrated into nucleosomes compared to H2A and H2B , the modifications on H3 and H4 can act as long-term memory of epigenetic regulation[2].
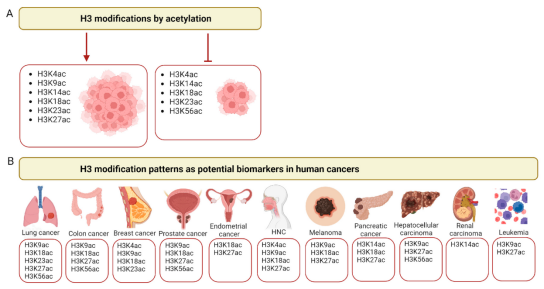
Histone H3 has been the most extensively modified post-translationally among all histones . Thirteen acetylated K residues have been identified in human histone H3 , according to the CPLM 4.0 database[3],including K4, K9, K14, K18, K23, K27, K36, K37, K56, K64, K79, K115 and K122. Most of them were reported to have an impact on patients' outcomes in different cancer types[4]. Notably, in Eukaryotes, histone variants exist, with several variants for histone H3 identified in humans. These are categorized into canonical variants (H3.1 and H3.2) and replacement variants (H3.3, CENP-A, H3t, H3.X, and H3.Y). H3.1, H3.2 and H3.3 are the most prevalent variants, sharing a high degree of sequence similarity (over 96% for H3.1/H3.2 vs. H3.3, and over 99% for H3.1 vs. H3.2). These variants may, therefore, have similar PTMs on conserved amino acid residues. However, H3.1 and H3.2 are found predominantly in heterochromatin, while H3.3 is associated with euchromatin [5].
Modifications on histone H4 are also known to be involved in gene regulation and genome maintenance [6]. Lysine residues in H4 N-terminal tail (i.e., H4K5, H4K8, H4K12, and H4K16) are major acetylation sites . These acetylations are predominantly associated with euchromatin, contributing to chromatin decondensation and transcriptional regulation . H4K16ac is also known to be associated with DNA damage repair and cell senescence. In addition, H4K5ac and H4K12ac are associated with newly assembled chromatin since H4 in predeposition complexes is diacetylated at K5 and K12 by a histone acetyltransferase (HAT)[7]. Although the diacetylation of H4 is not a prerequisite for histone assembly, these modifications may stimulate nuclear import and contribute to the recovery from replication block-mediated DNA damage. After being assembled into chromatin, H4 becomes deacetylated in heterochromatin . In contrast to these four lysines that are acetylated, H4 lysine 20 (H4K20) is subject to methylation[8] . Monomethylation of H4K20 (H4K20me1) may play multiple roles in genome regulation, including transcriptional control, DNA replication licensing, DNA damage response, and chromosome segregation . Dimethylation of H4K20 (H4K20me2) is one of the most abundant modifications in mouse fibroblasts and HeLa cells, and is involved in DNA damage repair signaling [9].
Acetyl-Histone H3 Relevant antibodies
| Catalog# | Product Name | Reactivity | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMRe21336 | Histone H3 Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC,IF,IP,ELISA |
| APRab00847 | Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys9) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB |
| AMRe03273 | Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys14) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Rat | WB,ICC/IF,IP |
| AMRe84527 | Acetyl-Histone H3(Lys18) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IP,IHC,ICC,FC,IF |
| AMRe04172 | Acetyl-Histone H3 (Lys27) (17F16) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC-P,ICC/IF,FC |
| APS0635 | HRP-conjugated Polyclonal Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) Secondary Antibody | Rabbit | ELISA, WB, Dot blot |
| AMre80004 | GAPDH (12R9) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit,Dog,Monkey | WB,ELISA |
Acetyl-Histone H4 Relevant antibodies
| Catalog# | Product Name | Reactivity | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMRe03268 | Acetyl-Histone H4 (Lys5) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse | WB,IHC-F,IHC-P,ICC/IF,IP |
| APRab06216 | Histone H4 (Acetyl Lys8) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat,Monkey | WB,IHC-P,IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| APRab06212 | Histone H4 (Acetyl Lys12) Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat,Monkey | WB,IHC-P,IF-P,IF-F,ICC/IF,ELISA |
| AMRe21614 | Histone H4 Rabbit Monoclonal antibody | Human,Mouse,Rat | WB,IHC,IF,IP,ELISA |
| APS0631 | HRP-conjugated Polyclonal Goat Anti-Mouse IgG(H+L) Secondary Antibody | Mouse | ELISA, WB, Dot blot |
Related Products
- Hayashi-Takanaka Y, Maehara K, Harada A, et al. Distribution of histone H4 modifications as revealed by a panel of specific monoclonal antibodies. Chromosome Res. 2015 Dec;23(4):753-66. Epub 2015 Sep 5. [PMID: 26343042].
- Barman HK, Takami Y, Ono T, Nishijima H, Sanematsu F, et al. Histone acetyltransferase 1 is dispensable for replication-coupled chromatin assembly but contributes to recover DNA damages created following replication blockage in vertebrate cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Jul 14;345(4):1547-57. Epub 2006 May 23. [PMID: 16735025].
- Xu YM, Du JY, Lau AT. Posttranslational modifications of human histone H3: an update. Proteomics. 2014 Sep;14(17-18):2047-60. Epub 2014 Aug 8. [PMID: 25044606].
- Zhang W, Tan X, Lin S, Gou Y, Han C, et al. CPLM 4.0: an updated database with rich annotations for protein lysine modifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jan 7;50(D1):D451-D459. [ PMID: 34581824].
- Beck DB, Oda H, Shen SS, . PR-Set7 and H4K20me1: at the crossroads of genome integrity, cell cycle, chromosome condensation, and transcription. Genes Dev. 2012 Feb 15;26(4):325-37. [PMID: 22345514].
- Dang W, Steffen KK, Perry Ret al, Johnson FB, Shilatifard A, Kaeberlein M, Kennedy BK, Berger SL. Histone H4 lysine 16 acetylation regulates cellular lifespan. Nature. 2009 Jun 11;459(7248):802-7. [ PMID: 19516333].
- Dion MF, Altschuler SJ, Wu LF, Rando OJ. Genomic characterization reveals a simple histone H4 acetylation code. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Apr 12;102(15):5501-6. Epub 2005 Mar 28. [PMID: 15795371].
- Eberhart A, Kimura H, Leonhardt H,et al. Reliable detection of epigenetic histone marks and nuclear proteins in tissue cryosections. Chromosome Res. 2012 Oct;20(7):849-58. Epub 2012 Nov 2. [PMID: 23117894].
- Ejlassi-Lassallette A, Mocquard E, Arnaud MCet al. H4 replication-dependent diacetylation and Hat1 promote S-phase chromatin assembly in vivo. Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Jan 15;22(2):245-55. Epub 2010 Nov 30.[ PMID: 21118997].

