Size:50μL Price:$118
Size:100μL Price:$220
Size:200μL Price:$380
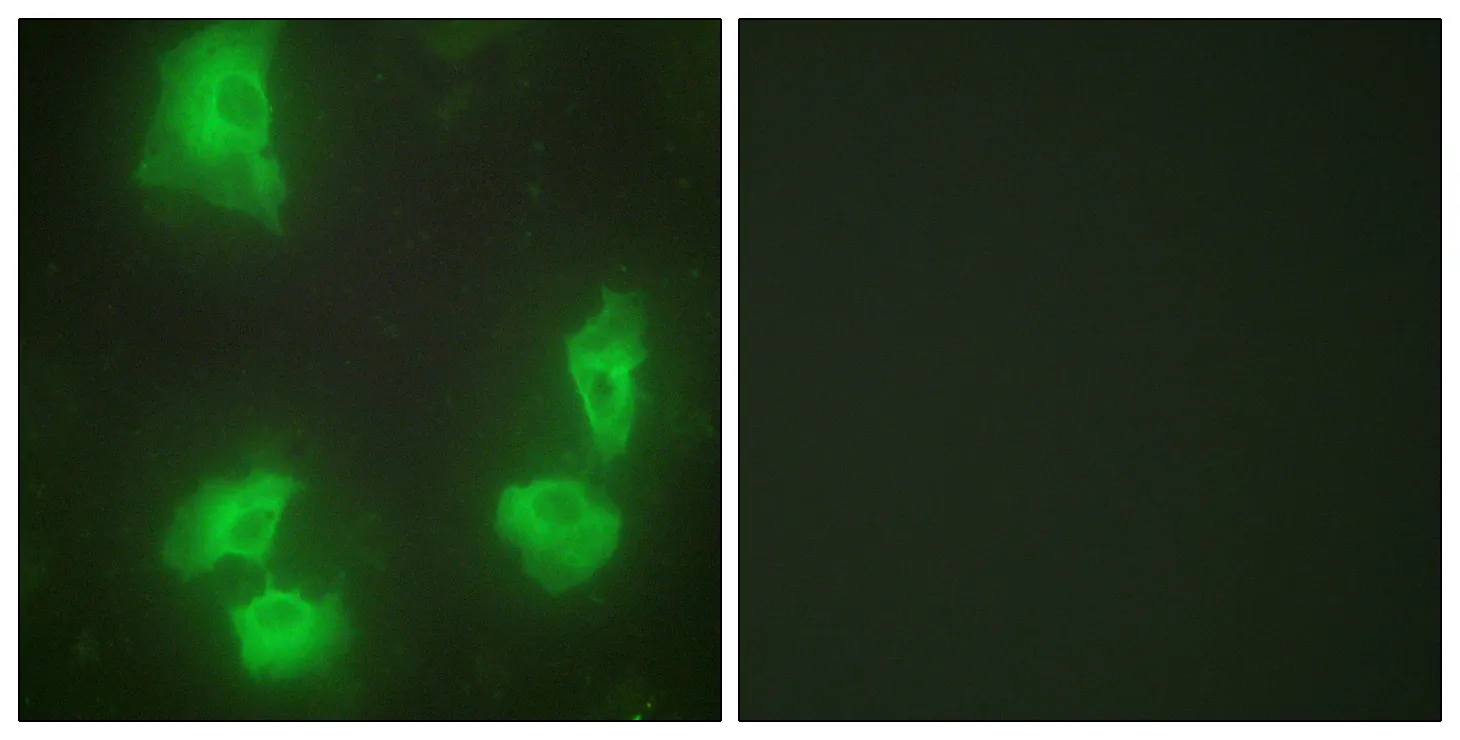
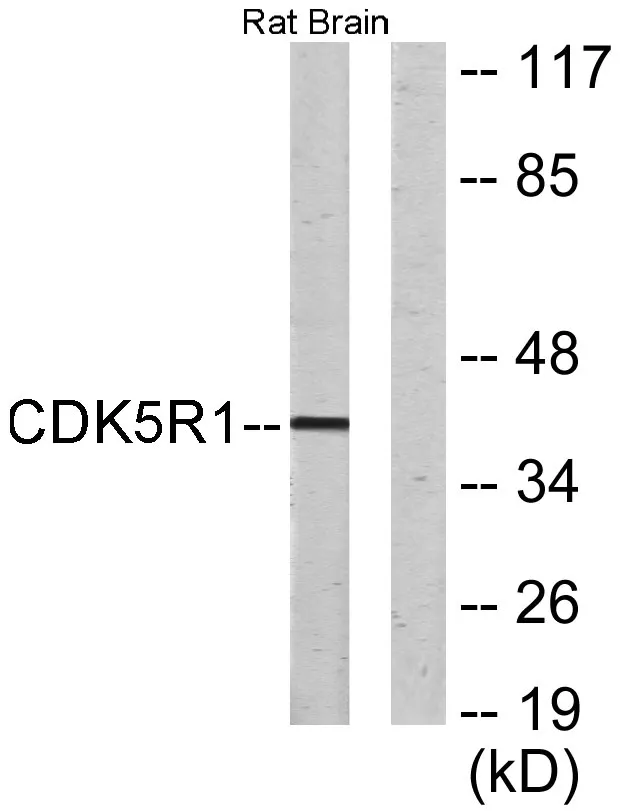
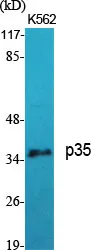
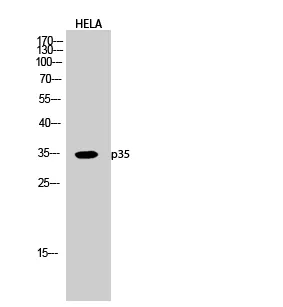
Application:WB,IHC,ICC/IF,ELISA
Reactivity:Human,Mouse,Rat
Conjugate:Unconjugated
Optional conjugates: Biotin, FITC (free of charge). See other 26 conjugates.
Gene Name:CDK5R1
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
The protein encoded by this gene (p35) is a neuron-specific activator of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5); the activation of CDK5 is required for proper development of the central nervous system. The p35 form of this protein is proteolytically cleaved by calpain, generating a p25 form. The cleavage of p35 into p25 results in relocalization of the protein from the cell periphery to nuclear and perinuclear regions. P25 deregulates CDK5 activity by prolonging its activation and changing its cellular location. The p25 form accumulates in the brain neurons of patients with Alzheimer's disease. This accumulation correlates with an increase in CDK5 kinase activity, and may lead to aberrantly phosphorylated forms of the microtubule-associated protein tau, which contributes to Alzheimer's disease. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],disease:Cleavage of p35 to p25 may be involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. The p25 form accumulates in neurons in the brain of patients with Alzheimer disease, but not in normal brain. This accumulation correlates with an increase in CDK5 kinase activity. Application of amyloid beta peptide A-beta(1-42) induced the conversion of p35 to p25 in primary cortical neurons. Expression of the p25/Cdk5 complex in cultured primary neurons induces cytoskeletal disruption, morphological degeneration and apoptosis.,function:p35 is a neuron specific activator of CDK5. The complex p35/CDK5 is required for neurite outgrowth and cortical lamination. Activator of TPKII.,PTM:Probably myristoylated. The Gly-2-Ala mutant is absent of the cell periphery, suggesting that a proper myristoylation signal is essential for the proper distribution of p35.,PTM:The p35 form is proteolytically cleaved by calpain, giving rise to the p25 form. P35 has a 5 to 10 fold shorter half-life compared to p25. The conversion results in deregulation of the CDK5 kinase: p25/CDK5 kinase displays an increased and altered tau phosphorylation in comparison to the p35/CDK5 kinase in vivo.,similarity:Belongs to the cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activator family.,subcellular location:In the primary cortical neurons, p35 is present in the peripheries and nerve terminals.,subcellular location:The conversion of p35 to p25 relocalizes the protein from the cell periphery to the cytoplasm, in nuclear and perinuclear regions. In the primary cortical neurons, p25 is primarily concentrated in the cell soma and is largely absent from neurites.,subunit:Heterodimer composed of CDK5 and CDK5R (p25) and macromolecular complex composed of at least CDK5, CDK5R (p35) and CDK5RAP1 or CDK5RAP2 or CDK5RAP3. Only the heterodimer shows kinase activity (By similarity). Interacts with RASGRF2.,tissue specificity:Brain and neuron specific.,
Research Area
Alzheimer's disease;
