Summary
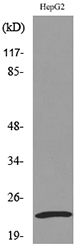
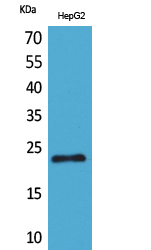
Performance
Immunogen
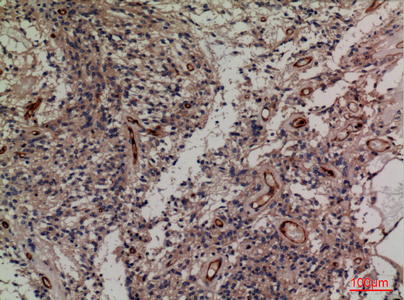
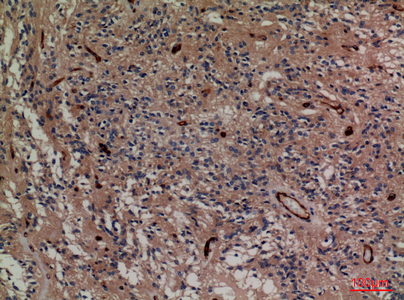
Application
Background
Specificity of vesicular transport is regulated, in part, by the interaction of a vesicle-associated membrane protein termed synaptobrevin/VAMP with a target compartment membrane protein termed syntaxin. These proteins, together with SNAP25 (synaptosome-associated protein of 25 kDa), form a complex which serves as a binding site for the general membrane fusion machinery. Synaptobrevin/VAMP and syntaxin are believed to be involved in vesicular transport in most, if not all cells, while SNAP25 is present almost exclusively in the brain, suggesting that a ubiquitously expressed homolog of SNAP25 exists to facilitate transport vesicle/target membrane fusion in other tissues. The protein encoded by this gene is structurally and functionally similar to SNAP25 and binds tightly to multiple syntaxins and synaptobrevins/VAMPs. It is an essential component of the high affinity receptor for thefunction:Essential component of the high affinity receptor for the general membrane fusion machinery and an important regulator of transport vesicle docking and fusion.,similarity:Belongs to the SNAP-25 family.,similarity:Contains 2 t-SNARE coiled-coil homology domains.,subcellular location:Mainly localized to the plasma membrane.,subunit:Binds simultaneously to SNAP25BP and SYN4. Found in a complex with VAMP8 and STX4 in pancreas (By similarity). Binds tightly to multiple syntaxins and synaptobrevins/VAMPs. Found in a complex with VAMP8 and STX1A.,tissue specificity:Ubiquitous. Highest levels where found in placenta.,
Research Area
SNARE interactions in vesicular transport;