Size:50μL Price:$118
Size:100μL Price:$220
Size:200μL Price:$380
Application:WB,IHC,ELISA
Reactivity:Human,Mouse,Rat,Monkey
Conjugate:Unconjugated
Optional conjugates: Biotin, FITC (free of charge). See other 26 conjugates.
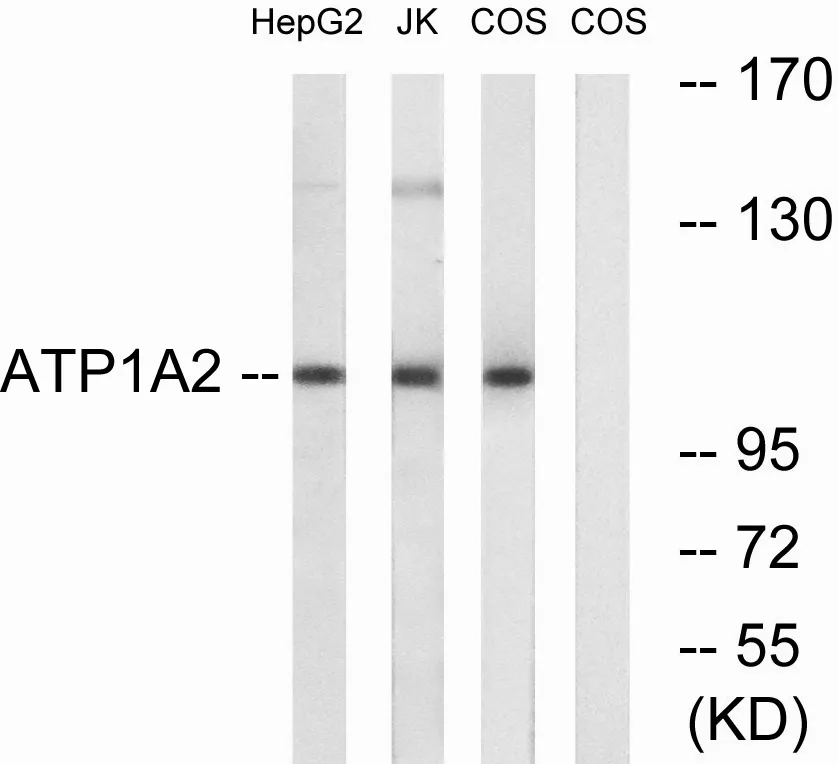
Gene Name:ATP1A2
Summary
| Production Name | Na+/K+-ATPase α2 Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody |
| Description | Rabbit polyclonal Antibody |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Application | WB,IHC,ELISA |
| Reactivity | Human,Mouse,Rat,Monkey |
Performance
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Modification | Unmodified |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Form | Liquid |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Buffer | Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% protective protein and 0.02% New type preservative N. |
| Purification | Affinity purification |
Immunogen
| Gene Name | ATP1A2 |
| Alternative Names | ATP1A2; KIAA0778; Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-2; Na(+)/K(+) ATPase alpha-2 subunit; Sodium pump subunit alpha-2 |
| Gene ID | 477 |
| SwissProt ID | P50993 |
Application
| Dilution Ratio | WB 1:500-1:2000,IHC 1:50-1:300,ELISA 1:2000-1:20000 |
| Molecular Weight | 112kDa |
Background
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the family of P-type cation transport ATPases, and to the subfamily of Na+/K+ -ATPases. Na+/K+ -ATPase is an integral membrane protein responsible for establishing and maintaining the electrochemical gradients of Na and K ions across the plasma membrane. These gradients are essential for osmoregulation, for sodium-coupled transport of a variety of organic and inorganic molecules, and for electrical excitability of nerve and muscle. This enzyme is composed of two subunits, a large catalytic subunit (alpha) and a smaller glycoprotein subunit (beta). The catalytic subunit of Na+/K+ -ATPase is encoded by multiple genes. This gene encodes an alpha 2 subunit. Mutations in this gene result in familial basilar or hemiplegic migraines, and in a rare syndrome known as alternating hemiplegia of childhood. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008],catalytic activity:ATP + H(2)O + Na(+)(In) + K(+)(Out) = ADP + phosphate + Na(+)(Out) + K(+)(In).,disease:Defects in ATP1A2 are a cause of alternating hemiplegia of childhood (AHC) [MIM:104290]. AHC is typically distinguished from familial hemiplegic migraine by infantile onset of the symptoms and high prevalence of associated neurological deficits that become increasingly obvious with age.,disease:Defects in ATP1A2 are the cause of familial hemiplegic migraine 2 (FHM2) [MIM:602481]. Familial hemiplegic migraine is a rare, severe, autosomal dominant subtype of migraine characterized by aura and some hemiparesis.,function:This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.,similarity:Belongs to the cation transport ATPase (P-type) family. Type IIC subfamily.,subunit:Composed of three subunits: alpha (catalytic), beta and gamma.,
Research Area
Cardiac muscle contraction;Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption;
