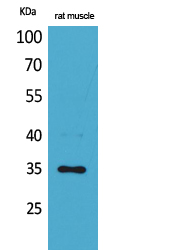
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
Carbonic anhydrases (CAs) are a large family of zinc metalloenzymes that catalyze the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. They participate in a variety of biological processes, including respiration, calcification, acid-base balance, bone resorption, and the formation of aqueous humor, cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, and gastric acid. They show extensive diversity in tissue distribution and in their subcellular localization. This gene encodes a glycosylphosphatidyl-inositol-anchored membrane isozyme expressed on the luminal surfaces of pulmonary (and certain other) capillaries and proximal renal tubules. Its exact function is not known; however, it may have a role in inherited renal abnormalities of bicarbonate transport. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],catalytic activity:H(2)CO(3) = CO(2) + H(2)O.,cofactor:Zinc.,disease:Defects in CA4 are the cause of retinitis pigmentosa type 17 (RP17) [MIM:600852]. RP leads to degeneration of retinal photoreceptor cells. Patients typically have night vision blindness and loss of midperipheral visual field. As their condition progresses, they lose their far peripheral visual field and eventually central vision as well. RP17 inheritance is autosomal dominant.,enzyme regulation:Inhibited by acetazolamide.,function:Reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. May stimulate the sodium/bicarbonate transporter activity of SLC4A4.,similarity:Belongs to the alpha-carbonic anhydrase family.,subunit:Interacts with SLC4A4.,tissue specificity:Expressed in the endothelium of the choriocapillaris in eyes (at protein level).,
Research Area
Nitrogen metabolism;