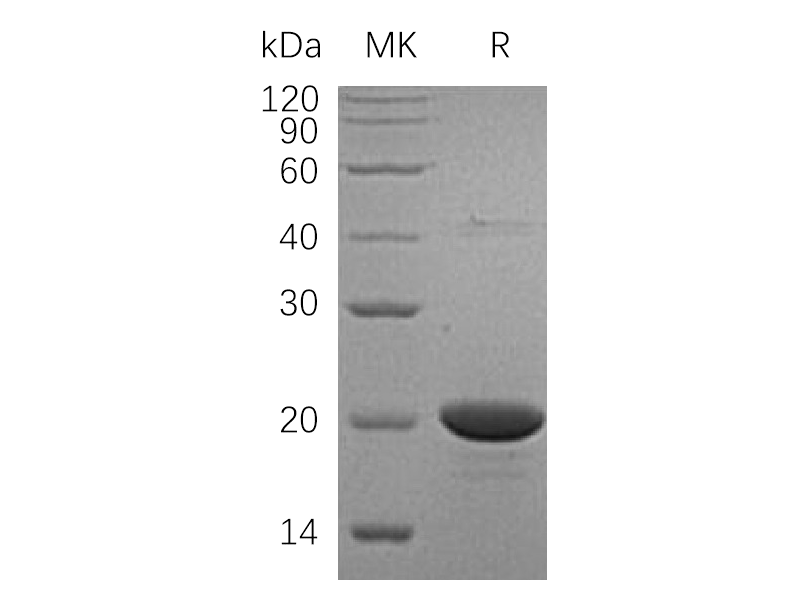
Alternative Names
Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase A; NDK A; NDP Kinase A; Granzyme A-Activated DNase; GAAD; Metastasis Inhibition Factor nm23; Tumor Metastatic Process-Associated Protein; nm23-H1; NME1; NDPKA; NM23
Background
Nucleoside-Diphosphate Kinases (NDKs) are enzymes that catalyze the exchange of phosphate groups between different nucleoside diphosphates. NDKs Possesse nucleoside-diphosphate kinase, serine/threonine-specific protein kinase, geranyl and farnesyl pyrophosphate kinase, histidine protein kinase and 3-5 exonuclease activities. NDKs involved in cell proliferation, differentiation and development, signal transduction, G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis, and gene expression and required for neural development including neural patterning and cell fate determination. Prokaryotic NDK forms a functional homotetramer.There are two isoforms of NDK in humans: NDK-A and NDK-B. Both have very similar structure, and can combine in any proportion to form functional NDK hexamers.
Note
For Research Use Only , Not for Diagnostic Use.