Size:100μL Price:$300
Size:200μL Price:$520
Application:WB,IHC,ICC/IF
Reactivity:Human, Mouse, Rat
Conjugate:Unconjugated
Optional conjugates: Biotin, FITC (free of charge). See other 26 conjugates.
Gene Name:H3C1
Summary
| Production Name | MonoMethyl-Histone H3 (Lys9) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody |
| Description | Recombinant rabbit monoclonal antibody |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Application | WB,IHC,ICC/IF |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
Performance
| Conjugation | Unconjugated |
| Modification | Methylated |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Form | Liquid |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Buffer | Liquid in 50mM Tris-Glycine(pH 7.4), 0.15M NaCl, 40%Glycerol, 0.01% sodium azide and 0.05% protective protein. |
| Purification | Affinity Purification |
Immunogen
| Gene Name | H3C1 |
| Alternative Names | H3K9me; Histone H3/b;Histone H3/c;Histone H3/d;Histone H3/f |
| Gene ID | 8350 |
| SwissProt ID | P68431 |
Application
| Dilution Ratio | WB 1:500-1:1000,IHC 1:50-1:100,ICC/IF 1:50-1:200 |
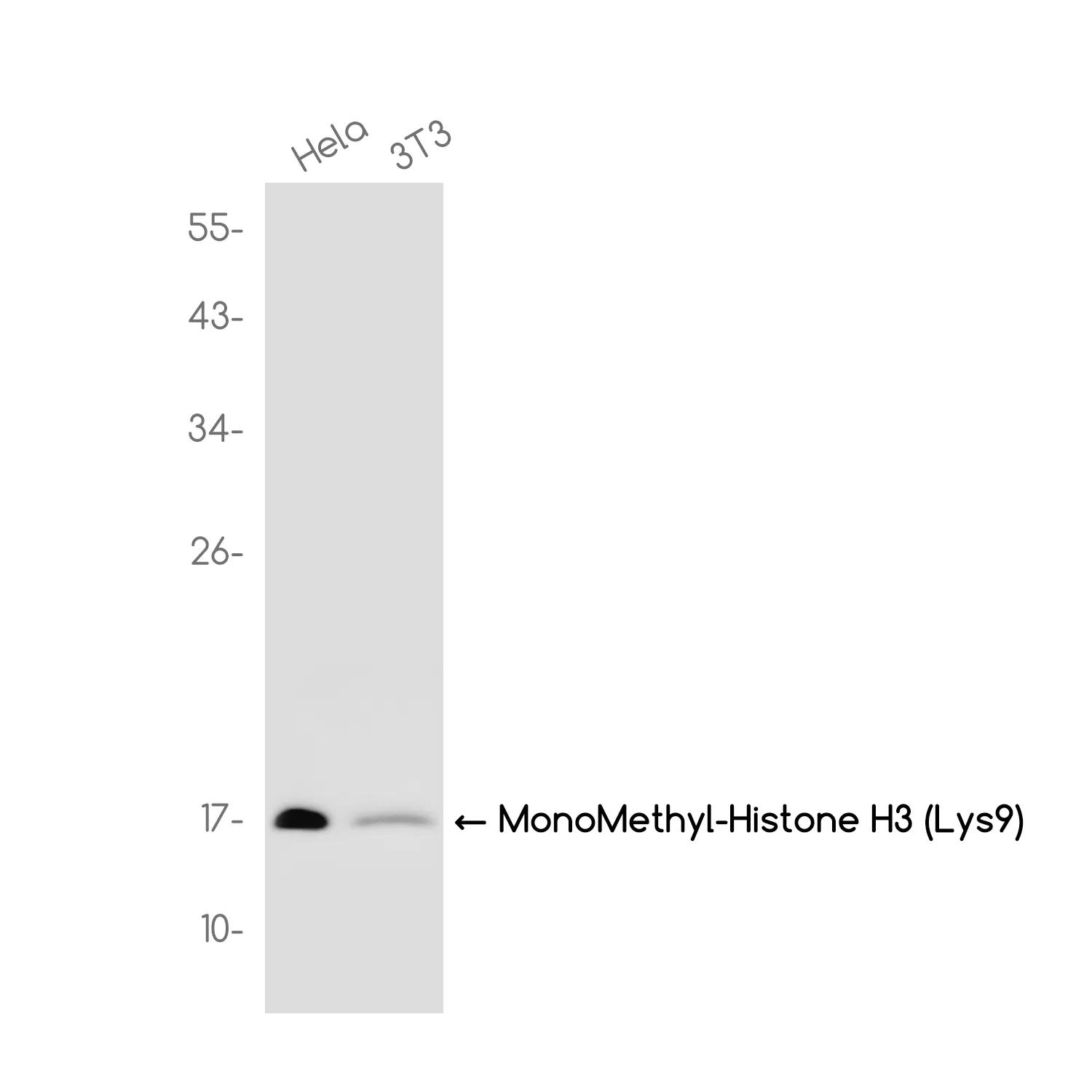
| Molecular Weight | Calculated MW:15 kDa;Observed MW: 17 kDa |
Background
Histone post-translational modifications (PTMs) are key mechanisms of epigenetics that modulate chromatin structures, termed as “histone code”. The PTMs on histone including acetylation, methylation, phosphorylation and novel acylations directly affect the accessibility of chromatin to transcription factors and other epigenetic regulators, altering genome stability, gene transcription, etc. Histone methylation occurs primarily at lysine and arginine residues on the amino terminal of core histones. Methylation of histones can either increase or decrease transcription of genes, depending on which amino acids (Lys or Arg) in the histones are methylated and how many methyl groups are attached (mono-, di-, tri-methylation on Lys, mono-di-symmetric/asymmetric methylation on Arg). Mostly, lysine methylation occurs primarily on histone H3 Lys4, 9, 27, 36, 79 and H4 Lys20, while Arginine methylation occurs primarily on histone H3 Arg2, 8, 17, 26 and H4 Arg3. Histone methylases (HMTs) and histone demethylases (HDMs) are major regulating factors.
Research Area
Epigenetics and Nuclear Signaling
