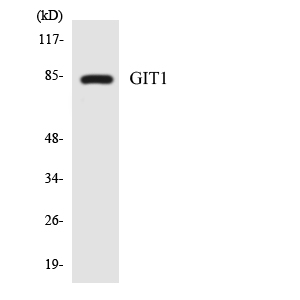
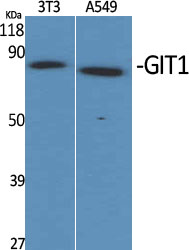
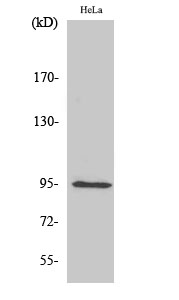
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
domain:The paxillin-binding domain is masked in the full-length protein and is regulated by ARHGEF6.,function:GTPase-activating protein for the ADP ribosylation factor family. May serve as a scaffold to bring together molecules to form signaling modules controlling vesicle trafficking, adhesion and cytoskeletal organization. Increases the speed of cell migration, as well as the size and rate of formation of protrusions, possibly by targeting PAK1 to adhesions and the leading edge of lamellipodia. Sequesters inactive non-tyrosine-phosphorylated paxillin in cytoplasmic complexes.,PTM:Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by PTK2 and SRC in growing fibroblasts. Tyrosine-phosphorylation is increased following cell spreading on fibronectin, decreased in cells arrested in mitosis and increased in the ensuing G1 phase.,similarity:Contains 1 Arf-GAP domain.,similarity:Contains 3 ANK repeats.,subcellular location:Cycles between at least 3 distinct intracellular compartments, including focal adhesions, cytoplasmic complexes and membrane protrusions. During cell migration, when cells detach, moves from the adhesions into the cytoplasmic complexes towards the leading edge, while, when cells adhere, it is found in vinculin-containing adhesions. Recruitment to adhesions may be mediated by active tyrosine-phosphorylated paxillin.,subunit:Interacts with G protein-coupled receptor kinases: ADRBK1/GRK2, PPFIA1 and PPFIA4. Interacts with ARHGEF6/alpha-PIX, with ARHGEF7/beta-PIX, with PXN/paxillin and with PTK2/FAK (By similarity). Component of cytoplasmic complexes, which also contain PXN, ARHGEF6 and PAK1. Interacts with TGFB1I1.,domain:The paxillin-binding domain is masked in the full-length protein and is regulated by ARHGEF6.,function:GTPase-activating protein for the ADP ribosylation factor family. May serve as a scaffold to bring together molecules to form signaling modules controlling vesicle trafficking, adhesion and cytoskeletal organization. Increases the speed of cell migration, as well as the size and rate of formation of protrusions, possibly by targeting PAK1 to adhesions and the leading edge of lamellipodia. Sequesters inactive non-tyrosine-phosphorylated paxillin in cytoplasmic complexes.,PTM:Phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by PTK2 and SRC in growing fibroblasts. Tyrosine-phosphorylation is increased following cell spreading on fibronectin, decreased in cells arrested in mitosis and increased in the ensuing G1 phase.,similarity:Contains 1 Arf-GAP domain.,similarity:Contains 3 ANK repeats.,subcellular location:Cycles between at least 3 distinct intracellular compartments, including focal adhesions, cytoplasmic complexes and membrane protrusions. During cell migration, when cells detach, moves from the adhesions into the cytoplasmic complexes towards the leading edge, while, when cells adhere, it is found in vinculin-containing adhesions. Recruitment to adhesions may be mediated by active tyrosine-phosphorylated paxillin.,subunit:Interacts with G protein-coupled receptor kinases: ADRBK1/GRK2, PPFIA1 and PPFIA4. Interacts with ARHGEF6/alpha-PIX, with ARHGEF7/beta-PIX, with PXN/paxillin and with PTK2/FAK (By similarity). Component of cytoplasmic complexes, which also contain PXN, ARHGEF6 and PAK1. Interacts with TGFB1I1.,
Research Area
Endocytosis;Regulates Actin and Cytoskeleton;Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection;