Summary
Performance
Immunogen
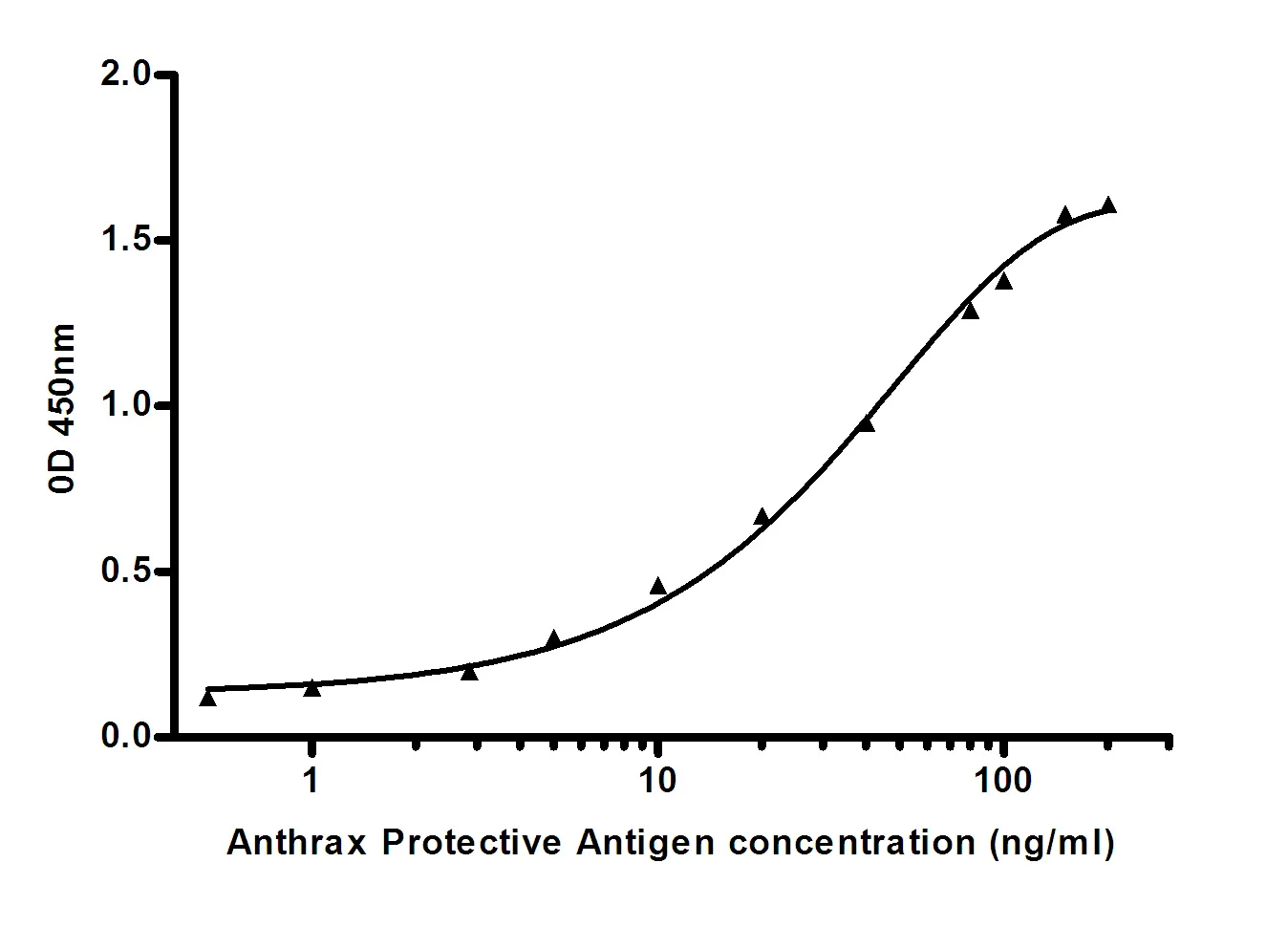
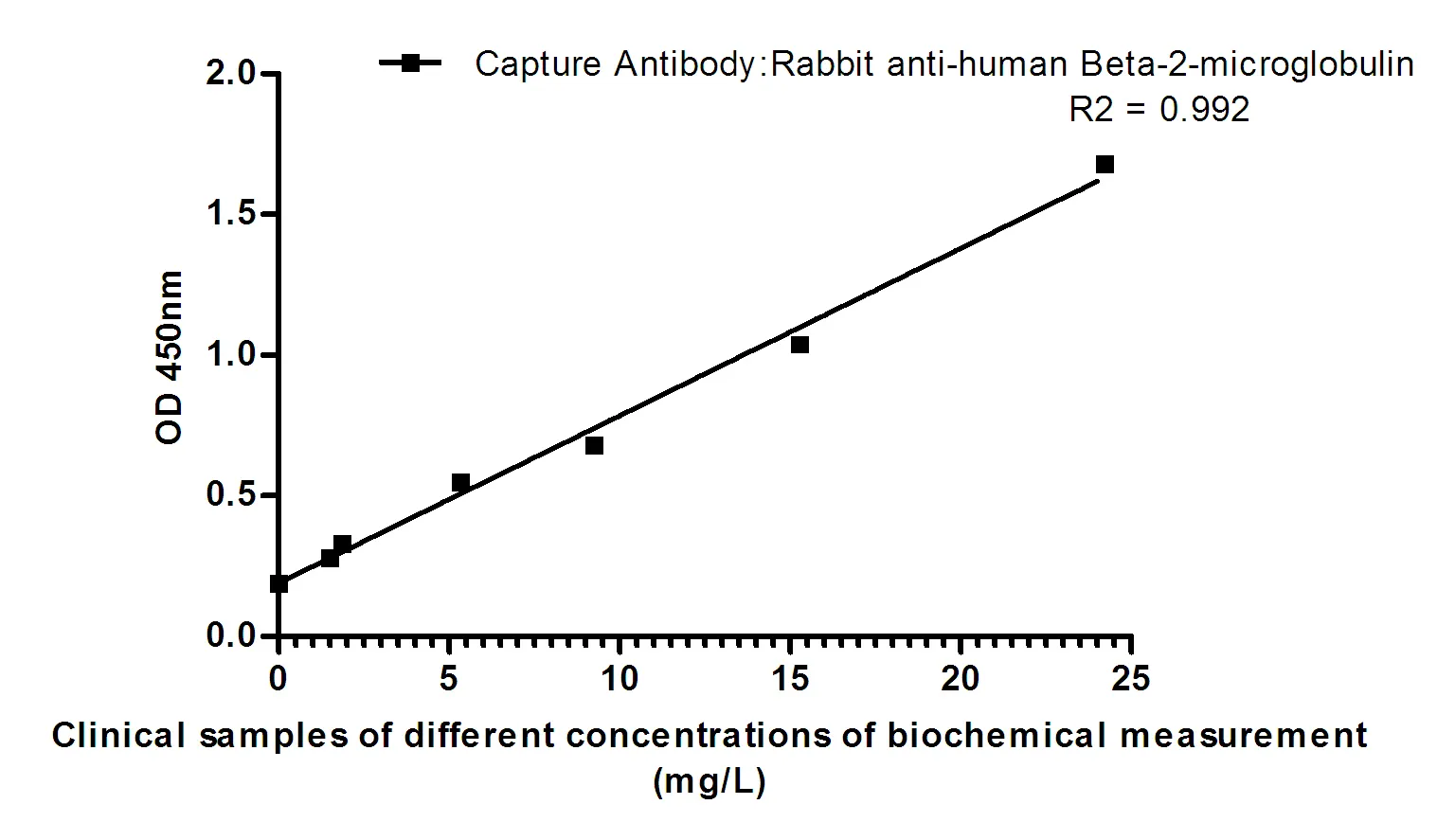
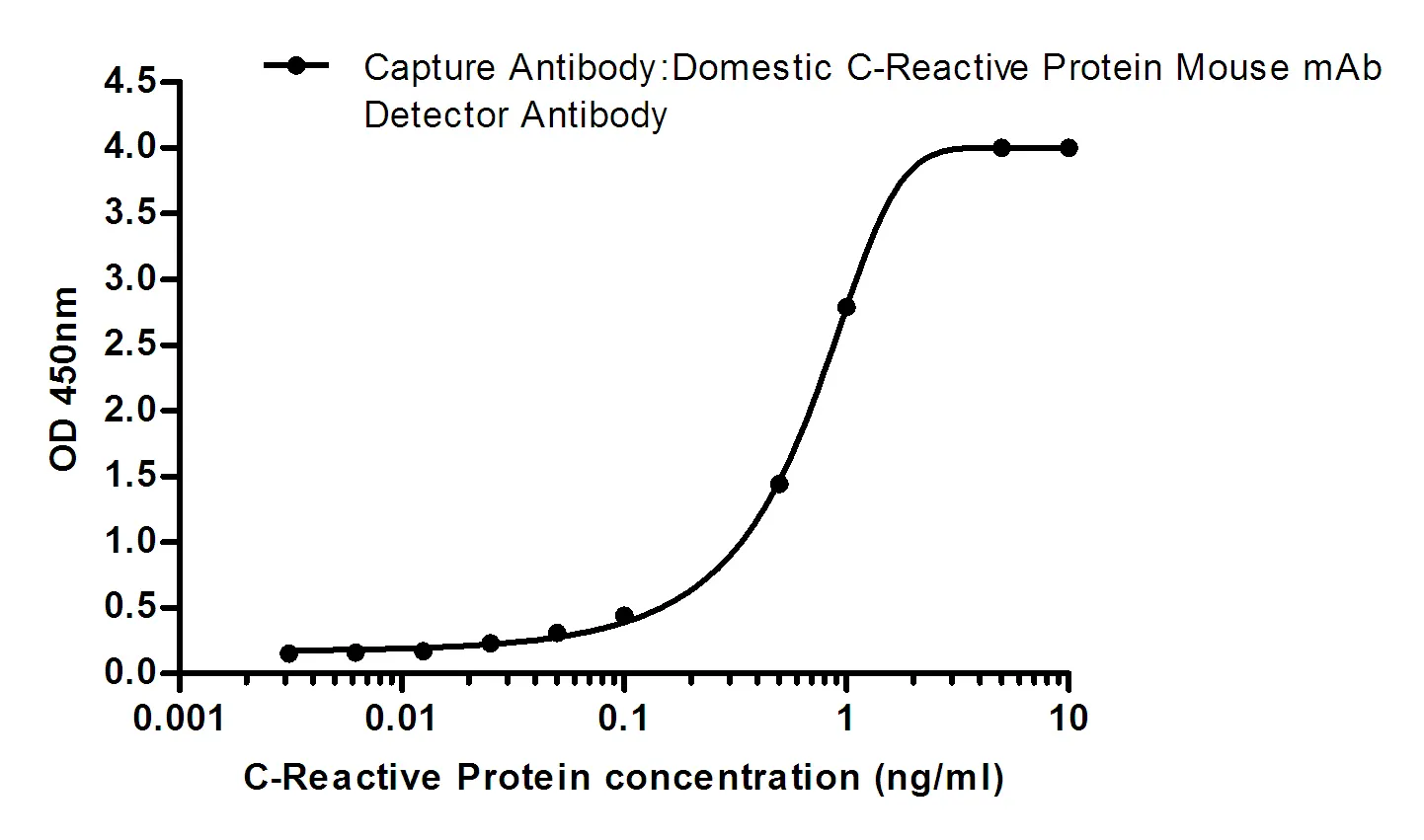
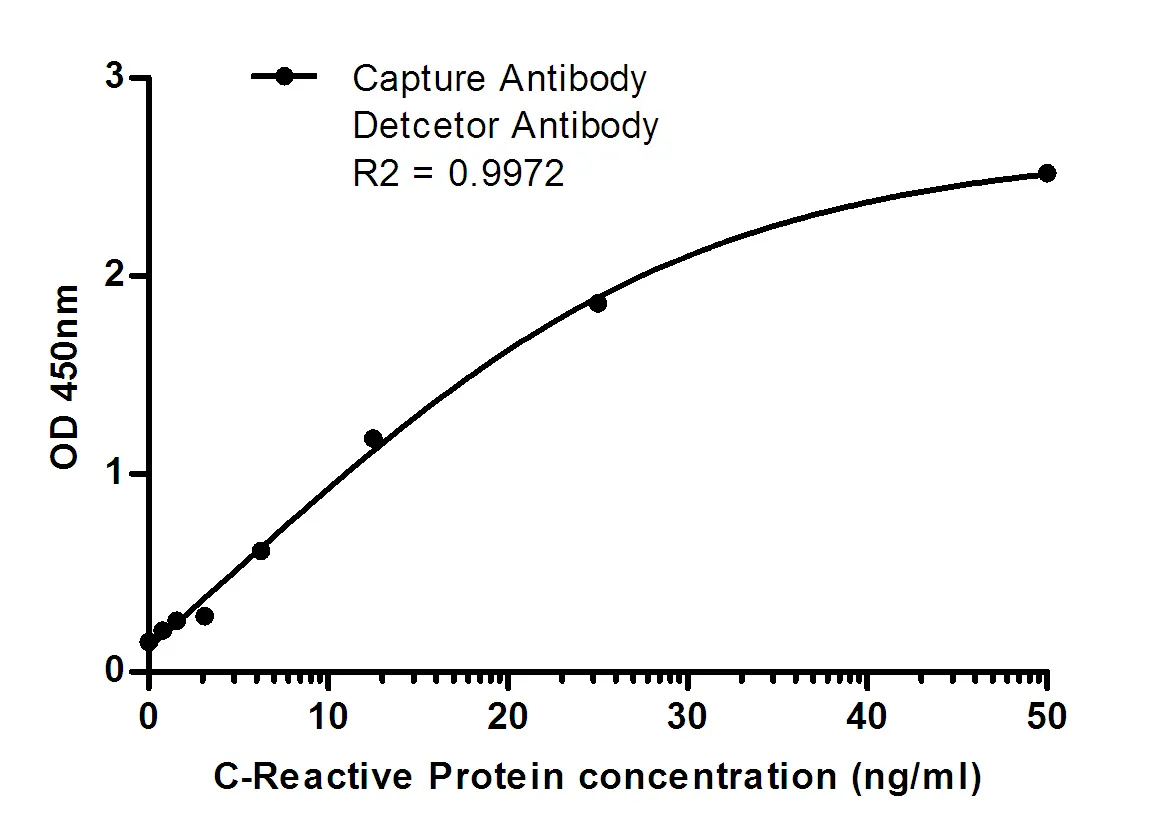
Application
Background
NF-kappa-B is a ubiquitous transcription factor involved in several biological processes. It is held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state by specific inhibitors. Upon degradation of the inhibitor, NF-kappa-B moves to the nucleus and activates transcription of specific genes. NF-kappa-B is composed of NFKB1 or NFKB2 bound to either REL, RELA, or RELB. The most abundant form of NF-kappa-B is NFKB1 complexed with the product of this gene, RELA. Four transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2011],function:NF-kappa-B is a pleiotropic transcription factor which is present in almost all cell types and is involved in many biological processed such as inflammation, immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis. NF-kappa-B is a homo- or heterodimeric complex formed by the Rel-like domain-containing proteins RELA/p65, RELB, NFKB1/p105, NFKB1/p50, REL and NFKB2/p52 and the heterodimeric p65-p50 complex appears to be most abundant one. The dimers bind at kappa-B sites in the DNA of their target genes and the individual dimers have distinct preferences for different kappa-B sites that they can bind with distinguishable affinity and specificity. Different dimer combinations act as transcriptional activators or repressors, respectively. NF-kappa-B is controlled by various mechanisms of post-translational modification and subcellular compartmentalization as well as by interactions with other cofactors or corepressors. NF-kappa-B complexes are held in the cytoplasm in an inactive state complexed with members of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor (I-kappa-B) family. In a conventional activation pathway, I-kappa-B is phosphorylated by I-kappa-B kinases (IKKs) in response to different activators, subsequently degraded thus liberating the active NF-kappa-B complex which translocates to the nucleus. NF-kappa-B heterodimeric p65-p50 and p65-c-Rel complexes are transcriptional activators. The NF-kappa-B p65-p65 complex appears to be involved in invasin-mediated activation of IL-8 expression. The inhibitory effect of I-kappa-B upon NF-kappa-B the cytoplasm is exerted primarily through the interaction with p65. p65 shows a weak DNA-binding site which could contribute directly to DNA binding in the NF-kappa-B complex.,PTM:Phosphorylation on 'Ser-536' stimulates acetylation on 'Lys-310' and interaction with CBP; the phosphorylated and acetylated forms show enhanced transcriptional activity.,PTM:Reversibly acetylated; the acetylation seems to be mediated by CBP, the deacetylation by HDAC3. Acetylation at 'Lys-122' enhances DNA binding and impairs association with NFKBIA. Acetylation at 'Lys-310' is required for full transcriptional activity in the absence of effects on DNA binding and NFKBIA association. Acetylation can also lower DNA-binding and results in nuclear export.,PTM:Ubiquitinated, leading to its proteosomal degradation. Degradation is required for termination of NF-kappa-B response.,similarity:Contains 1 RHD (Rel-like) domain.,subcellular location:Nuclear, but also found in the cytoplasm in an inactive form complexed to an inhibitor (I-kappa-B).,subunit:Component of the NF-kappa-B p65-p50 complex. Component of the NF-kappa-B p65-c-Rel complex. Homodimer; component of the NF-kappa-B p65-p65 complex. Component of the NF-kappa-B p65-p52 complex. May interact with ETHE1. Binds AES and TLE1. Interacts with TP53BP2. Binds to and is phosphorylated by the activated form of either RPS6KA4 or RPS6KA5. Interacts with ING4 and this interaction may be indirect. Interacts with CARM1, USP48 and UNC5CL. Interacts with IRAK1BP1 (By similarity).Interacts with NFKBID (By similarity). Interacts with NFKBIA. Interacts with GSK3B. Interacts with NFKBIB (By similarity). Interacts with NFKBIE. Interacts with NFKBIZ (By similarity). Part of a 70-90 kDa complex at least consisting of CHUK, IKBKB, NFKBIA, RELA, IKBKAP and MAP3K14. Interacts with HDAC3; HDAC3 mediates the deacetylation of RELA. Interacts with HDAC1; the interaction requires non-phosphorylated RELA. Interacts with CBP; the interaction requires phosphorylated RELA. Interacts (phosphorylated at 'Thr-254') with PIN1; the interaction inhibits p65 binding to NFKBIA. Interacts with SOCS1. Interacts with UXT. Interacts with MTDH. Interacts with human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV) protein M2-1.,
Research Area
MAPK_ERK_Growth;MAPK_G_Protein;Chemokine;Apoptosis_Inhibition;Apoptosis_Mitochondrial;Apoptosis_Overview;Toll_Like;NOD-like receptor;RIG-I-like receptor;Cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway;T_Cell_Receptor;B_Cell_Antigen;Neurotrophin;Adipocytokine;Epithelial cell signaling in Helicobacter pylori infection;Pathways in cancer;Pancreatic cancer;Prostate cancer;Chronic myeloid leukemia;Acute myeloid leukemia;Small cell lung cancer;