Summary
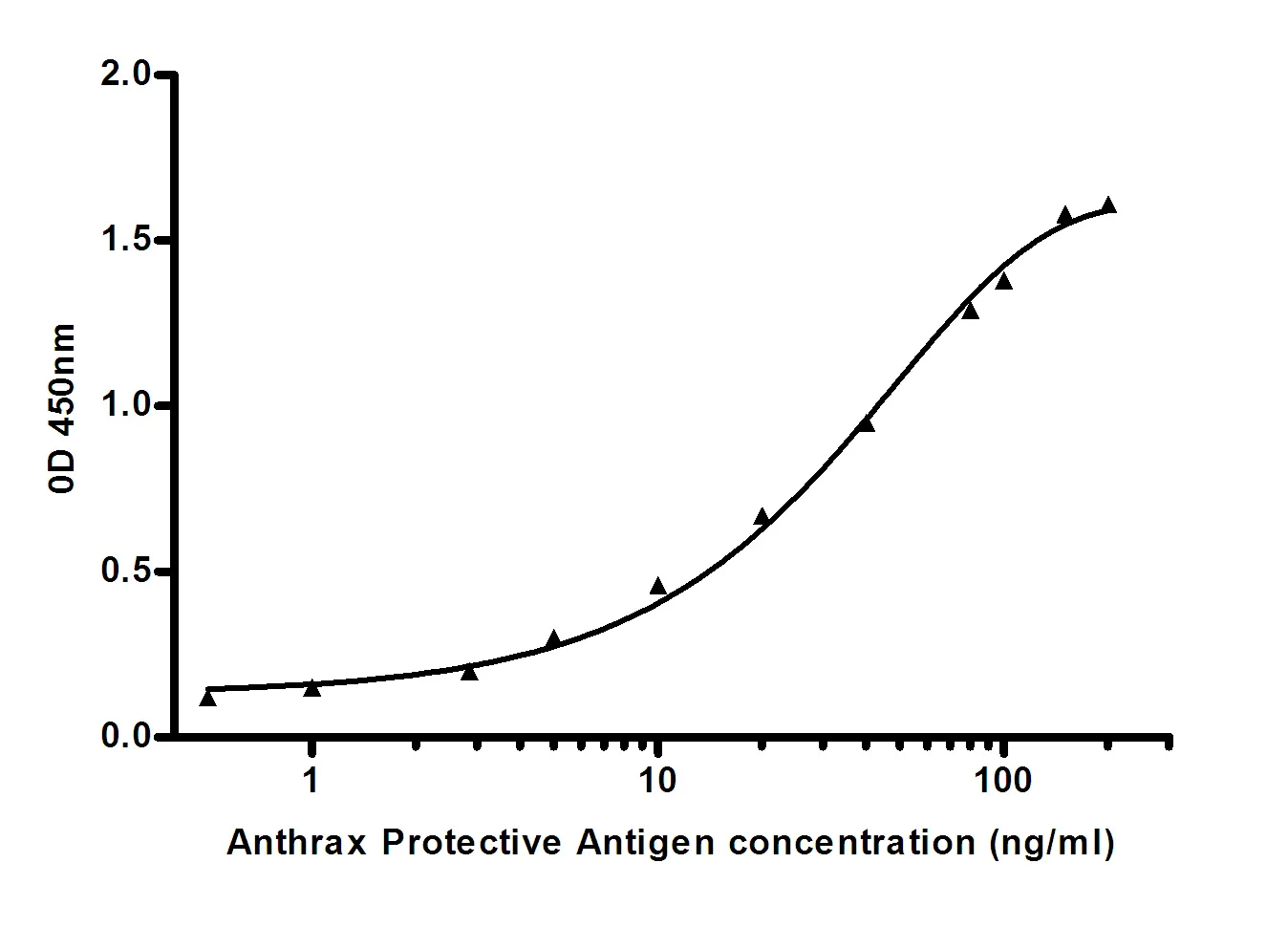
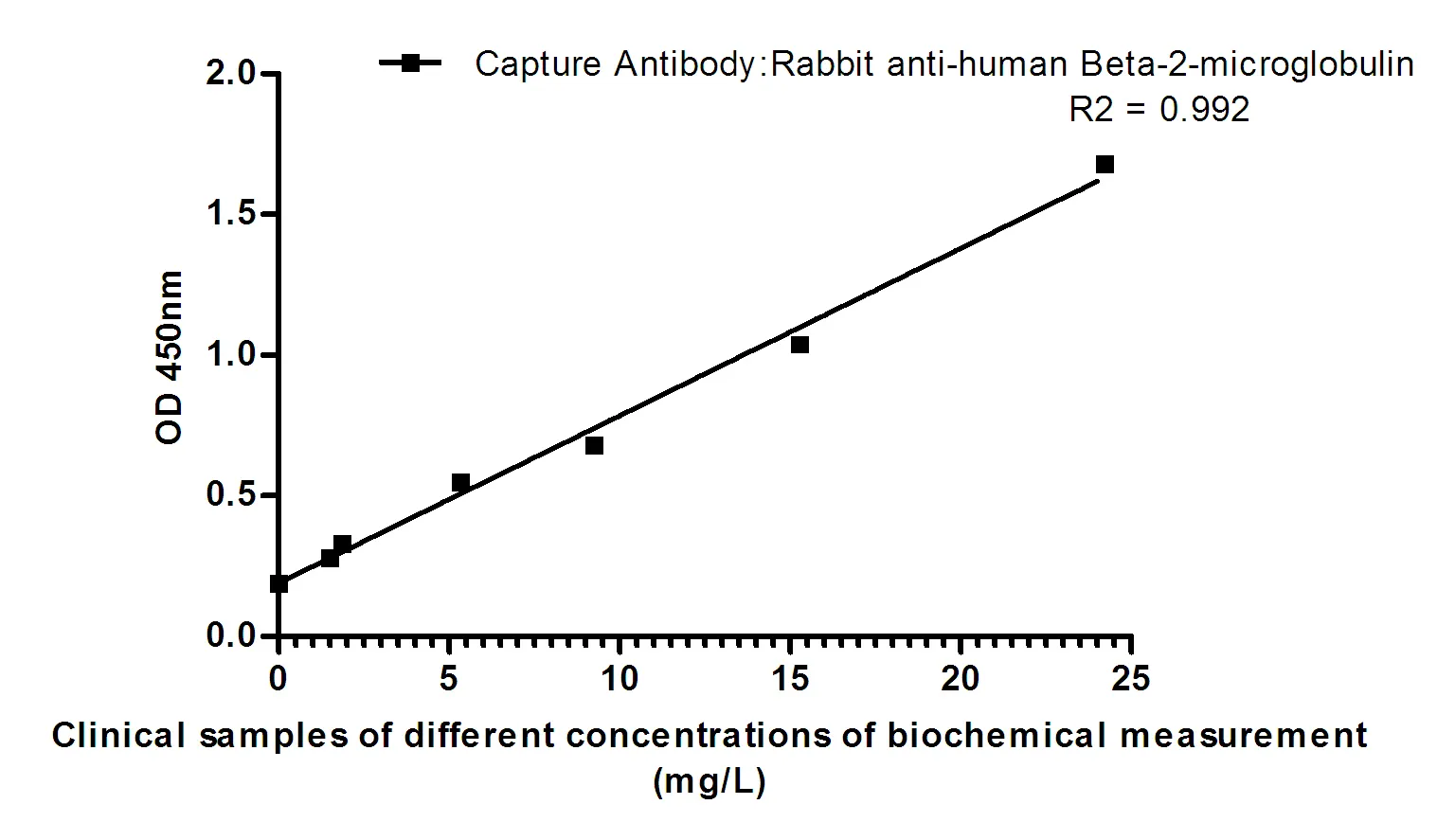
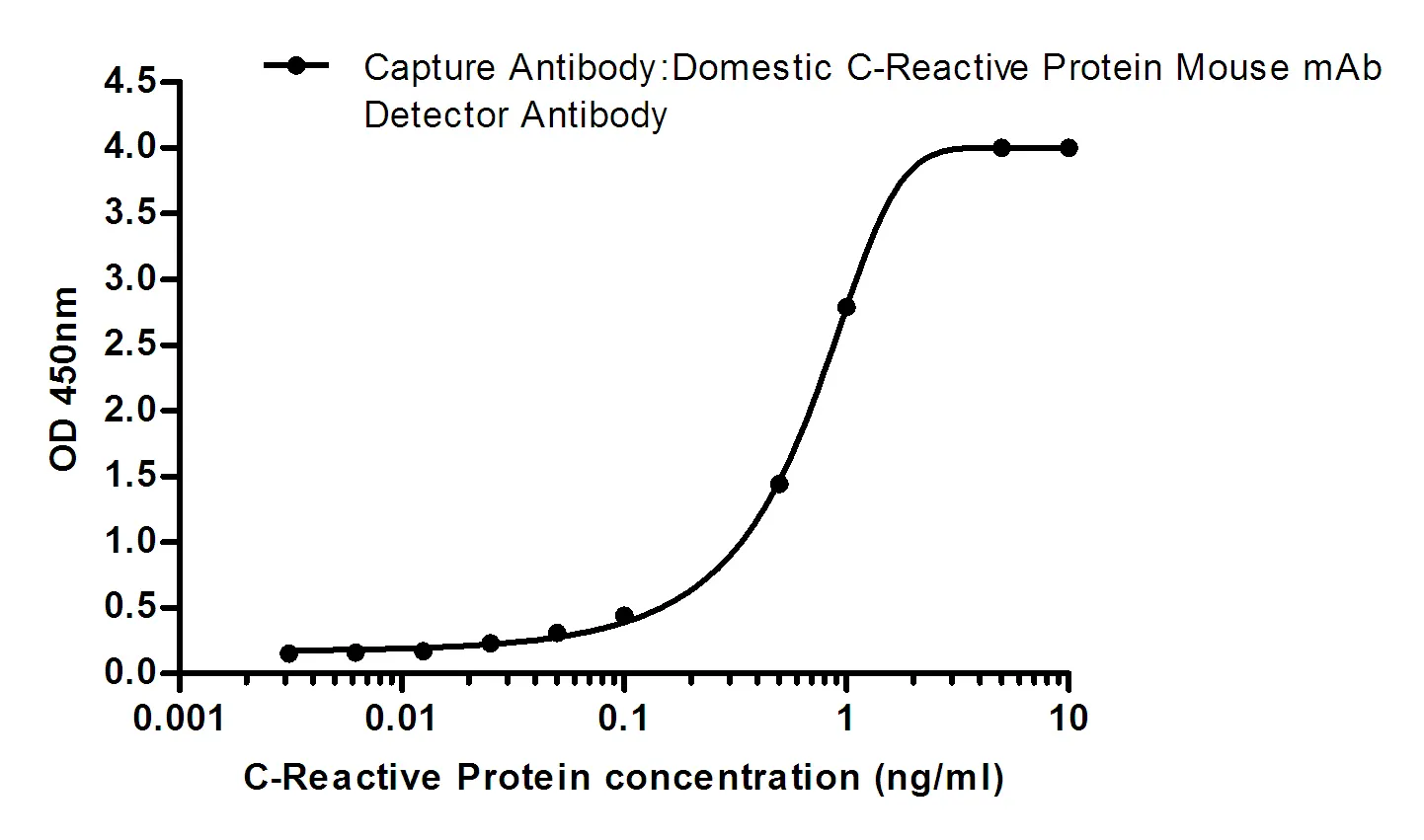
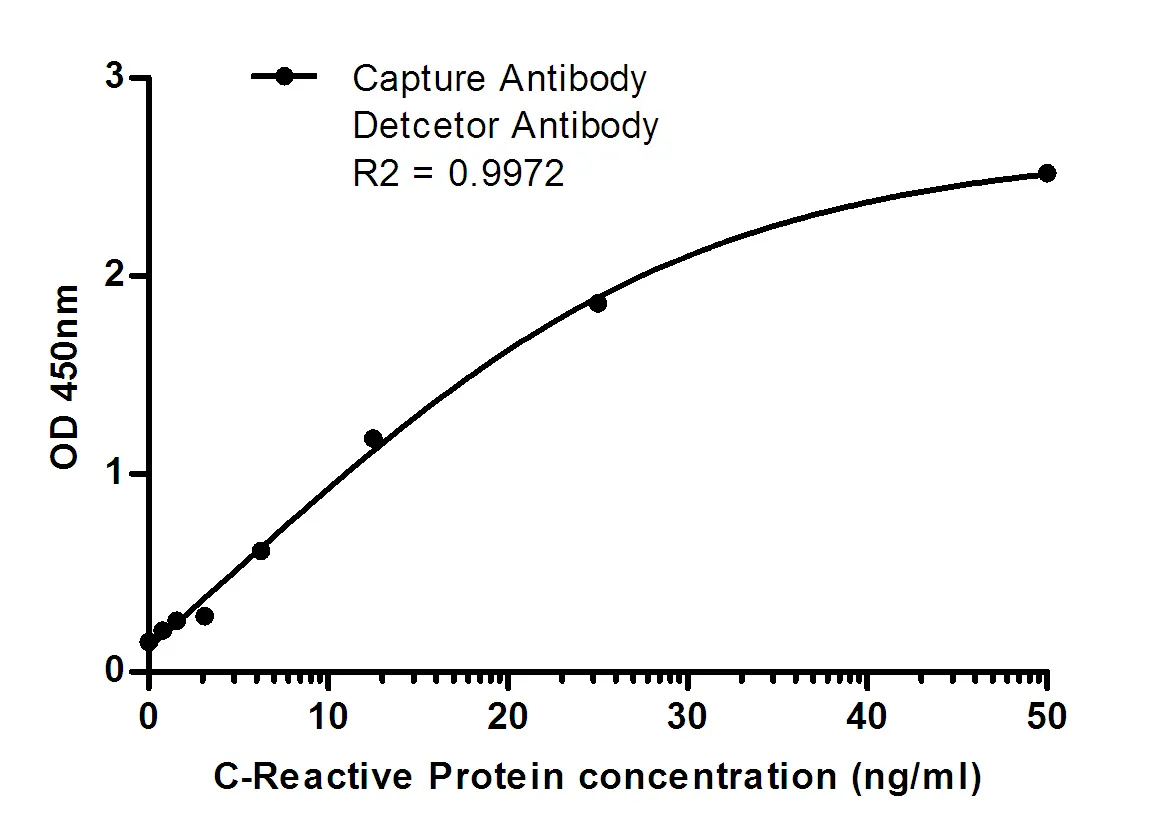
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
The protein encoded by this gene is an enzymatic component of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, or Krebs cycle, and catalyzes the formation of L-malate from fumarate. It exists in both a cytosolic form and an N-terminal extended form, differing only in the translation start site used. The N-terminal extended form is targeted to the mitochondrion, where the removal of the extension generates the same form as in the cytoplasm. It is similar to some thermostable class II fumarases and functions as a homotetramer. Mutations in this gene can cause fumarase deficiency and lead to progressive encephalopathy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008],catalytic activity:(S)-malate = fumarate + H(2)O.,disease:Defects in FH are the cause of fumarase deficiency (FD) [MIM:606812]; also known as fumaricaciduria. FD is characterized by progressive encephalopathy, developmental delay, hypotonia, cerebral atrophy and lactic and pyruvic acidemia.,disease:Defects in FH are the cause of hereditary leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer (HLRCC) [MIM:605839].,disease:Defects in FH are the cause of multiple cutaneous and uterine leiomyomata (MCUL1) [MIM:150800]. MCUL1 is an autosomal dominant condition in which affected individuals develop benign smooth muscle tumors (leiomyomata) of the skin. Affected females also usually develop leiomyomata of the uterus (fibroids).,function:Also acts as a tumor suppressor.,miscellaneous:There are 2 substrate binding sites: the catalytic A site, and the non-catalytic B site that may play a role in the transfer of substrate or product between the active site and the solvent. Alternatively, the B site may bind allosteric effectors.,pathway:Carbohydrate metabolism; tricarboxylic acid cycle.,PTM:Isoform Cytoplasmic is acetylated at position 2.,similarity:Belongs to the class-II fumarase/aspartase family. Fumarase subfamily.,subunit:Homotetramer.,
Research Area
Citrate cycle (TCA cycle);Pathways in cancer;Renal cell carcinoma;