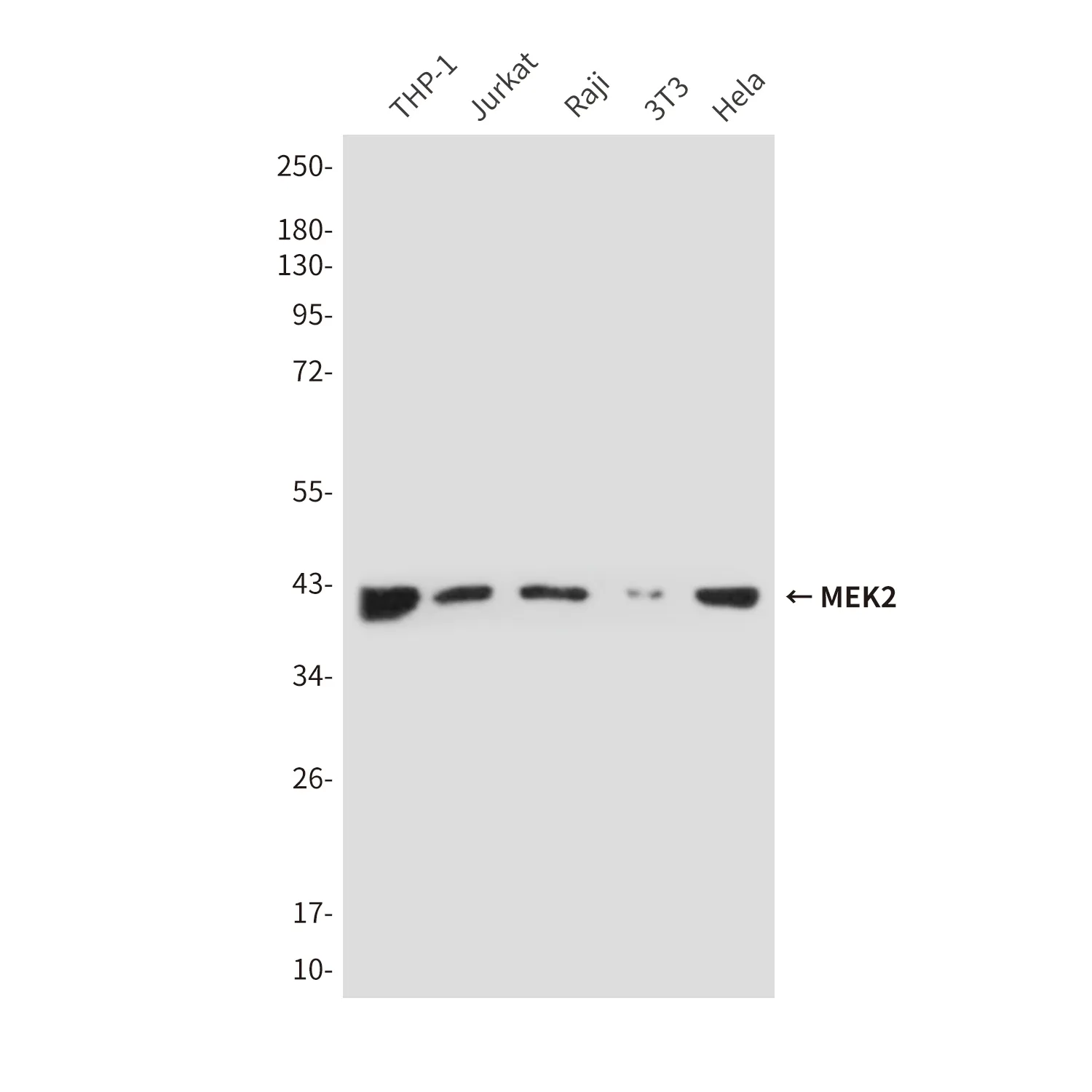
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
Involved in stable X chromosome inactivation. Inhibits the binding of transcription factors and interferes with the activity of remodeling SWI/SNF complexes. Inhibits histone acetylation by EP300 and recruits class I HDACs, which induces an hypoacetylated state of chromatin. Variant histone H2A which replaces conventional H2A in a subset of nucleosomes where it represses transcription (PubMed:12718888, PubMed:15621527, PubMed:16428466). Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. Involved in stable X chromosome inactivation (PubMed:15897469). Inhibits the binding of transcription factors, including NF-kappa-B, and interferes with the activity of remodeling SWI/SNF complexes (PubMed:12718888, PubMed:16428466). Inhibits histone acetylation by EP300 and recruits class I HDACs, which induces a hypoacetylated state of chromatin (PubMed:16428466, PubMed:16107708).
Research Area