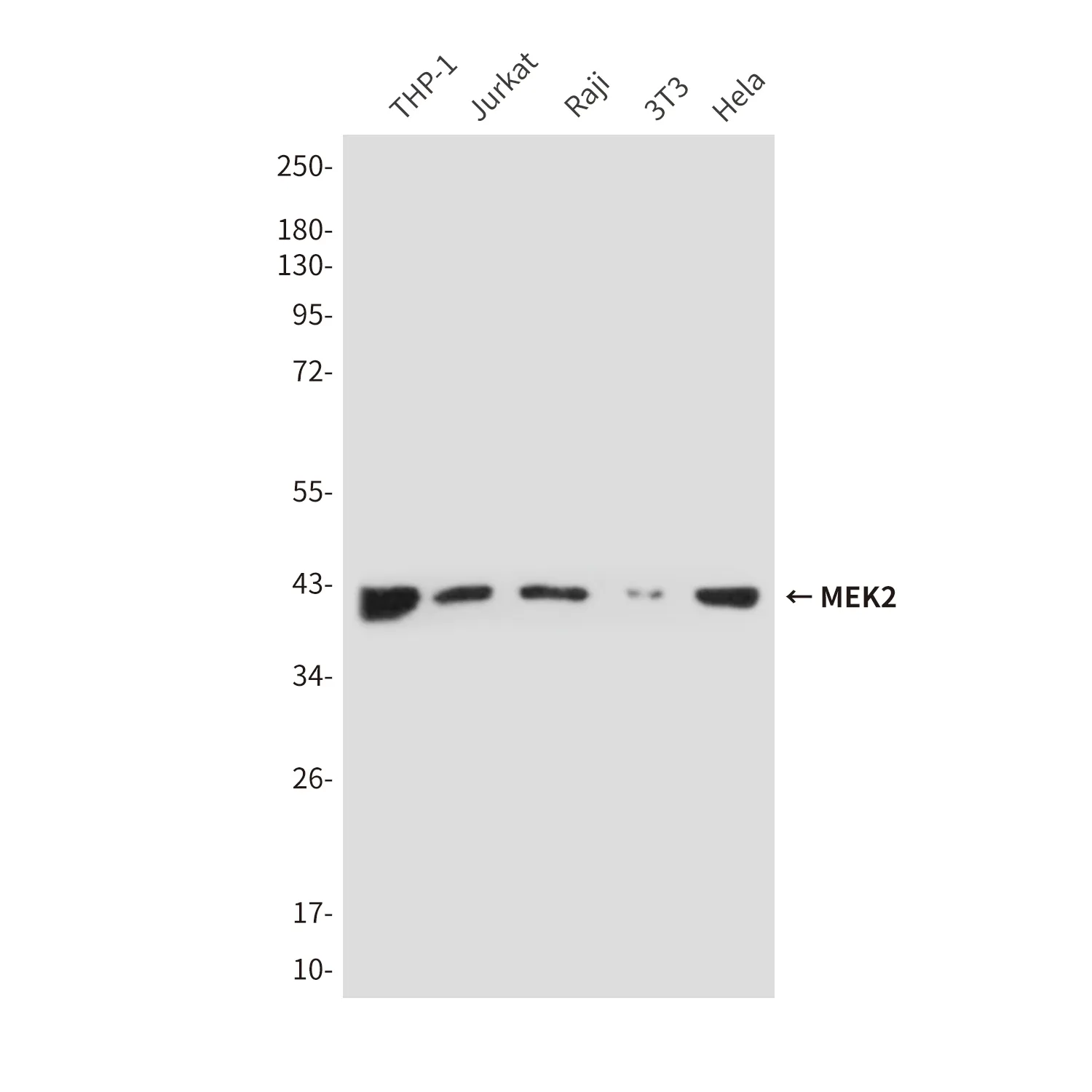
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
Integrin-linked kinases (ILKs) couple integrins and growth factors to downstream pathways involved in cell survival, cell cycle control, cell-cell adhesion and cell motility. ILK functions as a scaffold bridging the extracellular matrix (ECM) and growth factor receptors to the actin cytoskeleton through interactions with integrin, PINCH (which links ILK to the RTKs via Nck2), CH-ILKBP and affixin. Receptor-proximal protein kinase regulating integrin-mediated signal transduction (PubMed:8538749, PubMed:9736715). May act as a mediator of inside-out integrin signaling (PubMed:10712922). Focal adhesion protein part of the complex ILK-PINCH (PubMed:10712922). This complex is considered to be one of the convergence points of integrin- and growth factor-signaling pathway (PubMed:10712922). Could be implicated in mediating cell architecture, adhesion to integrin substrates and anchorage-dependent growth in epithelial cells (PubMed:10712922). Regulates cell motility by forming a complex with PARVB (PubMed:32528174). Phosphorylates beta-1 and beta-3 integrin subunit on serine and threonine residues, but also AKT1 and GSK3B (PubMed:8538749, PubMed:9736715).
Research Area