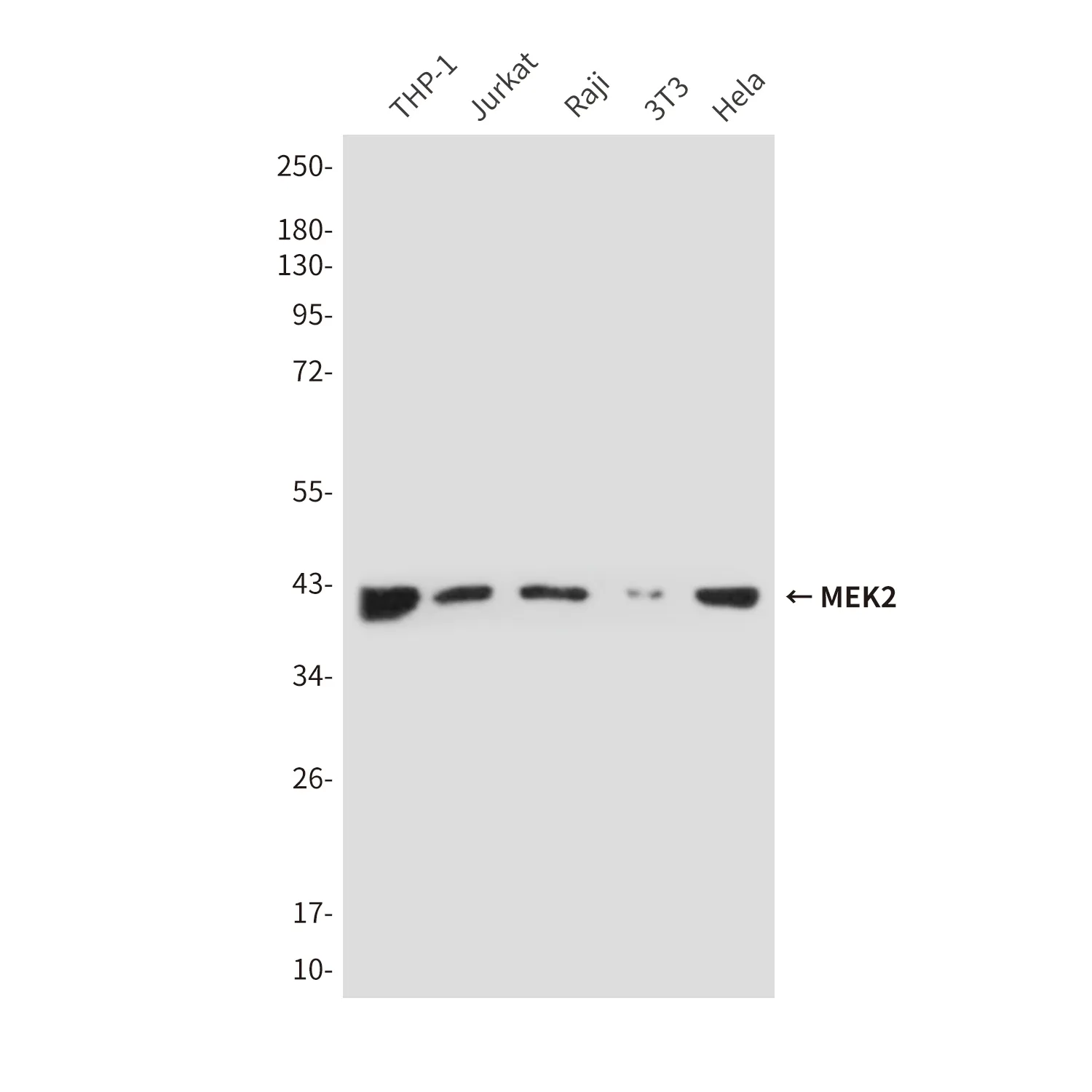
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
Required for DNA recombination, repair and replication. The activity of RP-A is mediated by single-stranded DNA binding and protein interactions. As part of the heterotrimeric replication protein A complex (RPA/RP-A), binds and stabilizes single-stranded DNA intermediates, that form during DNA replication or upon DNA stress. It prevents their reannealing and in parallel, recruits and activates different proteins and complexes involved in DNA metabolism. Thereby, it plays an essential role both in DNA replication and the cellular response to DNA damage. In the cellular response to DNA damage, the RPA complex controls DNA repair and DNA damage checkpoint activation. Through recruitment of ATRIP activates the ATR kinase a master regulator of the DNA damage response. It is required for the recruitment of the DNA double-strand break repair factors RAD51 and RAD52 to chromatin in response to DNA damage. Also recruits to sites of DNA damage proteins like XPA and XPG that are involved in nucleotide excision repair and is required for this mechanism of DNA repair. Plays also a role in base excision repair (BER) probably through interaction with UNG. Also recruits SMARCAL1/HARP, which is involved in replication fork restart, to sites of DNA damage. May also play a role in telomere maintenance.
Research Area