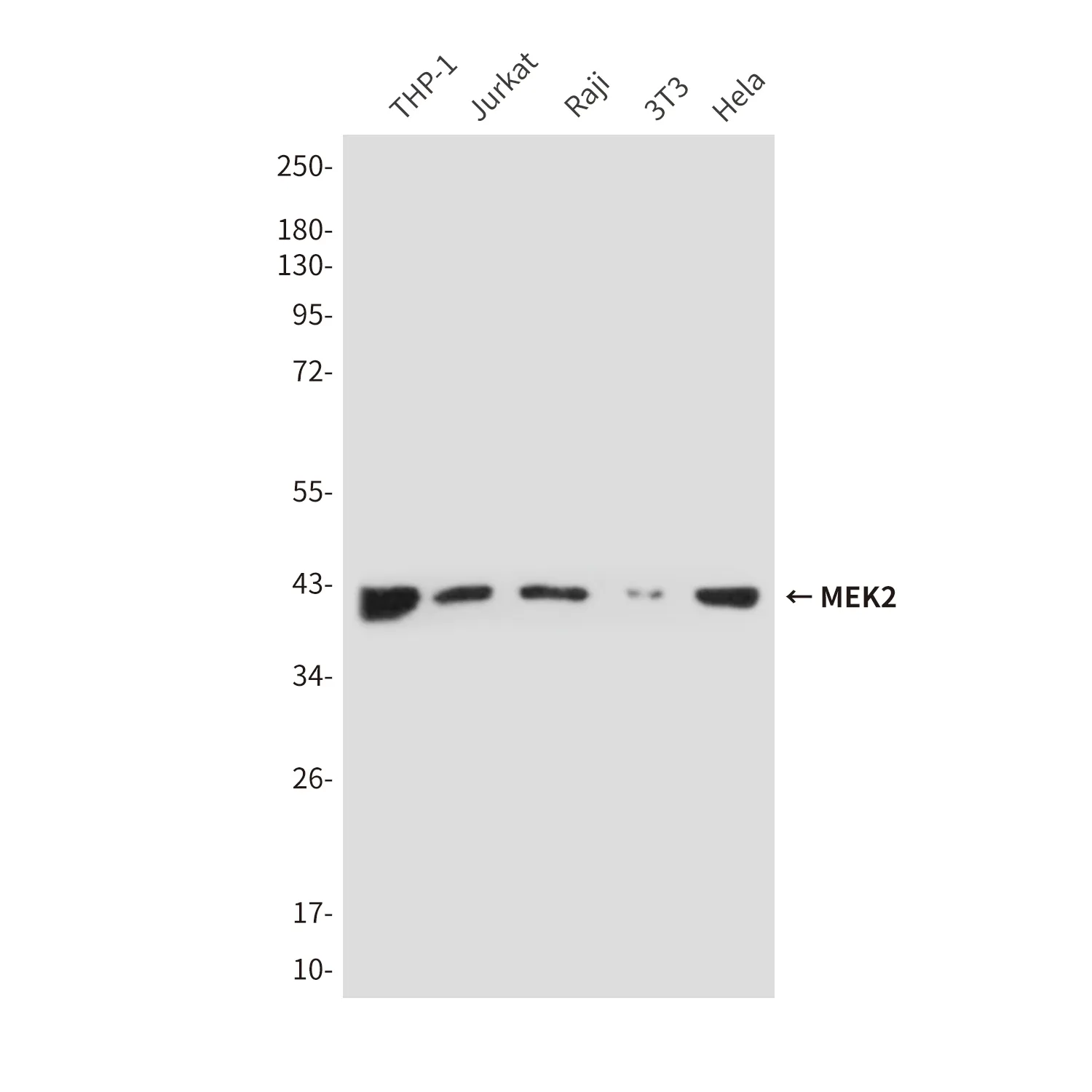
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
Catalyzes the initial step in triglyceride hydrolysis in adipocyte and non-adipocyte lipid droplets. Also has acylglycerol transacylase activity. May act coordinately with LIPE/HLS within the lipolytic cascade. Regulates adiposome size and may be involved in the degradation of adiposomes. Catalyzes the initial step in triglyceride hydrolysis in adipocyte and non-adipocyte lipid droplets (PubMed:15550674, PubMed:15364929, PubMed:16150821). Exhibits a strong preference for the hydrolysis of long-chain fatty acid esters at the sn-2 position of the glycerol backbone (By similarity). Also has acylglycerol transacylase activity. Acts coordinately with LIPE/HLS and DGAT2 within the lipolytic cascade (By similarity). Transfers fatty acid from triglyceride to retinol, hydrolyzes retinylesters, and generates 1,3- diacylglycerol from triglycerides (PubMed:17603008). Regulates adiposome size and may be involved in the degradation of adiposomes (PubMed:16239926). May play an important role in energy homeostasis. May play a role in the response of the organism to starvation, enhancing hydrolysis of triglycerides and providing free fatty acids to other tissues to be oxidized in situations of energy depletion (By similarity).
Research Area