Summary
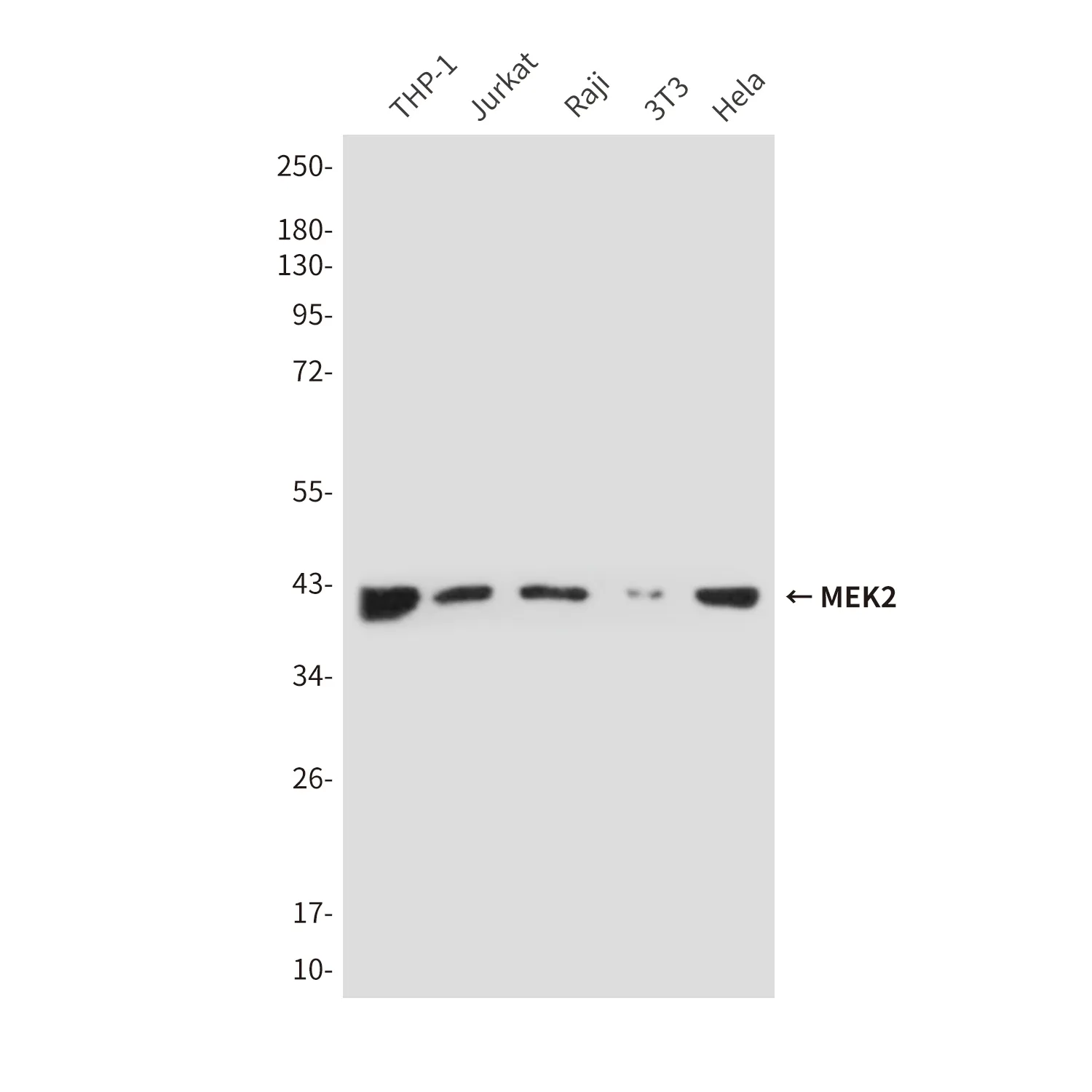
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
The activated kinase acts on a variety of targets. Likely to be the GTPase effector that links the Rho-related GTPases to the JNK MAP kinase pathway. Activated by CDC42 and RAC1. Involved in dissolution of stress fibers and reorganization of focal complexes. Involved in regulation of microtubule biogenesis through phosphorylation of TBCB. Protein kinase involved in intracellular signaling pathways downstream of integrins and receptor-type kinases that plays an important role in cytoskeleton dynamics, in cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, apoptosis, mitosis, and in vesicle-mediated transport processes (PubMed:11896197, PubMed:30290153). Can directly phosphorylate BAD and protects cells against apoptosis. Activated by interaction with CDC42 and RAC1. Functions as GTPase effector that links the Rho-related GTPases CDC42 and RAC1 to the JNK MAP kinase pathway. Phosphorylates and activates MAP2K1, and thereby mediates activation of downstream MAP kinases. Involved in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, actin stress fibers and of focal adhesion complexes. Phosphorylates the tubulin chaperone TBCB and thereby plays a role in the regulation of microtubule biogenesis and organization of the tubulin cytoskeleton. Plays a role in the regulation of insulin secretion in response to elevated glucose levels. Part of a ternary complex that contains PAK1, DVL1 and MUSK that is important for MUSK- dependent regulation of AChR clustering during the formation of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ). Activity is inhibited in cells undergoing apoptosis, potentially due to binding of CDC2L1 and CDC2L2. Phosphorylates MYL9/MLC2. Phosphorylates RAF1 at 'Ser-338' and 'Ser- 339' resulting in: activation of RAF1, stimulation of RAF1 translocation to mitochondria, phosphorylation of BAD by RAF1, and RAF1 binding to BCL2. Phosphorylates SNAI1 at 'Ser-246' promoting its transcriptional repressor activity by increasing its accumulation in the nucleus. In podocytes, promotes NR3C2 nuclear localization. Required for atypical chemokine receptor ACKR2-induced phosphorylation of LIMK1 and cofilin (CFL1) and for the up-regulation of ACKR2 from endosomal compartment to cell membrane, increasing its efficiency in chemokine uptake and degradation. In synapses, seems to mediate the regulation of F-actin cluster formation performed by SHANK3, maybe through CFL1 phosphorylation and inactivation. Plays a role in RUFY3- mediated facilitating gastric cancer cells migration and invasion (PubMed:25766321). In response to DNA damage, phosphorylates MORC2 which activates its ATPase activity and facilitates chromatin remodeling (PubMed:23260667). In neurons, plays a crucial role in regulating GABA(A) receptor synaptic stability and hence GABAergic inhibitory synaptic transmission through its role in F-actin stabilization (By similarity). In hippocampal neurons, necessary for the formation of dendritic spines and excitatory synapses; this function is dependent on kinase activity and may be exerted by the regulation of actomyosin contractility through the phosphorylation of myosin II regulatory light chain (MLC) (By similarity). Along with GIT1, positively regulates microtubule nucleation during interphase (PubMed:27012601).
Research Area