Summary
Performance
Immunogen
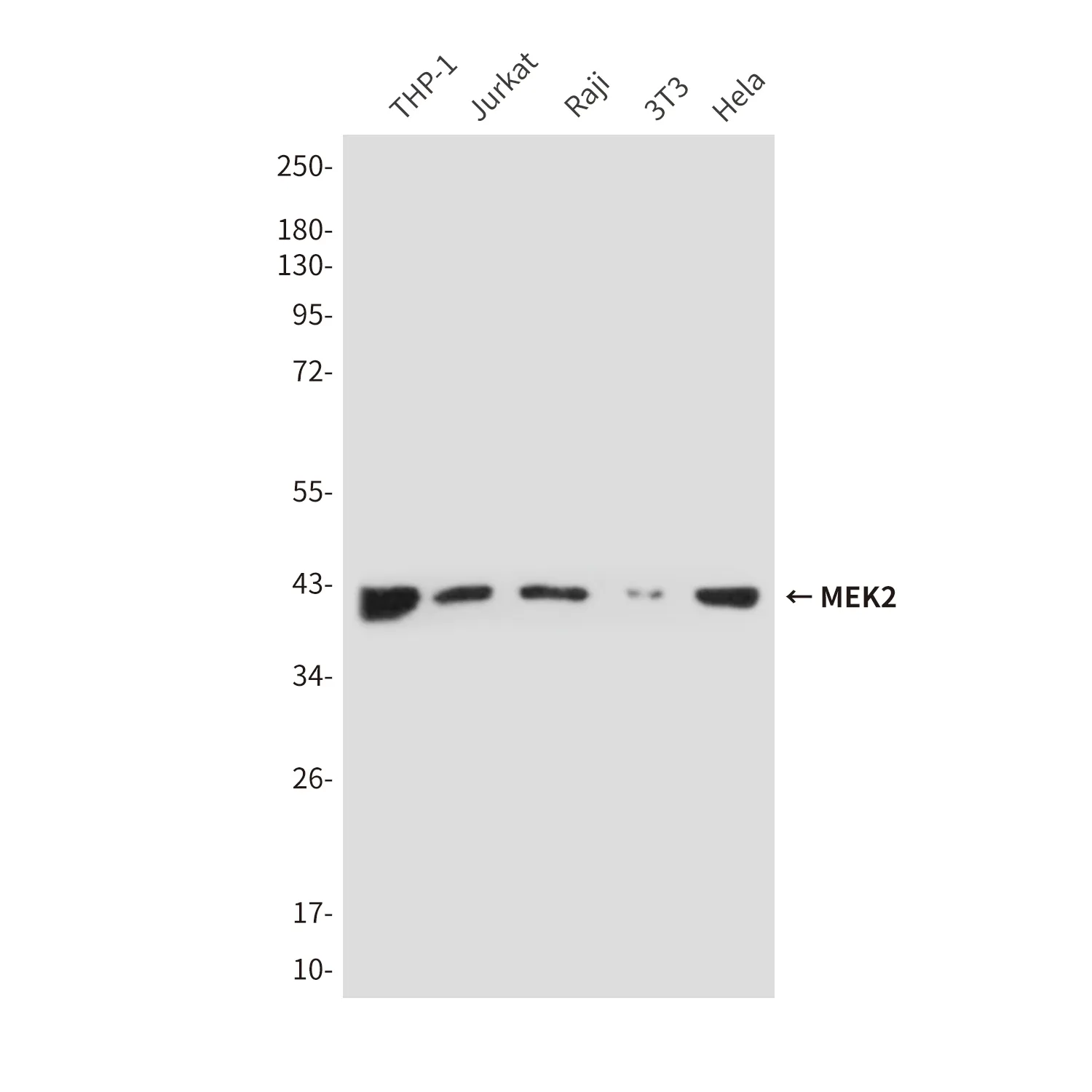
Application
Background
Core component of multiple cullin-RING-based E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complexes which mediate the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. The functional specificity of the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex depends on the variable substrate recognition subunit. CUL4B may act within the complex as a scaffold protein, contributing to catalysis through positioning of the substrate and the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Plays a role as part of the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex in polyubiquitination of CDT1, histone H2A, histone H3 and histone H4 in response to radiation-induced DNA damage. Targeted to UV damaged chromatin by DDB2 and may be important for DNA repair and DNA replication. Required for ubiquitination of cyclin E, and consequently, normal G1 cell cycle progression. Regulates the mammalian target-of-rapamycin (mTOR) pathway involved in control of cell growth, size and metabolism. Specific CUL4B regulation of the mTORC1-mediated pathway is dependent upon 26S proteasome function and requires interaction between CUL4B and MLST8.
Research Area
Cell Biology