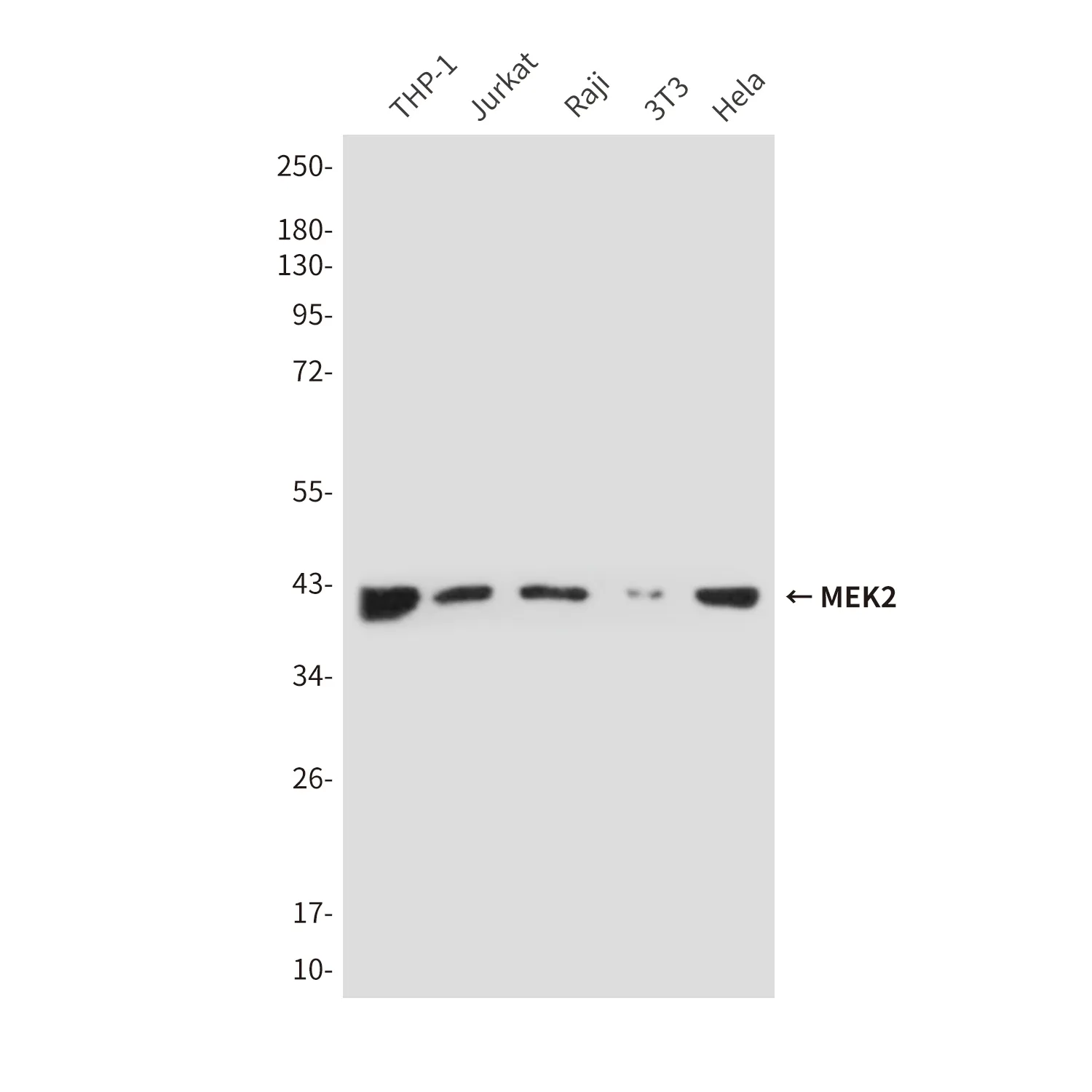
Summary
Performance
Immunogen
Application
Background
MAP kinases are inactivated by dual-specificity protein phosphatases (DUSP) that differ in their substrate specificity, tissue distribution, inducibility by extracellular stimuli and cellular localization. DUSPs, also known as MAPK phosphatases (MKP), specifically dephosphorylate both threonine and tyrosine residues in MAPK P-loops and have been shown to play important roles in regulating the function of the MAPK family. At least 13 members of the family (DUSP1-10, DUSp14, DUSP16, and DUSP22) display unique substrate specificities for various MAP kinases. Inactivates MAP kinases. Has a specificity for the ERK family (PubMed:9858808). Plays an important role in alleviating chronic postoperative pain. Necessary for the normal dephosphorylation of the long-lasting phosphorylated forms of spinal MAPK1/3 and MAP kinase p38 induced by peripheral surgery, which drives the resolution of acute postoperative allodynia (By similarity). Also important for dephosphorylation of MAPK1/3 in local wound tissue, which further contributes to resolution of acute pain (By similarity). Promotes cell differentiation by regulating MAPK1/MAPK3 activity and regulating the expression of AP1 transcription factors (PubMed:29043977).
Research Area